Abstract
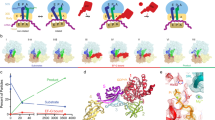
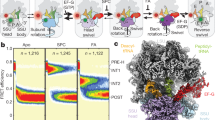
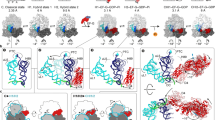
In bacteria, the translocation of tRNA and mRNA with respect to the ribosome is catalyzed by the conserved GTPase elongation factor-G (EF-G). To probe the rate-determining features in this process, we imaged EF-G–catalyzed translocation from two unique structural perspectives using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The data reveal that the rate at which the ribosome spontaneously achieves a transient, 'unlocked' state is closely correlated with the rate at which the tRNA-like domain IV-V element of EF-G engages the A site. After these structural transitions, translocation occurs comparatively fast, suggesting that conformational processes intrinsic to the ribosome determine the rate of translocation. Experiments conducted in the presence of non-hydrolyzable GTP analogs and specific antibiotics further reveal that allosterically linked conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome mediate rapid, directional substrate movement and EF-G release.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agirrezabala, X. & Frank, J. Elongation in translation as a dynamic interaction among the ribosome, tRNA, and elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu. Q. Rev. Biophys. 42, 159–200 (2009).
Shoji, S., Walker, S.E. & Fredrick, K. Ribosomal translocation: one step closer to the molecular mechanism. ACS Chem. Biol. 4, 93–107 (2009).
Wintermeyer, W. et al. Mechanisms of elongation on the ribosome: dynamics of a macromolecular machine. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 733–737 (2004).
Fredrick, K. & Noller, H. Catalysis of ribosomal translocation by sparsomycin. Science 300, 1159–1162 (2003).
Cukras, A.R., Southworth, D.R., Brunelle, J.L., Culver, G.M. & Green, R. Ribosomal proteins S12 and S13 function as control elements for translocation of the mRNA:tRNA complex. Mol. Cell 12, 321–328 (2003).
Gavrilova, L.P., Kostiashkina, O.E., Koteliansky, V.E., Rutkevitch, N.M. & Spirin, A.S. Factor-free (“non-enzymic”) and factor-dependent systems of translation of polyuridylic acid by Escherichia coli ribosomes. J. Mol. Biol. 101, 537–552 (1976).
Bergemann, K. & Nierhaus, K.H. Spontaneous, elongation factor G independent translocation of Escherichia coli ribosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 15105–15113 (1983).
Agirrezabala, X. et al. Visualization of the hybrid state of tRNA binding promoted by spontaneous ratcheting of the ribosome. Mol. Cell 32, 190–197 (2008).
Julián, P. et al. Structure of ratcheted ribosomes with tRNAs in hybrid states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 16924–16927 (2008).
Fei, J., Kosuri, P., MacDougall, D.D. & Gonzalez, R.L. Jr. Coupling of ribosomal L1 stalk and tRNA dynamics during translation elongation. Mol. Cell 30, 348–359 (2008).
Cornish, P.V., Ermolenko, D.N., Noller, H.F. & Ha, T. Spontaneous intersubunit rotation in single ribosomes. Mol. Cell 30, 578–588 (2008).
Cornish, P.V. et al. Following movement of the L1 stalk between three functional states in single ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2571–2576 (2009).
Munro, J.B. et al. Spontaneous formation of the unlocked state of the ribosome is a multistep process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 709–714 (2010).
Munro, J.B., Altman, R.B., Tung, C.S., Sanbonmatsu, K.Y. & Blanchard, S.C. A fast dynamic mode of the EF-G-bound ribosome. EMBO J (2010).
Munro, J.B., Altman, R.B., O'Connor, N. & Blanchard, S.C. Identification of two distinct hybrid state intermediates on the ribosome. Mol. Cell 25, 505–517 (2007).
Blanchard, S.C., Kim, H.D., Gonzalez, R.L. Jr., Puglisi, J.D. & Chu, S. tRNA dynamics on the ribosome during translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12893–12898 (2004).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H.F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature 342, 142–148 (1989).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J. 23, 1008–1019 (2004).
Valle, M. et al. Locking and unlocking of ribosomal motions. Cell 114, 123–134 (2003).
Katunin, V.I., Savelsbergh, A., Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. Coupling of GTP hydrolysis by elongation factor G to translocation and factor recycling on the ribosome. Biochemistry 41, 12806–12812 (2002).
Modolell, J. & Vazquez, D. The inhibition of ribosomal translocation by viomycin. Eur. J. Biochem. 81, 491–497 (1977).
Walker, S.E., Shoji, S., Pan, D., Cooperman, B.S. & Fredrick, K. Role of hybrid tRNA-binding states in ribosomal translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 9192–9197 (2008).
Connell, S.R. et al. Structural basis for interaction of the ribosome with the switch regions of GTP-bound elongation factors. Mol. Cell 25, 751–764 (2007).
Stark, H., Rodnina, M.V., Wieden, H.J., van Heel, M. & Wintermeyer, W. Large-scale movement of elongation factor G and extensive conformational change of the ribosome during translocation. Cell 100, 301–309 (2000).
Ticu, C., Nechifor, R., Nguyen, B., Desrosiers, M. & Wilson, K.S. Conformational changes in switch I of EF-G drive its directional cycling on and off the ribosome. EMBO J. 28, 2053–2065 (2009).
Peske, F., Matassova, N.B., Savelsbergh, A., Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. Conformationally restricted elongation factor G retains GTPase activity but is inactive in translocation on the ribosome. Mol. Cell 6, 501–505 (2000).
Peske, F., Savelsbergh, A., Katunin, V.I., Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. Conformational changes of the small ribosomal subunit during elongation factor G-dependent tRNA-mRNA translocation. J. Mol. Biol. 343, 1183–1194 (2004).
