Abstract
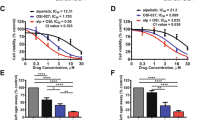
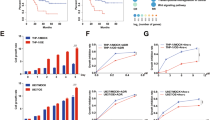
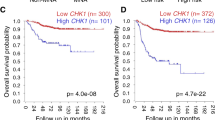
The failure of conventional therapies in glioblastoma (GBM) is largely due to an aberrant activity of survival cascades, such as PI3 kinase (PI3K)/Akt-mediated signaling. This study is the first to show that the class I PI3K inhibitor, PI-103, enhances chemotherapy-induced cell death of GBM cells. Concurrent treatment with PI-103 and DNA-damaging drugs, in particular doxorubicin, significantly increases apoptosis and reduces colony formation compared with chemotherapy treatment alone. The underlying molecular mechanism for this chemosensitization was shown by two independent approaches, that is, pharmacological and genetic inhibition of PI3K, DNA-PK and mTOR, to involve inhibition of DNA-PK-mediated DNA repair. Accordingly, blockage of PI3K or DNA-PK, but not of mTOR, significantly delays the resolution of doxorubicin-induced DNA damage and concomitantly increases apoptosis. Importantly, not only are several GBM cell lines chemosensitized by PI-103 but also GBM stem cells. Clinical relevance was further confirmed by the use of primary cultured GBM cells, which also exhibit increased cell death and reduced colony formation on combined treatment with PI-103 and doxorubicin. By identifying class I PI3K inhibitors as powerful agents in enhancing the lethality of DNA-damaging drugs, to which GBMs are usually considered unresponsive, our findings have important implications for the design of rational combination regimens in overcoming the frequent chemoresistance of GBM.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB et al. (2006). Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444: 756–760.
Bozulic L, Surucu B, Hynx D, Hemmings BA . (2008). PKBalpha/Akt1 acts downstream of DNA-PK in the DNA double-strand break response and promotes survival. Mol Cell 30: 203–213.
Brendler-Schwaab S, Hartmann A, Pfuhler S, Speit G . (2005). The in vivo comet assay: use and status in genotoxicity testing. Mutagenesis 20: 245–254.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008). Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455: 1061–1068.
Cavaliere R, Wen PY, Schiff D . (2007). Novel therapies for malignant gliomas. Neurol Clin 25: 1141–1171, x.
Chakravarti A, Zhai G, Suzuki Y, Sarkesh S, Black PM, Muzikansky A et al. (2004). The prognostic significance of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway activation in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol 22: 1926–1933.
Chen JS, Zhou LJ, Entin-Meer M, Yang X, Donker M, Knight ZA et al. (2008). Characterization of structurally distinct, isoform-selective phosphoinositide 3′-kinase inhibitors in combination with radiation in the treatment of glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 841–850.
Christmann M, Tomicic MT, Roos WP, Kaina B . (2003). Mechanisms of human DNA repair: an update. Toxicology 193: 3–34.
Colman H, Aldape K . (2008). Molecular predictors in glioblastoma: toward personalized therapy. Arch Neurol 65: 877–883.
DeAngelis LM . (2001). Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 344: 114–123.
Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A, Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G et al. (2006). Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death Differ 13: 1238–1241.
Fan QW, Cheng CK, Nicolaides TP, Hackett CS, Knight ZA, Shokat KM et al. (2007). A dual phosphoinositide-3-kinase alpha/mTOR inhibitor cooperates with blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor in PTEN-mutant glioma. Cancer Res 67: 7960–7965.
Fan QW, Knight ZA, Goldenberg DD, Yu W, Mostov KE, Stokoe D et al. (2006). A dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor reveals emergent efficacy in glioma. Cancer Cell 9: 341–349.
Feng J, Park J, Cron P, Hess D, Hemmings BA . (2004). Identification of a PKB/Akt hydrophobic motif Ser-473 kinase as DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 279: 41189–41196.
