Abstract
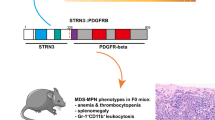
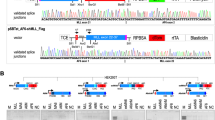
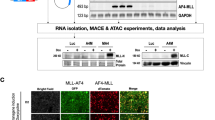
The AML1 gene is frequently rearranged by chromosomal translocations in acute leukemia. We identified that the LAF4 gene on 2q11.2–12 was fused to the AML1 gene on 21q22 in a pediatric patient having T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) with t(2;21)(q11;q22) using the bubble PCR method for cDNA. The genomic break points were within intron 7 of AML1 and of LAF4, resulting in the in-frame fusion of exon 7 of AML1 and exon 8 of LAF4. The LAF4 gene is a member of the AF4/FMR2 family and was previously identified as a fusion partner of MLL in B-precursor ALL with t(2;11)(q11;q23), although AML1-LAF4 was in T-ALL. LAF4 is the first gene fused with both AML1 and MLL in acute leukemia. Almost all AML1 translocations except for TEL-AML1 are associated with myeloid leukemia; however, AML1-LAF4 was associated with T-ALL as well as AML1-FGA7 in t(4;21)(q28;q22). These findings provide new insight into the common mechanism of AML1 and MLL fusion proteins in the pathogenesis of ALL. Furthermore, we successfully applied bubble PCR to clone the novel AML1-LAF4 fusion transcript. Bubble PCR is a powerful tool for detecting unknown fusion transcripts as well as genomic fusion points.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukemia
- ALL:
-
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
References
Agerstam H, Lilljebjorn H, Lassen C, Swedin A, Richter J, Vandenberghe P et al. (2007). Fusion gene-mediated truncation of RUNX1 as a potential mechanism underlying disease progression in the 8p11 myeloproliferative syndrome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 46: 635–643.
Asou N, Yanagida M, Huang L, Yamamoto M, Shigesada K, Mitsuya H et al. (2007). Concurrent transcriptional deregulation of AML1/RUNX1 and GATA factors by the AML1-TRPS1 chimeric gene in t(8;21)(q24;q22) acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 109: 4023–4027.
Bruch J, Wilda M, Teigler-Schlegel A, Harbott J, Borkhardt A, Metzler M . (2003). Occurrence of an MLL/LAF4 fusion gene caused by the insertion ins(11;2)(q23;q11.2q11.2) in an infant with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 37: 106–109.
Chaffanet M, Gressin L, Preudhomme C, Soenen-Cornu V, Birnbaum D, Pebusque MJ . (2000). MOZ is fused to p300 in an acute monocytic leukemia with t(8;22). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 28: 138–144.
Chan EM, Comer EM, Brown FC, Richkind KE, Holmes ML, Chong BH et al. (2005). AML1-FOG2 fusion protein in myelodysplasia. Blood 105: 4523–4526.
Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, Soreng AL, Reynolds TC, Smith SD et al. (1991). TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila Notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell 66: 649–661.
Erickson P, Gao J, Chang KS, Look T, Whisenant E, Raimondi S et al. (1992). Identification of breakpoints in t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia and isolation of a fusion transcript, AML1/ETO, with similarity to Drosophila segmentation gene, runt. Blood 80: 1825–1831.
Gamou T, Kitamura E, Hosoda F, Shimizu K, Shinohara K, Hayashi Y et al. (1998). The partner gene of AML1 in t(16;21) myeloid malignancies is a novel member of the MTG8 (ETO) family. Blood 91: 4028–4037.
Golub TR, Barker GF, Bohlander SK, Hiebert SW, Ward DC, Bray-Ward P et al. (1995). Fusion of the TEL gene on 12p13 to the AML1 gene on 21q22 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 4917–4921.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G et al. (1998). The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood 92: 2322–2333.
Hayashi Y . (2000). The molecular genetics of recurring chromosome abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol 37: 368–380.
Hiwatari M, Taki T, Taketani T, Taniwaki M, Sugita K, Okuya M et al. (2003). Fusion of an AF4-related gene, LAF4, to MLL in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(2;11)(q11;q23). Oncogene 22: 2851–2855.
Ichikawa M, Asai T, Saito T, Seo S, Yamazaki I, Yamagata T et al. (2004). AML-1 is required for megakaryocytic maturation and lymphocytic differentiation, but not for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells in adult hematopoiesis. Nat Med 10: 299–304.
Ida K, Kitabayashi I, Taki T, Taniwaki M, Noro K, Yamamoto M et al. (1997). Adenoviral E1A-associated protein p300 is involved in acute myeloid leukemia with t(11;22)(q23;q13). Blood 90: 4699–4704.
Isnard P, Core N, Naquet P, Djabali M . (2000). Altered lymphoid development in mice deficient for the mAF4 proto-oncogene. Blood 96: 705–710.
James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C et al. (2005). A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 434: 1144–1148.
Kurokawa M, Hirai H . (2003). Role of AML1/Runx1 in the pathogenesis of hematological malignancies. Cancer Sci 94: 841–846.
Lacronique V, Boureux A, Valle VD, Poirel H, Quang CT, Mauchauffe M et al. (1997). A TEL-JAK2 fusion protein with constitutive kinase activity in human leukemia. Science 278: 1309–1312.
Ma C, Staudt LM . (1996). LAF-4 encodes a lymphoid nuclear protein with transactivation potential that is homologous to AF-4, the gene fused to MLL in t(4;11) leukemias. Blood 87: 734–745.
Megonigal MD, Rappaport EF, Wilson RB, Jones DH, Whitlock JA, Ortega JA et al. (2000). Panhandle PCR for cDNA: a rapid method for isolation of MLL fusion transcripts involving unknown partner genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 9597–9602.
