Abstract
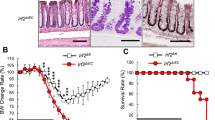
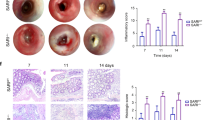
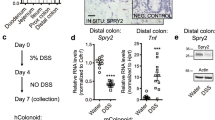
Intestinal injury or chronic inflammation induce cytokines that promote crypt regeneration and mucosal repair. If excessive or prolonged, such mechanisms may increase colon cancer risk. Factors that terminate or limit cytokine action in intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) may protect against crypt hyperplasia and neoplasia. We hypothesized that suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) is such a factor. Mice with Vilin-promoter/Cre-recombinase (VC)-mediated IEC-specific SOCS3 gene disruption (VC/HO), WT/HO littermates with floxed but intact SOCS3 genes and VC/WT mice were studied. Colon was examined after acute dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced mucosal injury or after azoxymethane (AOM) and chronic DSS. Signaling pathways were examined in colon, cultured IEC or colon cancer cell lines. VC/HO mice showed no basal phenotype. After acute DSS, VC/HO exhibited enhanced crypt proliferation and crypt hyperplasia and reduced transforming growth factor (TGF) β expression in colon. Inflammation and mucosal damage were similar across genotypes. Following AOM/DSS, VC/HO mice had increased size, number and load of colonic tumors and increased STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation in colon. In vitro, SOCS3 overexpression reduced proliferation, IL-6-mediated STAT3 activation and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α-mediated NF-κB activation. We conclude that cytokine induction of SOCS3 normally provides an intrinsic mechanism to limit injury-induced crypt hyperproliferation and inflammation-associated colon cancer by regulating both STAT3 and NF-κB pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonzi T, Newton IP, Bryce PJ, Di Carlo E, Lattanzio G, Tripodi M et al. (2004). Induced somatic inactivation of STAT3 in mice triggers the development of a fulminant form of enterocolitis. Cytokine 26: 45–56.
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA, Wirtz S, Nikolaev A et al. (2004). TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 21: 491–501.
Campbell JS, Prichard L, Schaper F, Schmitz J, Stephenson-Famy A, Rosenfeld ME et al. (2001). Expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling during liver regeneration. J Clin Invest 107: 1285–1292.
Chen Z, Laurence A, Kanno Y, Pacher-Zavisin M, Zhu BM, Tato C et al. (2006). Selective regulatory function of Socs3 in the formation of IL-17-secreting T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 8137–8142.
Chung YC, Chang YF . (2003). Serum interleukin-6 levels reflect the disease status of colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 83: 222–226.
Croker BA, Krebs DL, Zhang JG, Wormald S, Willson TA, Stanley EG et al. (2003). SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat Immunol 4: 540–545.
Greenhalgh CJ, Miller ME, Hilton DJ, Lund PK . (2002). Suppressors of cytokine signaling: relevance to gastrointestinal function and disease. Gastroenterology 123: 2064–2081.
Hanada T, Kobayashi T, Chinen T, Saeki K, Takaki H, Koga K et al. (2006). IFNgamma-dependent, spontaneous development of colorectal carcinomas in SOCS1-deficient mice. J Exp Med 203: 1391–1397.
He B, You L, Uematsu K, Zang K, Xu Z, Lee AY et al. (2003). SOCS-3 is frequently silenced by hypermethylation and suppresses cell growth in human lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 14133–14138.
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns HM, Muller-Newen G, Schaper F . (2003). Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J 374: 1–20.
Itzkowitz S . (2003). Colon carcinogenesis in inflammatory bowel disease: applying molecular genetics to clinical practice. J Clin Gastroenterol 36: 70–74.
Judd LM, Alderman BM, Howlett M, Shulkes A, Dow C, Moverley J et al. (2004). Gastric cancer development in mice lacking the SHP2 binding site on the IL-6 family co-receptor gp130. Gastroenterology 126: 196–207.
Judd LM, Bredin K, Kalantzis A, Jenkins BJ, Ernst M, Giraud AS . (2006). STAT3 activation regulates growth, inflammation, and vascularization in a mouse model of gastric tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 131: 1073–1085.
Kimura A, Naka T, Nagata S, Kawase I, Kishimoto T . (2004). SOCS-1 suppresses TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis through the regulation of Jak activation. Int Immunol 16: 991–999.
Landi S, Moreno V, Gioia-Patricola L, Guino E, Navarro M, de Oca J et al. (2003). Association of common polymorphisms in inflammatory genes interleukin (IL)6, IL8, tumor necrosis factor alpha, NFKB1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 63: 3560–3566.
Miller ME, Goebel HN, Williams KL, Keku TO, Pucilowska JB, Sartor RB et al. (2000). Suppressor of cytokine signalling-3 (SOCS-3) mRNA is preferentially induced during experimental enterocolitis, ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Regulatory Peptides 94: 67–68.
Miller ME, Michaylira CZ, Simmons JG, Ney DM, Dahly EM, Heath JK et al. (2004). Suppressor of cytokine signaling-2: a growth hormone-inducible inhibitor of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. Gastroenterology 127: 570–581.
