Abstract
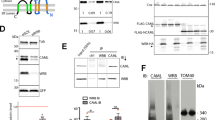
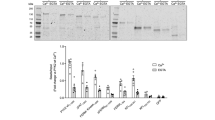
We demonstrate using Ca2+-dependent calmodulin (CaM)-affinity chromatography and overlay with biotinylated CaM that the adaptor proteins growth factor receptor bound (Grb)7 and Grb7V (a naturally occurring variant lacking the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain) are CaM-binding proteins. Deletion of an amphiphilic basic amino-acid sequence (residues 243–256) predicted to form an α-helix located in the proximal region of its pleckstrin homology (PH) domain demonstrates the location of the CaM-binding domain. This site is identical in human and rodents Grb7, and shares great homology with similar regions of Grb10 and Grb14, and the Mig10 protein from Caenorhabditis elegans. We show that Grb7 and Grb7V are present in the cytosol and bound to membranes, while the deletion mutants (Grb7Δ and Grb7VΔ) have less capacity to be associated to membranes. Grb7Δ maintains in part the capacity to bind phosphoinositides, and CaM competes for phosphoinositide binding. Activation of ErbB2 by heregulin β1 decreases the pool of Grb7 associated to membranes. The cell-permeable CaM antagonist W7 (N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide), but not the CaM-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor KN93, prevents this effect. Highly specific cell-permeable CaM inhibitory peptides decrease the association of Grb7 to membranes. This suggests that CaM regulates the intracellular mobilization of Grb7 in living cells. Direct interaction between enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP)-Grb7 and enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (ECFP)-CaM chimeras at the plasma membrane of living cells was demonstrated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). The FRET signal dramatically decreased in cells loaded with a cell-permeable Ca2+ chelator, and was significantly attenuated when enhanced yellow fluorescent protein-Grb7 chimera (EYFP-Grb7)Δ instead of EYFP-Grb7 was used. Finally, we show that conditioned media from cells transiently transfected with Grb7Δ and Grb7VΔ lost its angiogenic activity, in contrast to those from cells transiently transfected with their wild-type counterparts.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aCtrl-P:
-
acylated control peptide
- aMLCK-P:
-
acylated myosin light-chain kinase peptide
- BAPTA-AM:
-
[1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid tetra(acetoxymethyl) ester]
- B-CaM:
-
biotinylated calmodulin
- CaM:
-
calmodulin
- CaM-BD:
-
CaM-binding domain
- CaMK-II:
-
CaM-dependent protein kinase II
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco‘s modified Eagle's medium
- ECFP-CaM:
-
enhanced cyan fluorescent protein-calmodulin chimera
- EYFP-Grb7:
-
enhanced yellow fluorescent protein-Grb7 chimera
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- EGFR:
-
EGF receptor
- EGFR-GFP:
-
EGFR-green fluorescent protein chimera
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EGTA:
-
[ethylene bis(oxyethylenenitrilo)]-tetraacetic acid
- FAK:
-
focal adhesion kinase
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- FRET:
-
fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- Grb:
-
growth factor receptor bound
- HEPES:
-
N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- HRGβ1:
-
heregulin β1
- IPTG:
-
isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside
- mCtrl-P:
-
myristoylated control peptide
- mMLCK-P:
-
myristoylated myosin light-chain kinase peptide
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PH:
-
pleckstrin homology
- Pipes:
-
piperazine-N,N′-bis(ethanesulfonic acid)
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- P-Tyr:
-
phosphotyrosine
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene fluoride
- SH2:
-
Src homology 2
- W7:
-
N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide
References
Bähler M and Rhoads A . (2002). FEBS Lett., 513, 107–113.
Billingsley ML, Pennypacker KR, Hoover CG, Brigati DJ and Kincaid RL . (1985). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82, 7585–7589.
Cariou B, Bereziat V, Moncoq K, Kasus-Jacobi A, Perdereau D, Le Marcis V and Burnol AF . (2004). Front. Biosci., 9, 1626–1636.
Chin D and Means AR . (2000). Trends Cell Biol., 10, 322–328.
Daly RJ . (1998). Cell. Signal., 10, 613–618.
Daly RJ, Sanderson GM, Janes PW and Sutherland RL . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 12502–12510.
Feinmesser RL, Gray K, Means AR and Chantry A . (1996). Oncogene, 12, 2725–2730.
Fiddes RJ, Campbell DH, Janes PW, Sivertsen SP, Sasaki H, Wallasch C and Daly RJ . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 7717–7724.
Goldenring JR, Vallano ML, Lasher RS, Ueda T and DeLorenzo RJ . (1986). Prog. Brain Res., 69, 341–354.
Han DC and Guan J-L . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 24425–24430.
Han DC, Shen TL and Guan JL . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 28911–28917.
Han DC, Shen T-L and Guan J-L . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 6315–6321.
Han DC, Shen TL, Miao H, Wang B and Guan JL . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 45655–45661.
Hayashi N, Matsubara M, Takasaki A, Titani K and Taniguchi H . (1998). Prot. Express. Purif., 12, 25–28.
Hoeflich KP and Ikura M . (2002). Cell, 108, 739–742.