Fernandez-Capetillo O, Celeste A, Nussenzweig A . (2003). Focusing on foci: H2AX and the recruitment of DNA-damage response factors. Cell Cycle 2: 426–427.
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC . (1998). Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 481–507.
Fulda S, Sieverts H, Friesen C, Herr I, Debatin KM . (1997). The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system mediates drug-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 57: 3823–3829.
Giagkousiklidis S, Vogler M, Westhoff MA, Kasperczyk H, Debatin KM, Fulda S . (2005). Sensitization for gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis by second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase. Cancer Res 65: 10502–10513.
Glas M, Koch H, Hirschmann B, Jauch T, Steinbrecher A, Herrlinger U et al. (2007). Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in recurrent malignant glioma: analysis of a case series. Oncology 72: 302–307.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM . (2007). Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 12: 9–22.
Hau P, Fabel K, Baumgart U, Rummele P, Grauer O, Bock A et al. (2004). Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin-efficacy in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Cancer 100: 1199–1207.
Ihle NT, Powis G . (2009). Take your PIK: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors race through the clinic and toward cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 8: 1–9.
Ishii H, Iwatsuki M, Ieta K, Ohta D, Haraguchi N, Mimori K et al. (2008). Cancer stem cells and chemoradiation resistance. Cancer Sci 99: 1871–1877.
Ishii N, Maier D, Merlo A, Tada M, Sawamura Y, Diserens AC et al. (1999). Frequent co-alterations of TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol 9: 469–479.
Jackson SP . (2002). Sensing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis 23: 687–696.
Jiang BH, Liu LZ . (2008). PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784: 150–158.
Kao GD, Jiang Z, Fernandes AM, Gupta AK, Maity A . (2007). Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/Akt signaling impairs DNA repair in glioblastoma cells following ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem 282: 21206–21212.
Koehn H, Magan N, Isaacs RJ, Stowell KM . (2007). Differential regulation of DNA damage repair protein Rad51 in human tumour cell lines exposed to doxorubicin. Anticancer Drugs 18: 419–425.
Kreisl TN, Lassman AB, Mischel PS, Rosen N, Scher HI, Teruya-Feldstein J et al. (2009). A pilot study of everolimus and gefitinib in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma (GBM). J Neurooncol 92: 99–105.
Lees-Miller SP . (2008). PIKK-ing a new partner: a new role for PKB in the DNA damage response. Cancer Cell 13: 379–380.
Maira SM, Stauffer F, Schnell C, Garcia-Echeverria C . (2009). PI3K inhibitors for cancer treatment: where do we stand? Biochem Soc Trans 37: 265–272.
Maira SM, Voliva C, Garcia-Echeverria C . (2008). Class IA phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: from their biologic implication in human cancers to drug discovery. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12: 223–238.
Newton HB . (2008). Glioblastoma multiforme. Curr Treat Options Neurol 10: 285–294.
Nitiss JL . (2002). DNA topoisomerases in cancer chemotherapy: using enzymes to generate selective DNA damage. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3: 1512–1516.
Ohgaki H, Dessen P, Jourde B, Horstmann S, Nishikawa T, Di Patre PL et al. (2004). Genetic pathways to glioblastoma: a population-based study. Cancer Res 64: 6892–6899.
Opel D, Poremba C, Simon T, Debatin KM, Fulda S . (2007). Activation of Akt predicts poor outcome in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 67: 735–745.
Opel D, Westhoff MA, Bender A, Braun V, Debatin KM, Fulda S . (2008). Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition broadly sensitizes glioblastoma cells to death receptor- and drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 68: 6271–6280.
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P et al. (2008). An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science 321: 1807–1812.
Pawelczak KS, Turchi JJ . (2008). A mechanism for DNA-PK activation requiring unique contributions from each strand of a DNA terminus and implications for microhomology-mediated nonhomologous DNA end joining. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 4022–4031.