Miscia S, Marchisio M, Grilli A, Di VV, Centurione L, Sabatino G et al. (2002). Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) activates Jak1/Stat3-Stat5B signaling through TNFR-1 in human B cells. Cell Growth Differ 13: 13–18.
Mizoguchi E, Xavier RJ, Reinecker HC, Uchino H, Bhan AK, Podolsky DK et al. (2003). Colonic epithelial functional phenotype varies with type and phase of experimental colitis. Gastroenterology 125: 148–161.
Munkholm P . (2003). Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18(Suppl 2): 1–5.
Nakamura Y, Chang CC, Mori T, Sato K, Ohtsuki K, Upham BL et al. (2004). Augmentation of differentiation and gap junction function by kaempferol in partially-differentiated colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 26: 665–671.
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A, Matsubara K, Kitagawa T et al. (2005). Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 24: 6406–6417.
Ogata H, Chinen T, Yoshida T, Kinjyo I, Takaesu G, Shiraishi H et al. (2006a). Loss of SOCS3 in the liver promotes fibrosis by enhancing STAT3-mediated TGF-beta1 production. Oncogene 25: 2520–2530.
Ogata H, Kobayashi T, Chinen T, Takaki H, Sanada T, Minoda Y et al. (2006b). Deletion of the SOCS3 gene in liver parenchymal cells promotes hepatitis-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 131: 179–193.
Oshimo Y, Kuraoka K, Nakayama H, Kitadai Y, Yoshida K, Chayama K et al. (2004). Epigenetic inactivation of SOCS-1 by CpG island hypermethylation in human gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 112: 1003–1009.
Rivat C, Wever OD, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Gespach C, Attoub S . (2004). Disruption of STAT3 signaling leads to tumor cell invasion through alterations of homotypic cell-cell adhesion complexes. Oncogene 23: 3317–3327.
Schneider MR, Hoeflich A, Fischer JR, Wolf E, Sordat B, Lahm H . (2000). Interleukin-6 stimulates clonogenic growth of primary and metastatic human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 151: 31–38.
Sutherland KD, Lindeman GJ, Choong DY, Wittlin S, Brentzell L, Phillips W et al. (2004). Differential hypermethylation of SOCS genes in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Oncogene 23: 7726–7733.
Suzuki A, Hanada T, Mitsuyama K, Yoshida T, Kamizono S, Hoshino T et al. (2001). CIS3/SOCS3/SSI3 plays a negative regulatory role in STAT3 activation and intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 193: 471–481.
Tebbutt NC, Giraud AS, Inglese M, Jenkins B, Waring P, Clay FJ et al. (2002). Reciprocal regulation of gastrointestinal homeostasis by SHP2 and STAT-mediated trefoil gene activation in gp130 mutant mice. Nat Med 8: 1089–1097.
Ulshen MH, Dowling RH, Fuller CR, Zimmermann EM, Lund PK . (1993). Enhanced growth of small bowel in transgenic mice overexpressing bovine growth hormone. Gastroenterology 104: 973–980.
Wang L, Walia B, Evans J, Gewirtz AT, Merlin D, Sitaraman SV . (2003). IL-6 induces NF-kappa B activation in the intestinal epithelia. J Immunol 171: 3194–3201.
Weber A, Hengge UR, Bardenheuer W, Tischoff I, Sommerer F, Markwarth A et al. (2005). SOCS-3 is frequently methylated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its precursor lesions and causes growth inhibition. Oncogene 24: 6699–6708.
Williams KL, Fuller CR, Dieleman LA, DaCosta CM, Haldeman KM, Sartor RB et al. (2001). Enhanced survival and mucosal repair after dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in transgenic mice that overexpress growth hormone. Gastroenterology 120: 925–937.
Yasukawa H, Ohishi M, Mori H, Murakami M, Chinen T, Aki D et al. (2003). IL-6 induces an anti-inflammatory response in the absence of SOCS3 in macrophages. Nat Immunol 4: 551–556.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kirk McNaughton for assistance with histology and immunohistochemistry, Dr Daniel Meechan for help with real-time PCR, Victoria Newton for assistance with BrdU cell counting and Eileen Hoyt for guidance with EMSA assays. This work was supported by a senior research award and post-doctoral fellowship from the Crohns' and Colitis foundation of America. Gene therapy and imaging core facilities of the Center for Gastrointestinal Biology and Disease (#P30 DK34987) assisted this work. We thank Dr Richard Furlanetto and Dr Robert Coffrey for provision of plasmids and cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigby, R., Simmons, J., Greenhalgh, C. et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) limits damage-induced crypt hyper-proliferation and inflammation-associated tumorigenesis in the colon. Oncogene 26, 4833–4841 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210286
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210286
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Detrimental Effects of Alcohol-Induced Inflammation on Brain Health: From Neurogenesis to Neurodegeneration
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Trillin prevents proliferation and induces apoptosis through inhibiting STAT3 nuclear translocation in hepatoma carcinoma cells
Medical Oncology (2020)
-
Identification of potential biomarkers related to glioma survival by gene expression profile analysis
BMC Medical Genomics (2019)
-
Bacteriophages targeting intestinal epithelial cells: a potential novel form of immunotherapy
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
Tissue-resident stem cell activity: a view from the adult Drosophila gastrointestinal tract
Cell Communication and Signaling (2017)