Mikhail FM, Coignet L, Hatem N, Mourad ZI, Farawela HM, El Kaffash DM et al. (2004). FGA7, is fused to RUNX1/AML1 in a t(4;21)(q28;q22) in a patient with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 39: 110–118.
Mitani K, Ogawa S, Tanaka T, Miyoshi H, Kurokawa M, Mano H et al. (1994). Generation of the AML1-EVI-1 fusion gene in the t(3;21)(q26;q22) causes blastic crisis in chronic myelocytic leukemia. EMBO J 13: 504–510.
Miyoshi H, Kozu T, Shimizu K, Enomoto K, Maseki N, Kaneko Y et al. (1993). The t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia results in production of an AML1-MTG8 fusion transcript. EMBO J 12: 2715–2721.
Miyoshi H, Shimizu K, Kozu T, Maseki N, Kaneko Y, Ohki M . (1991). t(8;21) breakpoints on chromosome 21 in acute myeloid leukemia are clustered within a limited region of a single gene, AML1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10431–10434.
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL et al. (1994). Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 263: 1281–1284.
Nguyen TT, Ma LN, Slovak ML, Bangs CD, Cherry AM, Arber DA . (2006). Identification of novel Runx1 (AML1) translocation partner genes SH3D19, YTHDf2, and ZNF687 in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45: 918–932.
Ohnishi H, Kawamura M, Ida K, Sheng XM, Hanada R, Nobori T et al. (1995). Homozygous deletions of p16/MTS1 gene are frequent but mutations are infrequent in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 86: 1269–1275.
Okuda T, Cai Z, Yang S, Lenny N, Lyu CJ, van Deursen JM et al. (1998). Expression of a knocked-in AML1-ETO leukemia gene inhibits the establishment of normal definitive hematopoiesis and directly generates dysplastic hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 91: 3134–3143.
Paulsson K, Bekassy AN, Olofsson T, Mitelman F, Johansson B, Panagopoulos I . (2006). A novel and cytogenetically cryptic t(7;21)(p22;q22) in acute myeloid leukemia results in fusion of RUNX1 with the ubiquitin-specific protease gene USP42. Leukemia 20: 224–229.
Rowley JD . (1999). The role of chromosome translocations in leukemogenesis. Semin Hematol 36: 59–72.
Smith DR . (1992). Ligation-mediated PCR of restriction fragments from large DNA molecules. PCR Methods Appl 2: 21–27.
Taketani T, Taki T, Shibuya N, Ito E, Kitazawa J, Terui K et al. (2002). The HOXD11 gene is fused to the NUP98 gene in acute myeloid leukemia with t(2;11)(q31;p15). Cancer Res 62: 33–37.
Taki T, Sako M, Tsuchida M, Hayashi Y . (1997). The t(11;16)(q23;p13) translocation in myelodysplastic syndrome fuses the MLL gene to the CBP gene. Blood 89: 3945–3950.
Taki T, Taniwaki M . (2006). Chromosomal translocations in cancer and their relevance for therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 18: 62–68.
Taniwaki M, Matsuda F, Jauch A, Nishida K, Takashima T, Tagawa S et al. (1994). Detection of 14q32 translocations in B-cell malignancies by in situ hybridization with yeast artificial chromosome clones containing the human IgH gene locus. Blood 83: 2962–2969.
Von Bergh AR, Beverloo HB, Rombout P, van Wering ER, van Weel MH, Beverstock GC et al. (2002). LAF4, an AF4-related gene, is fused to MLL in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 37: 106–109.
Wang J, Hoshino T, Redner RL, Kajigaya S, Liu JM . (1998). ETO, fusion partner in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia, represses transcription by interaction with the human N-CoR/mSin3/HDAC1 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 10860–10865.
Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, Lee W, Morris IV JP, Silverman LB et al. (2004). Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science 306: 269–271.
Yan M, Burel SA, Peterson LF, Kanbe E, Iwasaki H, Boyapati A et al. (2004). Deletion of an AML1-ETO C-terminal NcoR/SMRT-interacting region strongly induces leukemia development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 17186–17191.
Zhang JG, Goldman JM, Cross NC . (1995). Characterization of genomic BCR-ABL breakpoints in chronic myeloid leukemia by PCR. Br J Haematol 90: 138–146.
Zhang Y, Emmanuel N, Kamboj G, Chen J, Shurafa M, Van Dyke DL et al. (2004). PRDX4, a member of the peroxiredoxin family, is fused to AML1 (RUNX1) in an acute myeloid leukemia patient with a t(X;21)(p22;q22). Genes Chromosomes Cancer 40: 365–370.
Acknowledgements
We express our appreciation for the outstanding technical assistance of Kozue Sugimoto, Minako Goto and Kayoko Kurita. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and the Takeda Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chinen, Y., Taki, T., Nishida, K. et al. Identification of the novel AML1 fusion partner gene, LAF4, a fusion partner of MLL, in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(2;21)(q11;q22) by bubble PCR method for cDNA. Oncogene 27, 2249–2256 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210857
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210857
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Truncated RUNX1 protein generated by a novel t(1;21)(p32;q22) chromosomal translocation impairs the proliferation and differentiation of human hematopoietic progenitors
Oncogene (2016)
-
Monosomy 13 in metaphase spreads is a predictor of poor long-term outcome after bortezomib plus dexamethasone treatment for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
International Journal of Hematology (2012)
-
Deregulated transcription factors in leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2011)
-
Possible involvement of RasGRP4 in leukemogenesis
International Journal of Hematology (2009)
-
Complementing mutations in core binding factor leukemias: from mouse models to clinical applications
Oncogene (2008)