Abstract
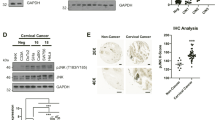
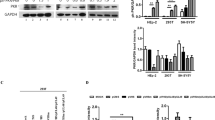
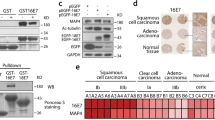
Protein kinase B (PKB) or Akt is one of several second messenger kinases that are activated by cell attachment and growth factor signaling, and that transmit signals to the cell nucleus to inhibit apoptosis and thereby increase cell survival during proliferation. Other viral proteins target this pathway by increasing PKB/Akt phosphorylation, and this pathway has been implicated in the transformation of human keratinocytes by HPV E6 and E7, together with activated notch 1. Here, we examine how HPV E7 expression affects the phosphorylation of PKB. We show that HPV-16 E7 increases the level of phosphorylation of PKB in response to serum stimulation, by a mechanism independent of downregulation of PTEN phosphatase, a known inhibitor of the PI3K (PI3 kinase) pathway. The use of specific antibodies shows that some proportion of PKB/Akt that is phosphorylated both on threonine 308 and serine 473 is maintained in the presence of E7 in a PI3 kinase-independent manner, and is activated for phosphorylation of BAD, a known downstream target of PKB/Akt. Use of E7 mutants has ruled out both an inhibition of IGFBP-3, a known E7 target and PKB/Akt modulator, and the interaction of E7 with cellular pocket proteins, as being the mechanism for the PKB/Akt stimulation. PKB binds PP2A and is a known substrate of PP2A. Here, we show that HPV E7 also binds to both the 35 kDa catalytic and 65 kDa structural subunits of PP2A, an interaction that sequesters these subunits and inhibits their interaction with PKB, thereby maintaining PKB/Akt signaling by inhibiting its dephosphorylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andjelkovic M, Kakubowicz T, Cron P, Ming XF, Han JW and Hemmings BA . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 5699–5704.
Banks L, Edmonds C and Vousden KH . (1990). Oncogene, 5, 1383–1389.
Borgatti P, Zauli G, Colamussi M, Gibellini G, Previati M, Cantley L and Capitani S . (1997). Eur. J. Immunol., 27, 2805–2811.
Brazil D and Hemmings BA . (2001). Trends Biochem. Sci., 26, 657–664.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond M, Lin M, Juo P, Hu L, Anderson M, Arden K, Blenis J and Greenberg M . (1999). Cell, 96, 857–868.
Crusius K, Auvinen E and Alonso A . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 1437–1444.
Dajee M, Tarutani M, Deng H, Cai T and Khavari PA . (2002). Oncogene, 21, 1527–1538.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME . (1997). Cell, 91, 231–241.
Delcommene M, Tan C, Gray V, Rue L, Woodget J and Dedhar S . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 11211–11216.
Dilworth SM and Horner VP . (1993). J. Virol., 67, 2235–2244.
Dyson N, Howley PM, Münger K and Harlow E . (1989). Science, 243, 934–936.
Frese KK, Lee SS, Thomas DL, Latorre IJ, Weiss RS, Glaunsinger BA and Javier RT . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 710–721.
Fujisaki H and Hattori S . (2002). Exp. Cell. Res., 280, 255–269.
Graham FL and van der Eb AJ . (1973). Virology, 52, 456–467.
Gu Z and Matlashewski G . (1995). J. Virol., 69, 8051–8056.
Hanada M, Feng J and Hemmings BA . (2004). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1697, 3–16.
Harlow E and Lane D . (1988). Antibodies, A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Publications, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Hawley-Nelson P, Vousden KH, Hubbert NL, Lowy DR and Schiller JT . (1989). EMBO J., 8, 3905–3910.
He Y, Nakao H, Tan S-L, Polyak SJ, Neddermann P, Vijaysri S, Jacobs BL and Katze MG . (2002). J. Virol., 76, 9207–9217.
Huynh H, Chow PK, Ooi LL and Soo KC . (2002). Cell Growth Differ., 13, 115–122.
Ishiwatari H, Hayasaka N, Inoue H, Yutsudo M and Hakura A . (1994). J. Med. Virol., 44, 243–249.
Johnston D, Hall H, DiLorenzo TP and Steinberg BM . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 968–974.
