Abstract
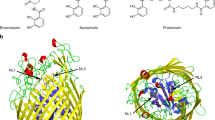
Integral outer membrane receptors for iron chelates and vitamin B 12 carry out specific ligand transport against a concentration gradient. Energy for active transport is obtained from the proton–motive force of the inner membrane through physical interaction with TonB–ExbB–ExbD, an inner membrane complex. Here we report the crystal structure of an active transport, outer membrane receptor at 2.4 Å resolution. Two distinct functional domains are revealed: (i) a 22–stranded β–barrel that spans the outer membrane and contains large extracellular loops which appear to function in ligand binding; and (ii) a globular N–terminal domain that folds into the barrel pore, inhibiting access to the periplasm and contributing two additional loops for potential ligand binding. These loops could provide a signaling pathway between the processes of ligand recognition and TonB–mediated transport. The blockage of the pore suggests that the N–terminal domain must undergo a conformational rearrangement to allow ligand transport into the periplasm.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, V., Hantke, K. & Köster, W. Bacterial iron transport: Mechanisms, genetics, and regulation. in Metal ions in biological systems volume 35: iron transport and storage in microorganisms, plants, and animals (eds Sigel, A. & Sigel, H.) 67–145 (Marcel Dekker, New York; 1998 ).
Stephens, D.L., Choe, M.D. & Earhart, C.F. Escherichia coli periplasmic protein FepB binds ferrienterobactin. Microbiology 141, 1647–1654 (1995).
Chenault, S.S. & Earhart, C.F. Organization of genes encoding membrane proteins of the Escherichia coli ferrienterobactin permease. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 1405– 1413 (1991).
Shea, C.M. & McIntosh, M.A. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the ferric enterobactin transport system: homology to other periplasmic binding protein–dependent systems in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 1415– 1428 (1991).
Langman, L., Young, I.G., Frost, G.E., Rosenberg, H. & Gibson, F. Enterochelin system of iron transport in Escherichia coli: mutations affecting ferric–enterochelin esterase. J. Bacteriol. 112, 1142–1149 (1972).
Loomis, L.D. & Raymond, K.N. Solution equilibria of enterobactin and metal–enterobactin complexes. Inorg. Chem. 30, 906–911 (1991).
Karpishin, T.B., Dewey, T.M. & Raymond, K.N. The vanadium (IV) enterobactin complex: structural, spectroscopic, and electrochemical characterization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 1842–1851 (1993).
Ecker, D.J., Matzanke, B.F. & Raymond, K.N. Recognition and transport of ferric enterobactin in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 167, 666–673 (1986).
Zhou, X.H., Van der Helm, D. & Adjimani, J. Purification of outer membrane iron transport receptors from Echerichia coli by fast protein liquid chromatography: FepA and FecA. Biometals 6, 25–35 (1993).
Payne, M.A. et al. Biphasic binding kinetics between FepA and its ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 21950–21955 (1997).
Bradbeer, C. The proton motive force drives the outer membrane transport of cobalamin in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 175, 3146–3150 (1993).
Braun, V. Energy–coupled transport and signal transduction through the gram–negative outer membrane via TonB–ExbB–ExbD–dependent receptor proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 16, 295– 307 (1995).
Skare, J.T., Ahmer, B.M., Seachord, C.L., Darveau, R.P. & Postle, K. Energy transduction between membranes. TonB, a cytoplasmic membrane protein, can be chemically cross–linked in vivo to the outer membrane receptor FepA. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 16302–16308 (1993).
Larsen, R.A., Foster–Hartnett, D., McIntosh, M.A. & Postle, K. Regions of Escherichia coli TonB and FepA proteins essential for in vivo physical interactions. J. Bacteriol. 179, 3213–3221 (1997).
Kadner, R.J. Vitamin B12 transport in Escherichia coli: energy coupling between membranes. Mol. Microbiol. 4, 2027– 2033 (1990).
Smith, B.S. et al. Crystallization and preliminary X–ray analysis of ferric enterobactin receptor FepA, an integral membrane protein from Escherichia coli. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 697– 699 (1998).
Michel, H. Crystallization of membrane proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 8, 56–59 (1983).
Weiss, M.S., Wacker, T., Weckesser, J., Welte, W. & Schulz, G.E. The three–dimensional structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus at 3 Å resolution. FEBS Lett. 267, 268–272 (1990).
Cowan, S.W. et al. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature 358, 727– 733 (1992).
Schirmer, T., Keller, T.A., Wang, Y.–F. & Rosenbusch, J.P. Structural basis for sugar translocation through maltoporin channels at 3.1 Å resolution. Science 267, 512– 514 (1995).
Forst, D., Welte, W., Wacker, T. & Diederichs, K. Structure of the sucrose–specific porin ScrY from Salmonella typhimurium and its complex with sucrose. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 37–46 (1998).
Lesk, A.M., Brändén, C.–I. & Chothia, C. Structural principles of a/b barrel proteins: the packing of the interior of the sheet. Proteins 5, 139–148 (1989).
Struyve, M., Moons, M. & Tommassen, J. Carboxy–terminal phenylalanine is essential for the correct assembly of a bacterial outer membrane protein. J. Mol. Biol. 218, 141–148 (1991).