Janes PW, Lackmann M, Church WB, Sanderson GM, Sutherland RL and Daly RJ . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 8490–8497.
Jurado LA, Chockalingam PS and Jarret HW . (1999). Physiol. Rev., 79, 661–682.
Kasus-Jacobi A, Perdereau D, Auzan C, Clauser E, van Obberghen E, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Girard J and Burnol AF . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 26026–26035.
Kishi T, Sasaki H, Akiyama N, Ishizuka T, Sakamoto H, Aizawa S, Sugimura T and Terada M . (1997). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 232, 5–9.
Klee CB and Vanaman TC . (1982). Advan. Prot. Chem., 35, 213–321.
Laemmli UK . (1970). Nature, 227, 680–685.
Li H, Ruano MJ and Villalobo A . (2004a). FEBS Lett., 559, 175–180.
Li H, Sánchez-Torres J, del Carpio A, Salas V and Villalobo A . (2004b). Biochem. J., 381, 257–266.
Li H and Villalobo A . (2002). Biochem. J., 362, 499–505.
Lim MA, Riedel H and Liu F . (2004). Front. Biosci., 9, 387–403.
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Snapp E and Kenworthy A . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2, 444–456.
Liu F and Roth RA . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 10287–10291.
Manser J and Wood WB . (1990). Dev. Genet., 11, 49–64.
Margolis B, Silvennoinen O, Comoglio F, Roonprapunt C, Skolnik E, Ullrich A and Schlessinger J . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 8894–8898.
Martín-Nieto J and Villalobo A . (1998). Biochemistry, 37, 227–236.
Means AR, Tash JS, Chafouleas JG, Lagace L and Guerriero V . (1982). Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 383, 69–84.
Morrione A . (2003). J. Cell. Physiol., 197, 307–311.
Nishikawa M, Tanaka T and Hidaka H . (1980). Nature, 287, 863–865.
O'Neil KT and DeGrado WF . (1990). Trends Biochem. Sci., 15, 59–64.
Ooi J, Yajnik V, Immanuel D, Gordon M, Moskow JJ, Buchberg AM and Margolis B . (1995). Oncogene, 10, 1621–1630.
Pandey A, Liu X, Dixon JE, Di Fiore PP and Dixit VM . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 10607–10610.
Riedel H . (2004). Front. Biosci., 9, 603–618.
Reilly JF, Mickey G and Maher PA . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 7771–7778.
San José E, Benguría A, Geller P and Villalobo A . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 15237–15245.
Shen T-L and Guan J-L . (2004). Front. Biosci., 9, 192–200.
Shen T-L, Han DC and Guan J-L . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 29069–29077.
Stanimirovic D, Morley P, Ball R, Hamel E, Mealing G and Durkin JP . (1996). J. Cell. Physiol., 169, 455–467.
Stein D, Wu J, Fuqua SAW, Roonprapunt C, Yajnik V, D'Eustachio P, Moskow J, Buchberg AM, Osborne CK and Margolis B . (1994). EMBO J., 13, 1331–1340.
Stoscheck CM . (1990). Methods Enzymol., 182, 50–68.
Tanaka S, Mori M, Akiyoshi T, Tanaka Y, Mafune K, Wands JR and Sugimachi K . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 28–31.
Tanaka S, Mori M, Akiyoshi T, Tanaka Y, Mafune K, Wands JR and Sugimachi K . (1998). J. Clin. Invest., 102, 821–827.
Thorogate R and Török K . (2004). J. Cell Sci., 117, 5923–5936.
Török K, Cowley DJ, Brandmeier BD, Howell S, Aitken A and Trentham DR . (1998b). Biochemistry, 37, 6188–6198.
Török K and Trentham DR . (1994). Biochemistry, 33, 12807–12820.
Török K, Wilding M, Groigno L, Patel R and Whitaker M . (1998a). Curr. Biol., 8, 692–699.
Villalobo A, Li H and Sánchez-Torres J . (2003). Curr. Topics Biochem. Res., 5, 105–114.
Villalobo A, Ruano MJ, Palomo-Jiménez PI, Li H and Martín-Nieto J . (2000) Pochet R, Donato R, Haiech J, Heizmann C and Gerke V (eds). Calcium: The Molecular Basis of Calcium Action in Biology and Medicine. Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, pp. 287–303.
Waterston R . (1998). Science, 282, 2012–2018.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professors Shinji Tanaka for Grb7 and Grb7V vectors, Nobuhiro Hayashi for recombinant calmodulin, Atushi Miyawaki for the ECFP-CaM vector, Carlos Enrich for PAE/EGFR-GFP cells, Ms M Dolores Morales-García for assistance with the FRET experiments, Ms Amparo Jiménez and Ms Marguerite Ball for technical assistance, and Dr Danica Stanimirovic for resources and facilities to perform the angiogenesis experiments. This work was financed by grants (to AV) from the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (SAF2002-03258) and the Instituto Carlos III, Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (RTICCC C03/10). HL was supported by the Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional (2002CN0013), and AFdC by the Fundación Carolina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Sánchez-Torres, J., del Carpio, A. et al. The adaptor Grb7 is a novel calmodulin-binding protein: functional implications of the interaction of calmodulin with Grb7. Oncogene 24, 4206–4219 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208591
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208591