Prevo R, Deutsch E, Sampson O, Diplexcito J, Cengel K, Harper J et al. (2008). Class I PI3 kinase inhibition by the pyridinylfuranopyrimidine inhibitor PI-103 enhances tumor radiosensitivity. Cancer Res 68: 5915–5923.
Proud CG . (2004). The multifaceted role of mTOR in cellular stress responses. DNA Repair (Amst) 3: 927–934.
Raynaud FI, Eccles S, Clarke PA, Hayes A, Nutley B, Alix S et al. (2007). Pharmacologic characterization of a potent inhibitor of class I phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases. Cancer Res 67: 5840–5850.
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF et al. (2006). Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assemply and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell 22: 159–168.
Shah NP, Kasap C, Weier C, Balbas M, Nicoll JM, Bleickardt E et al. (2008). Transient potent BCR-ABL inhibition is sufficient to commit chronic myeloid leukemia cells irreversibly to apoptosis. Cancer Cell 14: 485–493.
Stupp R, Hegi ME, van den Bent MJ, Mason WP, Weller M, Mirimanoff RO et al. (2006). Changing paradigms—an update on the multidisciplinary management of malignant glioma. Oncologist 11: 165–180.
Tisdale MJ . (1985). Antitumour imidazotetrazines--XI: effect of 8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3 H)-one [CCRG 81045; M and B 39831 NSC 362856] on poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism. Br J Cancer 52: 789–792.
Toulany M, Kasten-Pisula U, Brammer I, Wang S, Chen J, Dittmann K et al. (2006). Blockage of epidermal growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling increases radiosensitivity of K-RAS mutated human tumor cells in vitro by affecting DNA repair. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4119–4126.
Toulany M, Kehlbach R, Florczak U, Sak A, Wang S, Chen J et al. (2008). Targeting of AKT1 enhances radiation toxicity of human tumor cells by inhibiting DNA-PKcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 1772–1781.
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Richardson CJ, Smith GC, Durkacz BW . (2003). Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by the combined use of novel inhibitiors of DNA-dependent proetin kinase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res 63: 6008–6015.
Yaneva M, Li H, Marple T, Hasty P . (2005). Non-homologous end joining, but not homologous recombination, enables survival for cells exposed to a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Nucleic Acids Res 33: 5320–5330.
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F, de Bono JS, Workman P . (2008). Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8: 393–412.
Yavuzer U, Smith GC, Bliss T, Werner D, Jackson SP . (1998). DNA end-independent activation of DNA-PK mediated via association with the DNA-binding protein C1D. Genes Dev 12: 2188–2199.
Yuan TL, Cantley LC . (2008). PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene 27: 5497–5510.
Acknowledgements
We thank H Lane (Novartis Institute for BioMedical Research, Oncology Basel, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland) for providing everolimus, R Pallini and R De Maria for glioblastoma-initiating cells and S Piater for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, European Community (ApopTrain, APO-SYS), Novartis Stiftung für therapeutische Forschung and IAP6/18 (to SF), and the University of Ulm junior research grant (to JAK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westhoff, MA., Kandenwein, J., Karl, S. et al. The pyridinylfuranopyrimidine inhibitor, PI-103, chemosensitizes glioblastoma cells for apoptosis by inhibiting DNA repair. Oncogene 28, 3586–3596 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.215
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.215
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The DNA Double-Strand Break Repair in Glioma: Molecular Players and Therapeutic Strategies
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Effects of oxygen on the antigenic landscape of prostate cancer cells
BMC Research Notes (2015)
-
Cisplatin associated with LY294002 increases cytotoxicity and induces changes in transcript profiles of glioblastoma cells
Molecular Biology Reports (2014)
-
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in glioblastoma: novel therapeutic agents and advances in understanding
Tumor Biology (2013)
-
MicroRNAs involved in chemo- and radioresistance of high-grade gliomas
Tumor Biology (2013)