Abstract
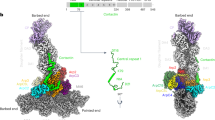
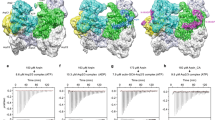
The Arp2/3 complex mediates formation of complex cellular structures such as lamellipodia by nucleating branched actin filaments. Arp2/3-complex activity is precisely controlled by over a dozen regulators, yet the structural mechanism by which regulators interact with the complex is unknown. GMF is a recently discovered regulator of the Arp2/3 complex that can inhibit nucleation and disassemble branches. We solved the structure of the 240-kDa assembly of Mus musculus GMF and Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex and found that GMF binds the barbed end of Arp2, overlapping with the proposed binding site of WASP-family proteins. The structure suggests that GMF can bind branch junctions in the manner that cofilin binds filament sides, consistent with a modified cofilin-like mechanism for debranching by GMF. The GMF-Arp2 interface reveals how the ADF-H actin-binding domain in GMF is exploited to specifically recognize Arp2/3 complex and not actin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rotty, J.D., Wu, C. & Bear, J.E. New insights into the regulation and cellular functions of the ARP2/3 complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 7–12 (2013).
Goley, E.D. & Welch, M.D. The ARP2/3 complex: an actin nucleator comes of age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 713–726 (2006).
Campellone, K.G. & Welch, M.D. A nucleator arms race: cellular control of actin assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 237–251 (2010).
Pollard, T.D. Regulation of actin filament assembly by Arp2/3 complex and formins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 36, 451–477 (2007).
Liu, S.L., Needham, K.M., May, J.R. & Nolen, B.J. Mechanism of a concentration-dependent switch between activation and inhibition of Arp2/3 complex by coronin. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 17039–17046 (2011).
Humphries, C.L. et al. Direct regulation of Arp2/3 complex activity and function by the actin binding protein coronin. J. Cell Biol. 159, 993–1004 (2002).
Maul, R.S. et al. EPLIN regulates actin dynamics by cross-linking and stabilizing filaments. J. Cell Biol. 160, 399–407 (2003).
Blanchoin, L., Pollard, T.D. & Hitchcock-DeGregori, S.E. Inhibition of the Arp2/3 complex-nucleated actin polymerization and branch formation by tropomyosin. Curr. Biol. 11, 1300–1304 (2001).
Maritzen, T. et al. Gadkin negatively regulates cell spreading and motility via sequestration of the actin-nucleating ARP2/3 complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 10382–10387 (2012).
Rocca, D.L., Martin, S., Jenkins, E.L. & Hanley, J.G. Inhibition of Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization by PICK1 regulates neuronal morphology and AMPA receptor endocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 259–271 (2008).
Yamakita, Y., Oosawa, F., Yamashiro, S. & Matsumura, F. Caldesmon inhibits Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 17937–17944 (2003).
Gandhi, M. et al. GMF is a cofilin homolog that binds Arp2/3 complex to stimulate filament debranching and inhibit actin nucleation. Curr. Biol. 20, 861–867 (2010).
Ti, S.C., Jurgenson, C.T., Nolen, B.J. & Pollard, T.D. Structural and biochemical characterization of two binding sites for nucleation-promoting factor WASp-VCA on Arp2/3 complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, E463–E471 (2011).
Nakano, K., Kuwayama, H., Kawasaki, M., Numata, O. & Takaine, M. GMF is an evolutionarily developed Adf/cofilin-super family protein involved in the Arp2/3 complex-mediated organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 67, 373–382 (2010).
Ikeda, K. et al. Glia maturation factor-γ is preferentially expressed in microvascular endothelial and inflammatory cells and modulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Circ. Res. 99, 424–433 (2006).
Poukkula, M., Kremneva, E., Serlachius, M. & Lappalainen, P. Actin-depolymerizing factor homology domain: a conserved fold performing diverse roles in cytoskeletal dynamics. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 68, 471–490 (2011).
Mooren, O.L., Galletta, B.J. & Cooper, J.A. Roles for actin assembly in endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 661–686 (2012).
Ydenberg, C. et al. GMF severs actin-Arp2/3 complex branch junctions by a cofilin-like mechanism. Curr. Biol. 23, 1–9 (2013).
Nolen, B.J., Littlefield, R.S. & Pollard, T.D. Crystal structures of actin-related protein 2/3 complex with bound ATP or ADP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15627–15632 (2004).
Paavilainen, V.O., Oksanen, E., Goldman, A. & Lappalainen, P. Structure of the actin-depolymerizing factor homology domain in complex with actin. J. Cell Biol. 182, 51–59 (2008).
Galkin, V.E. et al. Remodeling of actin filaments by ADF/cofilin proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 20568–20572 (2011).
Goroncy, A.K. et al. NMR solution structures of actin depolymerizing factor homology domains. Protein Sci. 18, 2384–2392 (2009).
Lappalainen, P., Fedorov, E.V., Fedorov, A.A., Almo, S.C. & Drubin, D.G. Essential functions and actin-binding surfaces of yeast cofilin revealed by systematic mutagenesis. EMBO J. 16, 5520–5530 (1997).
Bamburg, J.R. Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 185–230 (1999).
Dominguez, R. Actin-binding proteins: a unifying hypothesis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29, 572–578 (2004).
Nolen, B.J. & Pollard, T.D. Insights into the influence of nucleotides on actin family proteins from seven structures of Arp2/3 complex. Mol. Cell 26, 449–457 (2007).
Martin, A.C., Welch, M.D. & Drubin, D.G. Arp2/3 ATP hydrolysis-catalysed branch dissociation is critical for endocytic force generation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 826–833 (2006).