Murphy, C.K., Kalve, V.I. & Klebba, P.E. Surface topology of the Escherichia coli K–12 ferric enterobactin receptor. J. Bacteriol. 172, 2736–2746 (1990).
Klug, C.S., Su, W.Y. & Feix, J.B. Mapping of the residues involved in a proposed b–strand located in the ferric enterobactin receptor FepA using site–directed spin–labeling. Biochemistry 36, 13027–13033 (1997).
Lathrop, J.T., Wei, B.Y., Touchie, G.A. & Kadner, R.J. Sequences of the Escherichia coli BtuB protein essential for its insertion and function in the outer membrane. J. Bacteriol. 177, 6810–6819 (1995).
Carmel, G., Hellstern, D., Henning, D. & Coulton, J.W. Insertion mutagenesis of the gene encoding the ferrichrome–iron receptor of Escherichia coli K–12. J. Bacteriol. 172, 1861–1869 (1990).
Koebnik, R. & Braun, V. Insertion derivatives containing segments of up to 16 amino acids identify surface– and periplasm–exposed regions of the FhuA outer membrane receptor of Escherichia coli K–12. J. Bacteriol. 175, 826– 839 (1993).
Armstrong, S.K. & McIntosh, M.A. Epitope insertions define functional and topological features of the Escherichia coli ferric enterobactin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 2483–2488 (1995).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
Lundrigan, M.D. & Kadner, R.J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the ferrienterochelin receptor FepA in Escherichia coli. Homology among outer membrane receptors that interact with TonB. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 10797–10801 (1986).
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G. & Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position–specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994).
Van der Helm, D. The physical chemistry of bacterial outer–membrane siderophore receptor proteins. in Metal ions in biological systems Volume 35: iron transport and storage in microorganisms, plants, and animals (eds Sigel, A. & Sigel, H.) 355–401 (Marcel Dekker, New York; 1998).
Newton, S.M.C. et al. Double mutagenesis of a positive charge cluster in the ligand–binding site of the ferric enterobactin receptor, FepA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 4560–4565 (1997).
Postle, K. TonB protein and energy transduction between membranes. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 25, 591–601 (1993).
Moeck, G.S., Coulton, J.W. & Postle, K. Cell envelope signaling in Escherichia coli ligand binding to the ferrichrome–iron receptor FhuA promotes interaction with the energy–transducing protein TonB. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 28391–28397 (1997).
Miller, M.J. & Malouin, F. Microbial iron chelators as drug delivery agents: the rational design and synthesis of siderophore–drug conjugates. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 241– 249 (1993).
Wiener, M., Freymann, D., Ghosh, P. & Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of colicin Ia. Nature 385, 461– 464 (1997).
Rutz, J.M. et al. Formation of a gated channel by a ligand–specific transport protein in the bacterial outer membrane. Science 258, 471–475 (1992).
Liu, J., Rutz, J.M., Klebba, P.E. & Feix, J.B. A site–directed spin–labeling study of ligand–induced conformational change in the ferric enterobactin receptor, FepA. Biochemistry 33, 13274–13283 (1994).
Jalal, M.A.F. & Van der Helm, D. Purification and crystallization of ferric enterobactin receptor protein, FepA, from the outer membranes of Escherichia coli UT5600/pBB2. FEBS Lett. 243, 366–370 (1989).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X–ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Meth. Enz. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Collaborative Computational Project Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Otwinowski, Z. Maximum likelihood refinement of heavy atom parameters. in Isomorphous Replacement and Anomalous Scattering. Proceedings of the CCP4 study weekend 25–26 January 1991. (eds Wolf, W., Evans, P.R. & Leslie, A.G.W.) 80–86 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, UK; 1991).
Cowtan, K.D. & Main, P. Phase combination and cross validation in iterated density–modification calculations. Acta Crystallogr. D52, 43–48 (1996).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.–Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Xia, D. et al. Crystal structure of the cytochrome bc1 complex from bovine heart mitochondria. Science 277, 60–66 (1997).
Esnouf, R.M. An extensively modified version of Molscript that includes greatly enhanced coloring capabilities. J. Mol. Graph. 15, 133–138 (1997).
Evans, S.V. SETOR: hardware–lighted three–dimensional solid model representations of macromolecules. J. Mol. Graph. 11, 134–138 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We thank Z. Wang for help with in–house data collection; and M. Capel and C. Ogata for help with synchrotron data collection. D.v.d.H. acknowledges support from the NIH. S.K.B. acknowledges support from the American Cancer Society. J.D. is an Investigator in the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchanan, S., Smith, B., Venkatramani, L. et al. Crystal structure of the outer membrane active transporter FepA from Escherichia coli. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 56–63 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/4931
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/4931
This article is cited by
-
Surveying membrane landscapes: a new look at the bacterial cell surface
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2023)
-
The Thermodynamic Stability of Membrane Proteins in Micelles and Lipid Bilayers Investigated with the Ferrichrom Receptor FhuA
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2022)
-
Mechanism of TonB-dependent transport system in Halomonas alkalicola CICC 11012s in response to alkaline stress
Extremophiles (2021)
-
Metagenomic and chemical characterization of soil cobalamin production
The ISME Journal (2020)
-
Genetic and structural determinants on iron assimilation pathways in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri and Xanthomonas sp.
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2020)