Abstract
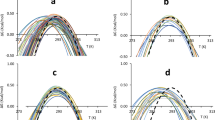
Folding of ribonuclease HI from Escherichia coli populates a kinetic intermediate detectable by stopped-flow circular dichroism. Pulse labelling hydrogen exchange reveals that this intermediate consists of a structured core region of the protein, namely helices A and D and β-strand 4. This kinetic intermediate resembles both the acid molten globule of ribonuclease HI and rarely populated, partially unfolded forms detected under native conditions. These results indicate that the first portion of ribonuclease HI to fold is the most thermodynamically stable region of the native state, and that folding of this protein follows a hierarchical process.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, P.S. & Baldwin, R.L. Specific intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins and the mechanism of protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 51, 459–489 (1982).
Kim, P.S. & Baldwin, R.L. Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660 (1990).
Matthews, C.R. Pathways of protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683 (1993).
Jackson, S.E. & Fersht, A.R. Folding of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2. 1. Evidence for a two-state transition. Biochemistry 30, 10428–10435 (1991).
Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L., Hiller, R. & Englander, S.W. The barriers in protein folding. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 149–156 (1994).
Schindler, T., Herrler, M., Marahiel, M.A. & Schmid, F.X. Extremely rapid protein folding in the absence of intermediates. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 663–673 (1995).
Ptitsyn, O.B. Structures of folding intermediates. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 5, 74–78 (1995).
Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state of α-lactalbumin. FASEB J. 10, 102–109 (1996).
Ptitsyn, O.B., Pain, R.H., Semisotnov, G.V., Zerovnik, E. & Razgulyaev, O.I. Evidence for a molten globule state as a general intermediate in protein folding. FEBS Lett. 262, 20–24 (1990).
Jennings, P.A. & Wright, P.E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science 262, 892–896 (1993).
Arai, M. & Kuwajima, K. Rapid formation of a molten globule intermediate in refolding of α-lactalbumin. Folding & Design 1, 275–287 (1996).
Bai, Y., Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Protein folding intermediates: native-state hydrogen exchange. Science 269, 192–197 (1995).
Chamberlain, A.K., Handel, T.M. & Marqusee, S. Detection of rare partially folded molecules in equilibrium with the native conformation of RNase H. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 782–787 (1996).
Katayanagi, K. et al. Three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease H from E. coli. Nature 347, 306–309 (1990).
Crouch, R.J. & Dirksen, M. Ribonucleases H. in Nucleases (ed. Linn, S.) 211–241 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1982).
Kanaya, S., Kimura, S., Katsuda, C. & Ikehara, M. Role of cysteine residues in ribonuclease H from Escherichia coli. Site-directed mutagenesis and chemical modification. Biochem. J. 271, 59–66 (1990).
Yamasaki, K., Ogasahara, K., Yutani, K., Oobatake, M. & Kanaya, S. Folding pathway of Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI: a circular dichroism, fluorescence, and NMR study. Biochemistry 34, 16552–16562 (1995).
Dabora, J.M. & Marqusee, S. Equilibrium unfolding of Escherichia coli ribonuclease H: characterization of a partially folded state. Protein Sci. 3, 1401–1408 (1994).
Dabora, J. & Marqusee, S. Structure of the acid state of Escherichia coli ribonuclease H1. Biochemistry 35, 11951–11958 (1996).
Kuwajima, K., Yamaya, H., Miwa, S., Sugai, S. & Nagamura, T. Rapid formation of secondary structure framework in protein folding studied by stopped-f low circular dichroism. FEBS Lett. 221, 115–118 (1987).
Baldwin, R.L. On-pathway versus off-pathway folding intermediates. Folding & Design 1, R1–R8 (1996).
Khorasanizadeh, S., Peters, I.D. & Roder, H. Evidence for a three-state model of protein folding from kinetic analysis of ubiquitin variants with altered core residues. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 193–205 (1996).
Matouschek, A., Kellis, J.T., Serrano, L., Bycroft, M. & Fersht, A.R. Transient folding intermediates characterized by protein engineering. Nature 346, 440–445 (1990).
Kiefhaber, T. Kinetic traps in lysozyme folding. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9029–9033 (1995).
Roder, H., Elove, G.A. & Englander, S.W. Structural characterization of folding intermediates in cytochrome c by H-exchange labelling and proton NMR. Nature 335, 700–704 (1988).
Udgaonkar, J.B. & Baldwin, R.L. NMR evidence for an early framework intermediate on the folding pathway of ribonuclease A. Nature 335, 694–699 (1988).
Elove, G.A. & Roder, H. Structure and stability of cytochrome c folding intermediates. in Protein Refolding (ed. Georgiou, G.) 51–63 (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1991).
Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state as a clue for understanding the folding and cooperativity of globular-protein structure. Proteins 6, 87–103 (1989).
Ptitsyn, O.B., Pain, R.H., Semisotnov, G.V., Zerovnik, E. & Razgulyaev, O.I. Evidence for a molten globule state as a general intermediate in protein folding. FEBS Lett. 262, 20–24 (1990).
Elove, G.A., Bhuyan, A.K. & Roder, H. Kinetic mechanism of cytochrome c folding: involvement of the heme and its ligands. Biochemistry 33, 6925–6935 (1994).
Chen, H., Hughes, D.D., Chan, T.-A., Sedat, J.W. & Agard, D.A. IVE (lmage Visualization Environment): A software platform for all three-dimensional microscopy applications. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 56–60 (1996).
Hvidt, A. & Nielsen, S.O. Hydrogen exchange in proteins. Adv. Prot. Chem. 21, 288–386 (1966).
Englander, S.W. & Kallenbach, N.R. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids. Q. Rev. Biophys. 16, 521–655 (1983).
Bai, Y., Milne, J.S., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange. Proteins 17, 75–86 (1993).
Connelly, G.P., Bai, Y., Jeng, M.F. & Englander, S.W. Isotope effects in peptide group hydrogen exchange. Proteins 17, 87–92 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raschke, T., Marqusee, S. The kinetic folding intermediate of ribonuclease H resembles the acid molten globule and partially unfolded molecules detected under native conditions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 4, 298–304 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0497-298
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0497-298