Abstract
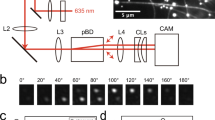
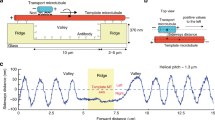
Mitotic kinesin Eg5 is a homotetrameric molecular motor that cross-links and slides microtubules. The extent to which Eg5 moves processively is not clear. Here we use three-dimensional tracking of a quantum dot attached to the microtubule in a motility assay to directly visualize the corkscrew motion of a sliding microtubule. We show that the rotational pitch of microtubule sliding conveniently reports on the processivity of the driving motors, confirming that two-headed Eg5 is much less processive than two-headed kinesin-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sawin, K.E., LeGuellec, K., Philippe, M. & Mitchison, T.J. Nature 359, 540–543 (1992).
Blangy, A. et al. Cell 83, 1159–1169 (1995).
Valentine, M.T., Fordyce, P.M., Krzysiak, T.C., Gilbert, S.P. & Block, S.M. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 470–476 (2006).
Kaseda, K., Crevel, I., Hirose, K. & Cross, R.A. EMBO Rep. 9, 761–765 (2008).
Howard, J., Hudspeth, A.J. & Vale, R.D. Nature 342, 154–158 (1989).
Vale, R.D. et al. Nature 380, 451–453 (1996).
Block, S.M., Goldstein, L.S. & Schnapp, B.J. Nature 348, 348–352 (1990).
Ray, S., Meyhöfer, E., Milligan, R.A. & Howard, J. J. Cell Biol. 121, 1083–1093 (1993).
Yajima, J. & Cross, R.A. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 338–341 (2005).
Walker, R.A., Salmon, E.D. & Endow, S.A. Nature 347, 780–782 (1990).
Okada, Y., Higuchi, H. & Hirokawa, N. Nature 424, 574–577 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank D.R. Drummond and R.A. Cross for critical comments and discussion on the manuscript, T. Usui (University of Tsukuba) for the Eg5 clone, T. Masaike and I. Terashima for supporting the experiments, and J. Ohkawa and K. Matsui for the microscope technique. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists (No. 20710170) to J.Y. and for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (No. 509 and 521) to T.N. from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and by the grant to T.N. from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Y. and K.M. contributed equally to this work: K.M. designed and developed the new microscopy method; J.Y. conceived the experiments, performed rotation measurements and the data analyses and wrote the manuscript. T.N. supervised this work.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Methods (PDF 13065 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
First ∼1 second shows a sliding rhodamine-labeled microtubule (0.7 s intervals, ×10 actual speed, rhodamine filter set, Nikon). Remaining ∼9 seconds shows a moving QD 525 (Invitrogen) fixed to the microtubule via a streptavidin-biotin interaction (2.8 s intervals ×300 actual speed, Qdot 525 filter set, Chroma). Image, 14 μm high × 52 μm wide. (MOV 751 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
The viewing angle is changed every 10 degrees by 360 degrees along a longitudinal axis of the microtubule. The colors (blue, sky blue, green, yellow) of the dots show the height of z-position. The blue is lowest and the yellow is highest. A distance between blue dot and yellow dot is ∼70 nm. See Fig. 1c (MOV 1594 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yajima, J., Mizutani, K. & Nishizaka, T. A torque component present in mitotic kinesin Eg5 revealed by three-dimensional tracking. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15, 1119–1121 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1491
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1491
This article is cited by
-
Membrane-bound myosin IC drives the chiral rotation of the gliding actin filament around its longitudinal axis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Mechanisms underlying spindle assembly and robustness
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2023)
-
Motor generated torque drives coupled yawing and orbital rotations of kinesin coated gold nanorods
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Anchoring geometry is a significant factor in determining the direction of kinesin-14 motility on microtubules
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Torque generating properties of Tetrahymena ciliary three-headed outer-arm dynein
Scientific Reports (2022)