Abstract
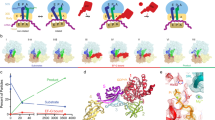
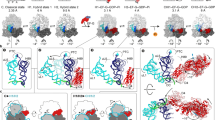
Cryo-electron microscopy has been used to visualize elongation factor G (EF-G) on the 70S ribosome in GDP and GTP states. GTP hydrolysis is required for binding of all the domains of EF-G to the pretranslocational complex and for the completion of translocation. In addition, large conformational changes have been identified in the ribosome. The head of the 30S subunit shifts toward the L1 protein side, and the L7/L12 stalk becomes bifurcated upon EF-G binding. Upon GTP hydrolysis, the bifurcation is reversed and an arc-like connection is formed between the base of the stalk and EF-G.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishizuka, Y. & Lipmann, F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 55, 212–219 (1966).
Chinali, G. & Parmeggiani, A. Eur. J. Biochem. 125, 415–421 (1982).
Spirin, A.S. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 32, 75– 114 (1985).
Modolell, J., Girbes, T. & Vazquez, D. FEBS Lett. 60, 109– 113 (1975).
Rodnina, M.V., Savelsbergh, A., Katunin, V.I. & Wintermeyer, W. Nature 385, 37–41 ( 1997).
Ævarsson, A. et al. EMBO J. 13, 3669–3677 (1994).
Czworkowski, J., Wang, J., Steitz, T.A. & Moore, P.B. EMBO J. 13, 3661–3668 (1994).
Agrawal, R.K., Penczek, P., Grassucci, R.A. & Frank, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6134– 6138 (1998).
Wilson, K.S. & Noller, H.F. Cell 92, 131–139 (1998).
Willie, G.R., Richman, N., Godtfredson, W.O. & Bodley, J.W., Biochemistry 14, 1713–1718 (1975).
Malhotra, A. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 280, 103– 116 (1998).
Agrawal, R.K. et al. Proc. 14th Intl. Congr. Electron Microscopy 1, 717–718 (1998).
Lill, R., & Wintermeyer, W. J. Mol. Biol. 196 , 137–148 (1987).
Agrawal, R.K. et al. Science 271, 1000– 1002 (1996).
Nissen, P. et al. Science 270, 1464– 1472 (1995).
Abel, K., Yoder, M.D., Hilgenfeld, R. & Jurnak, F. Structure 4, 1153–1159 ( 1996).
Czworkowski, J. & Moore, P.B. Biochemistry 36, 10327–10334 (1997).
Traut, R.R. et al. Biochem. Cell Biol. 73, 949– 958 (1995).
Stark, H. et al. Nature 389, 403–406 (1997).
Hamman, B.D., Oleinikov, A.V., Jokhadze, G.G., Traut, R.R. & Jameson, D.M. Biochemistry 35, 16672–16679 (1996).
Burma, D.P., Srivastava, S., Srivastava, A.K., Mahanti, S. & Dash, D., In Structure function and genetics of ribosomes (eds Hardesty, B. & Kramer, G.) 438– 453 (Springer-Verlag, New York; 1986).
Wool, I.G., Gluck, A. & Endo, Y. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17, 266–269 (1992).
Agrawal, R.K., Lata, K.R. & Frank, J., Intl. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31, 243–254 (1999).
Gabashvili, I.S., Agrawal, R.K., Grassucci, R.A. & Frank J. J. Mol. Biol. 286, 1285–1291 (1999).
Müller, F. & Brimacombe, R. J. Mol. Biol. 271, 524–544 ( 1997).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H.F. Nature 342, 142–148 (1989).
Agrawal, R.K. & Burma, D.P. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21285–21291 (1996).
Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. & Clark B.F., FASEB J. 10, 1347– 1368 (1996).
Nierhaus, K.H. Biochemistry 29, 4997–5012 (1990).
Wagenknecht, T., Grassucci, R. & Frank, J. J. Mol. Biol. 199, 137– 145 (1988).
Zhu, J., Penczek, P.A., Schröder, R. & Frank, J. J. Struct. Biol. 118, 197–219 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Moore for providing the all-atom coordinates of the EF-G–GDPX-ray structure. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, R., Heagle, A., Penczek, P. et al. EF-G-dependent GTP hydrolysis induces translocation accompanied by large conformational changes in the 70S ribosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 643–647 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/10695
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/10695
This article is cited by
-
Bias at the third nucleotide of codon pairs in virus and host genomes
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Structures of the human mitochondrial ribosome bound to EF-G1 reveal distinct features of mitochondrial translation elongation
Nature Communications (2020)
-
A SelB/EF-Tu/aIF2γ-like protein from Methanosarcina mazei in the GTP-bound form binds cysteinyl-tRNACys
Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics (2015)
-
The ABC-F protein EttA gates ribosome entry into the translation elongation cycle
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2014)
-
EttA regulates translation by binding the ribosomal E site and restricting ribosome-tRNA dynamics
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2014)