Ingerman, E., Hsiao, J.Y. & Mullins, R.D. Arp2/3 complex ATP hydrolysis promotes lamellipodial actin network disassembly but is dispensable for assembly. J. Cell Biol. 200, 619–633 (2013).
Otterbein, L.R., Graceffa, P. & Dominguez, R. The crystal structure of uncomplexed actin in the ADP state. Science 293, 708–711 (2001).
Hetrick, B., Han, M.S., Helgeson, L.A. & Nolen, B.J. Small molecules CK-666 and CK-869 inhibit Arp2/3 complex by blocking an activating conformational change. Chem. Biol. 701–712 (2013).
Padrick, S.B., Doolittle, L.K., Brautigam, C.A., King, D.S. & Rosen, M.K. Arp2/3 complex is bound and activated by two WASP proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, E472–E479 (2011).
Panchal, S.C., Kaiser, D.A., Torres, E., Pollard, T.D. & Rosen, M.K. A conserved amphipathic helix in WASP/Scar proteins is essential for activation of Arp2/3 complex. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 591–598 (2003).
Chereau, D. et al. Actin-bound structures of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-homology domain 2 and the implications for filament assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 16644–16649 (2005).
Irobi, E. et al. Structural basis of actin sequestration by thymosin-β4: implications for WH2 proteins. EMBO J. 23, 3599–3608 (2004).
Marchand, J.B., Kaiser, D.A., Pollard, T.D. & Higgs, H.N. Interaction of WASP/Scar proteins with actin and vertebrate Arp2/3 complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 76–82 (2001).
Balcer, H.I., Daugherty-Clarke, K. & Goode, B.L. The p40/ARPC1 subunit of Arp2/3 complex performs multiple essential roles in WASp-regulated actin nucleation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 8481–8491 (2010).
Chan, C., Beltzner, C.C. & Pollard, T.D. Cofilin dissociates Arp2/3 complex and branches from actin filaments. Curr. Biol. 19, 537–545 (2009).
Rouiller, I. et al. The structural basis of actin filament branching by the Arp2/3 complex. J. Cell Biol. 180, 887–895 (2008).
Boczkowska, M. et al. X-Ray scattering study of activated Arp2/3 complex with bound actin-WCA. Structure 16, 695–704 (2008).
Weaver, A.M. et al. Interaction of cortactin and N-WASp with Arp2/3 complex. Curr. Biol. 12, 1270–1278 (2002).
Uruno, T., Liu, J., Li, Y., Smith, N. & Zhan, X. Sequential interaction of actin-related proteins 2 and 3 (Arp2/3) complex with neural Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) and cortactin during branched actin filament network formation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 26086–26093 (2003).
Mahaffy, R.E. & Pollard, T.D. Kinetics of the formation and dissociation of actin filament branches mediated by Arp2/3 complex. Biophys. J. 91, 3519–3528 (2006).
Cai, L., Makhov, A.M., Schafer, D.A. & Bear, J.E. Coronin 1B antagonizes cortactin and remodels Arp2/3-containing actin branches in lamellipodia. Cell 134, 828–842 (2008).
Weaver, A.M. et al. Cortactin promotes and stabilizes Arp2/3-induced actin filament network formation. Curr. Biol. 11, 370–374 (2001).
Bernstein, B.W. & Bamburg, J.R. Tropomyosin binding to F-actin protects the F-actin from disassembly by brain actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF). Cell Motil. 2, 1–8 (1982).
Graceffa, P. & Dominguez, R. Crystal structure of monomeric actin in the ATP state. Structural basis of nucleotide-dependent actin dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 34172–34180 (2003).
Ashkenazy, H., Erez, E., Martz, E., Pupko, T. & Ben-Tal, N. ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W529–W533 (2010).
Nolen, B.J. & Pollard, T.D. Structure and biochemical properties of fission yeast ARP2/3 complex lacking the ARP2 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 26490–26498 (2008).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data dollected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
McCoy, A.J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Winn, M.D. et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 235–242 (2011).
Acknowledgements
Results shown in this report are derived from work performed at Argonne National Laboratory, Structural Biology Center at the Advanced Photon Source, beamline 19ID. Argonne is operated by University of Chicago Argonne, LLC, for the US Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research under contract DE-AC02-06CH11357. We thank S. Ginell, J. Lazarz, B. Nocek and Y. Kim for assistance with remote data collection. We thank B. Goode (Brandeis University, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) for sending mouse GMFγ expression plasmids and for discussing unpublished observations, and K. Needham for help with cloning and protein purification. We would also like to acknowledge K. Prehoda for comments on the manuscript. This work was financially supported by a US National Institutes of Health grant GM092917 (to B.J.N.) and the Pew Scholars in the Biomedical Sciences program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.L. and B.J.N. designed the research; Q.L. performed all experiments; Q.L. and B.J.N. analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5 (PDF 2370 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, Q., Nolen, B. Structural basis for regulation of Arp2/3 complex by GMF. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1062–1068 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2628
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2628
This article is cited by
-
Biochemical and mechanical regulation of actin dynamics
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2022)
-
Cryo-electron tomography structure of Arp2/3 complex in cells reveals new insights into the branch junction
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Cryo-EM reveals the transition of Arp2/3 complex from inactive to nucleation-competent state
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2020)
-
Cellular and pathophysiological consequences of Arp2/3 complex inhibition: role of inhibitory proteins and pharmacological compounds
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)
-
An AP-MS- and BioID-compatible MAC-tag enables comprehensive mapping of protein interactions and subcellular localizations
Nature Communications (2018)