Abstract
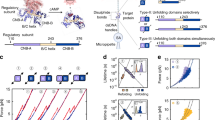
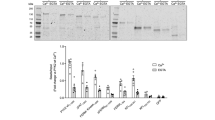
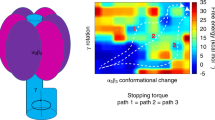
The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a heterotrimeric complex that is allosterically activated by AMP binding to the γ subunit. Cocrystal structures of the mammalian AMPK core reveal occlusion of nucleotide-binding site 3 of the γ subunit in the presence of ATP. However, site 3 is occupied in the presence of AMP. Mutagenesis studies indicate that sites 3 and 4 are important for AMPK allosteric activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardie, D.G., Carling, D. & Gamblin, S.J. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 470–477 (2011).
Fogarty, S. & Hardie, D.G. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804, 581–591 (2010).
Hawley, S.A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 27879–27887 (1996).
Oakhill, J.S. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 19237–19241 (2010).
Oakhill, J.S. et al. Science 332, 1433–1435 (2011).
Davies, S.P., Helps, N.R., Cohen, P.T. & Hardie, D.G. FEBS Lett. 377, 421–425 (1995).
Xiao, B. et al. Nature 472, 230–233 (2011).
Scott, J.W. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 274–284 (2004).
Suter, M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 32207–32216 (2006).
Adams, J. et al. Protein Sci. 13, 155–165 (2004).
Townley, R. & Shapiro, L. Science 315, 1726–1729 (2007).
Amodeo, G.A., Rudolph, M.J. & Tong, L. Nature 449, 492–495 (2007).
Xiao, B. et al. Nature 449, 496–500 (2007).
Chen, L. et al. Nature 459, 1146–1149 (2009).
Riek, U. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 18331–18343 (2008).
Zhu, L. et al. Structure 19, 515–522 (2011).
Steuber, H. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 363, 174–187 (2006).
Hillig, R.C. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 369, 735–745 (2007).
Neumann, D., Woods, A., Carling, D., Wallimann, T. & Schlattner, U. Protein Expr. Purif. 30, 230–237 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank S.C. Lin for critical discussions and reading of the manuscript. Crystallographic data were collected at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility beamline 17U. This work is supported in part by grant 2011CB910800 (National Key Basic Research Program of China) to J.-W.W. and Z.-X.W. and grants 31130062, 31070643 (Natural Science Foundation of China) and 09THZ02235 (Tsinghua University) to J.-W.W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.C., J.W. and Y.-Y.Z. performed experiments; S.F.Y., D.N., U.S., Z.-X.W. and J.-W.W. contributed to discussions and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5, Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Note (PDF 1641 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Wang, J., Zhang, YY. et al. AMP-activated protein kinase undergoes nucleotide-dependent conformational changes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 716–718 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2319
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2319
This article is cited by
-
AMPK pathway: an emerging target to control diabetes mellitus and its related complications
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2024)
-
Rapid metabolic reprogramming mediated by the AMP-activated protein kinase during the lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
Nature Communications (2023)
-
IKCa channels control breast cancer metabolism including AMPK-driven autophagy
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
AMPK: a key regulator of energy stress and calcium-induced autophagy
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Long-chain fatty acyl-CoA esters regulate metabolism via allosteric control of AMPK β1 isoforms
Nature Metabolism (2020)