Pan, D., Kirillov, S. & Cooperman, B.S. Kinetically competent intermediates in the translocation step of protein synthesis. Mol. Cell 25, 519–529 (2007).
Studer, S.M., Feinberg, J.S. & Joseph, S. Rapid kinetic analysis of EF-G-dependent mRNA translocation in the ribosome. J. Mol. Biol. 327, 369–381 (2003).
Dorner, S., Brunelle, J.L., Sharma, D. & Green, R. The hybrid state of tRNA binding is an authentic translation elongation intermediate. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 234–241 (2006).
Qin, F. Restoration of single-channel currents using the segmental k-means method based on hidden Markov modeling. Biophys. J. 86, 1488–1501 (2004).
Qin, F., Auerbach, A. & Sachs, F. Estimating single-channel kinetic parameters from idealized patch-clamp data containing missed events. Biophys. J. 70, 264–280 (1996).
Rodnina, M.V., Savelsbergh, A., Katunin, V.I. & Wintermeyer, W. Hydrolysis of GTP by elongation factor G drives tRNA movement on the ribosome. Nature 385, 37–41 (1997).
Zhou, Z. et al. Genetically encoded short peptide tags for orthogonal protein labeling by Sfp and AcpS phosphopantetheinyl transferases. ACS Chem. Biol. 2, 337–346 (2007).
Yin, J., Lin, A.J., Golan, D.E. & Walsh, C.T. Site-specific protein labeling by Sfp phosphopantetheinyl transferase. Nat. Protoc. 1, 280–285 (2006).
Wen, J.D. et al. Following translation by single ribosomes one codon at a time. Nature 452, 598–603 (2008).
Savelsbergh, A. et al. An elongation factor G-induced ribosome rearrangement precedes tRNA-mRNA translocation. Mol. Cell 11, 1517–1523 (2003).
Johansen, S.K., Maus, C.E., Plikaytis, B.B. & Douthwaite, S. Capreomycin binds across the ribosomal subunit interface using tlyA-encoded 2′-O-methylations in 16S and 23S rRNAs. Mol. Cell 23, 173–182 (2006).
Ermolenko, D.N. et al. The antibiotic viomycin traps the ribosome in an intermediate state of translocation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 493–497 (2007).
Feldman, M.B., Terry, D.S., Altman, R.B. & Blanchard, S.C. Aminoglycoside activity observed on single pre-translocation ribosome complexes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6, 54–62 (2010).
Gao, Y.G. et al. The structure of the ribosome with elongation factor G trapped in the posttranslocational state. Science 326, 694–699 (2009).
Rodnina, M.V. et al. Thiostrepton inhibits the turnover but not the GTPase of elongation factor G on the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 9586–9590 (1999).
Bodley, J.W., Zieve, F.J., Lin, L. & Zieve, S.T. Formation of the ribosome–G factor–GDP complex in the presence of fusidic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 37, 437–443 (1969).
Inoue-Yokosawa, N., Ishikawa, C. & Kaziro, Y. The role of guanosine triphosphate in translocation reaction catalyzed by elongation factor G. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 4321–4323 (1974).
Wang, Y. et al. Single-molecule structural dynamics of EF-G–ribosome interaction during translocation. Biochemistry 46, 10767–10775 (2007).
Zavialov, A.V. & Ehrenberg, M. Peptidyl-tRNA regulates the GTPase activity of translation factors. Cell 114, 113–122 (2003).
Schuwirth, B.S. et al. Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 A resolution. Science 310, 827–834 (2005).
Borovinskaya, M.A., Shoji, S., Holton, J.M., Fredrick, K. & Cate, J.H.D. A steric block in translation caused by the antibiotic spectinomycin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2, 545–552 (2007).
Wilson, D.N. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 44, 393–433 (2009).
Frank, J. & Agrawal, R.K. A ratchet-like inter-subunit reorganization of the ribosome during translocation. Nature 406, 318–322 (2000).
Munro, J.B., Sanbonmatsu, K.Y., Spahn, C.M. & Blanchard, S.C. Navigating the ribosome's metastable energy landscape. Trends Biochem. Sci. 34, 390–400 (2009).
Aitken, C.E., Marshall, R.A. & Puglisi, J.D. An oxygen scavenging system for improvement of dye stability in single-molecule fluorescence experiments. Biophys. J. 94, 1826–1835 (2008).
Dave, R., Terry, D.S., Munro, J.B. & Blanchard, S.C. Mitigating unwanted photophysical processes for improved single-molecule fluorescence imaging. Biophys. J. 96, 2371–2381 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank C. Walsh (Harvard University) and members of his laboratory for providing the Sfp expression vector and for their assistance with the fluorescent labeling of EF-G and K.Y. Sanbonmatsu and P. Whitford for structural models of the E. coli ribosome. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grant GM079238.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.B.M. and S.C.B. designed the experiments. J.B.M. and M.R.W. conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. R.B.A. and L.W. prepared reagents. J.B.M., M.R.W., R.B.A. and S.C.B. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–12 and Supplementary Tables 1–3 (PDF 2357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munro, J., Wasserman, M., Altman, R. et al. Correlated conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome regulate translocation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 1470–1477 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1925
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1925
This article is cited by
-
Altered tRNA dynamics during translocation on slippery mRNA as determinant of spontaneous ribosome frameshifting
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Insights into genome recoding from the mechanism of a classic +1-frameshifting tRNA
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Effect of Fusidic Acid on the Kinetics of Molecular Motions During EF-G-Induced Translocation on the Ribosome
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Multiperspective smFRET reveals rate-determining late intermediates of ribosomal translocation
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2016)
-
Choreography of molecular movements during ribosome progression along mRNA
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2016)