Abstract
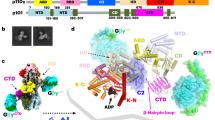
Rho family-specific guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (RhoGDIs) decrease the rate of nucleotide dissociation and release Rho proteins such as RhoA, Rac and Cdc42 from membranes, forming tight complexes that shuttle between cytosol and membrane compartments. We have solved the crystal structure of a complex between the RhoGDI homolog LyGDI and GDP-bound Rac2, which are abundant in leukocytes, representing the cytosolic, resting pool of Rho species to be activated by extracellular signals. The N-terminal domain of LyGDI (LyN), which has been reported to be flexible in isolated RhoGDIs, becomes ordered upon complex formation and contributes more than 60% to the interface area. The structure is consistent with the C-terminus of Rac2 binding to a hydrophobic cavity previously proposed as isoprenyl binding site. An inner segment of LyN forms a helical hairpin that contacts mainly the switch regions of Rac2. The architecture of the complex interface suggests a mechanism for the inhibition of guanine nucleotide dissociation that is based on the stabilization of the magnesium (Mg2+) ion in the nucleotide binding pocket.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Van Aelst, L. & D'Souza-Schorey, C. Genes Dev. 11, 2295–2322 (1997).
Bourne, H.R. & Sanders, D.A. Nature 348, 125–131 (1990).
Scherle, P., Behrens, T. & Staudt, L.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 7568–7572 (1993).
Keep, N.H. et al. Structure 5, 623–633 (1997).
Gosser, Y.Q. et al. Nature 387, 814–819 (1997).
Danley, D.E., Chuang, T.H. & Bokoch, G.M. J. Immunol. 157, 500–503 (1996).
Wei, Y. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 699–703 (1997).
Platko, J.V. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 2974–2978 (1995).
Na, S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 11209–11213 (1996).
Wu, W.J., Leonard, D.A., Cerione, R.A. & Manor, D. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26153–261538 (1997).
Hirshberg, M., Stockley, R.W., Dodson, G. & Webb, M.R. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 147–152 (1997).
Ueda, T., Kikuchi, A., Ohga, N., Yamamoto, J. & Takai, Y. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 9373–9380 (1990).
Sasaki, T., Kato, M. & Takai, Y. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 23959–23963 (1993).
Chuang, T.H., Xu, X., Knaus, U.G., Hart, M.J. & Bokoch, G.M. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 775–778 (1993).
Newcombe, A.R., Stockley, R.W., Hunter, J.L. & Webb, M.R. Biochemistry 38, 6879–6886 (1999).
Hancock, J.F. & Hall, A. EMBO J. 12, 1915–1921 (1993).
Nomanbhoy, T.K. & Cerione, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 10004–10009 (1996).
Hart, M.J. et al. Science 258, 812–815 (1992).
Rittinger, K., Walker, P.A., Eccleston, J.F., Smerdon, S.J. & Gamblin, S.J. Nature 389, 758–762 (1997).
Kikuchi, A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14611–14615 (1992).
Li, R. & Zheng, Y. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4671–4679 (1997).
Boriack-Sjodin, A., Margarit, S.M., Bar-Sagi, D. & Kuriyan, J. Nature 394, 337–343 (1998).
Goldberg, J. Cell 95, 237–248 (1998).
Abdul-Manan, N. et al. Nature 399, 379–383 (1999).
Mott, H.R. et al. Nature 399, 384–388 (1999).
Hori, Y. et al. Oncogene 6, 515–522 (1991).
Nomanbhoy, T.K., Erickson, J.W. & Cerione, R.A. Biochemistry 38, 1744–1750 (1999).
Feltham, J.L. et al. Biochemistry 36, 8755–8766 (1997).
Geyer, M., et al. Biochemistry. 35, 10308–10320 (1996).
Tanaka, K., Sasaki, T. & Takai, Y. Methods Enzymol. 256, 41–49 (1995).
Illenberger, D. et al. EMBO J. 17, 6241–6249 (1998).
Kabsch, W. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 795–800 (1993).
Collaborative Computational Project Number 4. CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Jones, T.A. & Kjelgaard, M. Methods Enzymol. 277, 173–208 (1997).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl.Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merrit, E.A. & Bacon, D.J. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A & Honig, B. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Longenecker, K. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 1503–1515 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Wittinghofer for initiating the collaboration, for critical comments on the manuscript and encouragement, the EMBL Grenoble outstation, in particular A. Perrakis for providing support for measurements on the microfocus beam line (ID13) at the ESRF under the European Union TMR/LSF Programme, EMBL Heidelberg for preliminary mass spectrometry experiments, B. Prakash and A. Becker for discussions, W. Kabsch for discussion of crystallography, and K. Holmes for continuous support. K.S. thanks the Peter und Traudl Engelhorn Stiftung (Penzberg, Germany) for support in the initial phase of the project. This work was supported in part by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Medical Faculty of the University of Ulm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheffzek, K., Stephan, I., Jensen, O. et al. The Rac–RhoGDI complex and the structural basis for the regulation of Rho proteins by RhoGDI. Nat Struct Mol Biol 7, 122–126 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/72392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/72392
This article is cited by
-
α2β1 integrins spatially restrict Cdc42 activity to stabilise adherens junctions
BMC Biology (2021)
-
The Rho GTPase signalling pathway in urothelial carcinoma
Nature Reviews Urology (2018)
-
PKCα phosphorylation of RhoGDI2 at Ser31 disrupts interactions with Rac1 and decreases GDI activity
Oncogene (2013)
-
G protein signaling in the parasite Entamoeba histolytica
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2013)
-
Rictor regulates cell migration by suppressing RhoGDI2
Oncogene (2013)