Mannhardt B, Weinzimer SA, Wagner M, Fiedler M, Cohen P, Jansen-Durr P and Zwerschke W . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 6483–6495.
Massimi P, Pim D and Banks L . (1997). J. Gen. Virol., 78, 2607–2613.
Matlashewski G, Schneider J, Banks L, Jones N, Murray A and Crawford L . (1987). EMBO J., 6, 1741–1746.
Meili R, Cron P, Hemmings BA and Ballmer-Hofer K . (1998). Oncogene, 16, 903–907.
Milburn CC, Deak M, Kelly SM, Price NC, Alessi DR and Van Aaltern DM . (2003). Biochem. J., 375, 531–538.
Münger K, Phelps WC, Bubb V, Howley PM and Schlegel R . (1989). J. Virol., 63, 4417–4423.
Pallas DC, Shahrik LK, Martin BL, Jaspers S, Miller TB, Brautigan DL and Roberts TM . (1990). Cell, 60, 167–176.
Pallas DC, Weller W, Jaspers S, Miller TB, Lane WS and Roberts TM . (1992). J. Virol., 66, 886–893.
Pankov R, Cukierman E, Clark K, Matsumoto K, Hahn C, Poulin B and Yamada KM . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 18671–18681.
Pim D, Collins M and Banks L . (1992). Oncogene, 7, 27–32.
Pim D, Massimi P and Banks L . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 257–264.
Pim D, Storey A, Thomas M, Massimi P and Banks L . (1994). Oncogene, 9, 1869–1876.
Pouliot N, Saunders NA and Kaur P . (2002). Exp. Dermatol., 11, 387–397.
Rangarajan A, Syal R, Selvarajah S, Chakrabarti O, Sarin A and Krishna S . (2001). Virology, 286, 23–30.
Resjo S, Goransson O, Harndahl L, Zolnierowicz S, Manganiello V and Degerman E . (2002). Cell Signal., 14, 231–238.
Sayama K, Yamasaki K, Hanakawa Y, Shirakata Y, Tokumaru S, Ijuin T and Hashimoto K . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 40390–40396.
Smith DB and Johnson KS . (1988). Gene, 67, 31–40.
Stambolic V, Mak TW and Woodgett JR . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6094–6103.
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Brothers GM, Mirtsos C, Sasaki T, Ruland J, Penninger JM, Siderovski DP and Mak TW . (1998). Cell, 95, 29–39.
Storey A, Pim D, Murray A, Osborn K, Banks L and Crawford LV . (1988). EMBO J., 7, 1815–1820.
Summers S, Lipfert L and Birnbaum M . (1998). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 246, 76–81.
Sun P, Wang XQ, Lopatka K, Bangash S and Paller AS . (2002). J. Invest. Dermatol., 19, 107–117.
Troussard AA, Mawji NM, Ong C, Mui A, St-Arnaud R and Dedhar S . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 22374–22378.
Velling T, Nilsson S, Stefansson A and Johansson S . (2004). EMBO Rep., 5, 901–905.
Werness B, Levine A and Howley PM . (1990). Science, 248, 76–79.
Westbrook TF, Nguyen DX, Thrash BR and McCance DJ . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 7041–7052.
Xu W, Yuan X, Jung YJ, Yang Y, Basso A, Rosen N, Chung EJ, Trepel J and Neckers L . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 7777–7778.
Zur Hausen H . (1999). Semin. Cancer Biol., 9, 405–411.
Acknowledgements
We thank David Evans for the kind gift of plasmid pcDNA3 PP2A Cα. This work was supported, in part, by a research grant from the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pim, D., Massimi, P., Dilworth, S. et al. Activation of the protein kinase B pathway by the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein occurs through a mechanism involving interaction with PP2A. Oncogene 24, 7830–7838 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208935
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208935
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Navigating therapeutic strategies: HPV classification in head and neck cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2024)
-
Mechanisms of action of Fu Fang Gang Liu liquid in treating condyloma acuminatum by network pharmacology and experimental validation
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2023)
-
The ubiquitin specific protease 7 stabilizes HPV16E7 to promote HPV-mediated carcinogenesis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Live and let die: signaling AKTivation and UPRegulation dynamics in SARS-CoVs infection and cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Increased O-GlcNAcylation promotes IGF-1 receptor/PhosphatidyI Inositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway in cervical cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2022)