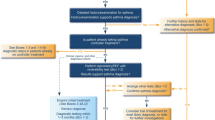
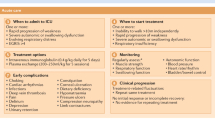
Key Points
-
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a common disability that can manifest in a variety of ways
-
Respiratory complications and psychosocial issues are often unrecognized in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia
-
Videofluoroscopy and fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing are the current gold-standard investigations for oropharyngeal dysphagia
-
Despite considerable effort, these conventional diagnostic methods have limited proven accuracy in predicting aspiration and respiratory disease
-
Emerging evidence shows that novel techniques such as high-resolution manometry with impedance, functional lumen imaging probe and accelerometry could have a role in the diagnosis of oropharyngeal dysphagia
-
Incorporation of measurable objective assessments into clinical diagnosis is needed and could reveal subtle abnormalities that are key to distinguish pathology of oropharyngeal dysphagia and develop new therapeutic strategies
Abstract
Swallowing disorders (dysphagia) have been recognized by the WHO as a medical disability associated with increased morbidity, mortality and costs of care. With increasing survival rates and ageing of the population, swallowing disorders and their role in causing pulmonary and nutritional pathologies are becoming exceedingly important. Over the past two decades, the study of oropharyngeal dysphagia has been approached from various disciplines with considerable progress in understanding its pathophysiology. This Review describes the most frequent manifestations of oropharyngeal dysphagia and the clinical as well as instrumental techniques that are available to diagnose patients with dysphagia. However, the clinical value of these diagnostic tests and their sensitivity to predict outcomes is limited. Despite considerable clinical research efforts, conventional diagnostic methods for oropharyngeal dysphagia have limited proven accuracy in predicting aspiration and respiratory disease. We contend that incorporation of measurable objective assessments into clinical diagnosis is needed and might be key in developing novel therapeutic strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. International classification of functioning, disability and health (ICF) (WHO, 2001).
Martino, R., Beaton, D. & Diamant, N. E. Perceptions of psychological issues related to dysphagia differ in acute and chronic patients. Dysphagia 25, 26–34 (2010).
McHorney, C. A. et al. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia 17, 97–114 (2002).
Gustafsson, B. & Tibbling, L. Dysphagia, an unrecognized handicap. Dysphagia 6, 193–199 (1991).
Stuchell, R. N. & Mandel, I. D. Salivary gland dysfunction and swallowing disorders. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 21, 649–661 (1988).
Altman, K. W., Yu, G.-P. & Schaefer, S. D. Consequence of dysphagia in the hospitalized patient: impact on prognosis and hospital resources. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 136, 784–789 (2010).
Roden, D. F. & Altman, K. W. Causes of dysphagia among different age groups: a systematic review of the literature. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 46, 965–987 (2013).
Doty, R. W. & Bosma, J. F. An electromyographic analysis of reflex deglutition. J. Neurophysiol. 19, 44–60 (1956).
Prosiegel, M. Dysphagia: Diagnosis and Treatment (2012).
Clavé, P., Terré, R., de Kraa, M. & Serra, M. Approaching oropharyngeal dysphagia. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 96, 119–131 (2004).
Wallace, K. L., Middleton, S. & Cook, I. J. Development and validation of a self-report symptom inventory to assess the severity of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia. Gastroenterology 118, 678–687 (2000).
Roy, N., Stemple, J., Merrill, R. M. & Thomas, L. Dysphagia in the elderly: preliminary evidence of prevalence, risk factors, and socioemotional effects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 116, 858–865 (2007).
Go, A. S. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics —2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 129, e28–e292 (2014).
Heuschmann, P. U. et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality and attributable risks of death after ischemic stroke: the German Stroke Registers Study Group. Arch. Intern. Med. 164, 1761–1768 (2004).
Martino, R. et al. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 36, 2756–2763 (2005).
Mann, G., Hankey, G. J. & Cameron, D. Swallowing function after stroke: prognosis and prognostic factors at 6 months. Stroke 30, 744–748 (1999).
Meng, N. H., Wang, T. G. & Lien, I. N. Dysphagia in patients with brainstem stroke: incidence and outcome. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 79, 170–175 (2000).
Teasell, R., Foley, N., Fisher, J. & Finestone, H. The incidence, management, and complications of dysphagia in patients with medullary strokes admitted to a rehabilitation unit. Dysphagia 17, 115–120 (2002).
Calis, E. A. et al. Dysphagia in children with severe generalized cerebral palsy and intellectual disability. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 50, 625–630 (2008).
Ward, E. C., Uriarte, M. & Conroy, A.-L. Duration of dysphagic symptoms and swallowing outcomes after thermal burn injury. J. Burn Care Rehabil. 22, 441–453 (2001).
Ward, E. C., Green, K. & Morton, A. L. Patterns and predictors of swallowing resolution following adult traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 22, 184–191 (2007).
Hutcheson, K. A. & Lewin, J. S. Functional outcomes after chemoradiotherapy of laryngeal and pharyngeal cancers. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 14, 158–165 (2012).
Frempong-Boadu, A. et al. Swallowing and speech dysfunction in patients undergoing anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: a prospective, objective preoperative and postoperative assessment. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 15, 362–368 (2002).
Sura, L., Madhavan, A., Carnaby, G. & Crary, M. A. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin. Interv. Aging 7, 287–298 (2012).
Cabre, M. et al. Prevalence and prognostic implications of dysphagia in elderly patients with pneumonia. Age Ageing 39, 39–45 (2010).
Oh, T. H. et al. Dysphagia in inflammatory myopathy: clinical characteristics, treatment strategies, and outcome in 62 patients. Mayo Clin. Proc. 82, 441–447 (2007).
Ko, E. H. & Rubin, A. D. Dysphagia due to inclusion body myositis: case presentation and review of the literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 123, 605–608 (2014).
Alagiakrishnan, K., Bhanji, R. A. & Kurian, M. Evaluation and management of oropharyngeal dysphagia in different types of dementia: a systematic review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 56, 1–9 (2013).
Mills, R., Bahroo, L. & Pagan, F. An update on the use of botulinum toxin therapy in Parkinson's disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 15, 511 (2015).
Logemann, J. A. Effects of aging on the swallowing mechanism. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 23, 1045–1056 (1990).
Feinberg, M. J., Ekberg, O., Segall, L. & Tully, J. Deglutition in elderly patients with dementia: findings of videofluorographic evaluation and impact on staging and management. Radiology 183, 811–814 (1992).
Kalf, J. G., de Swart, B. J., Bloem, B. R. & Munneke, M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson's disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 18, 311–315 (2012).
Palmer, J. B., Drennan, J. C. & Baba, M. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing impairments. Am. Fam. Physician 61, 2453–2462 (2000).
Bartlett, J. G. Aspiration pneumonia in adults. UpToDate [online], (2010).
Baine, W. B., Yu, W. & Summe, J. P. Epidemiologic trends in the hospitalization of elderly Medicare patients for pneumonia, 1991–1998. Am. J. Publ. Health 91, 1121–1123 (2001).
Connolly, M. J. Of proverbs and prevention: aspiration and its consequences in older patients. Age Ageing 39, 2–4 (2010).
Marik, P. E. & Kaplan, D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest 124, 328–336 (2003).
Tablan, O. C., Anderson, L. J., Besser, R., Bridges, C. & Hajjeh, R. Guidelines for preventing health-care-associated pneumonia: recommendations of CDC and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 53, 1–36 (2004).
Leibovitz, A. et al. Dehydration among long-term care elderly patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gerontology 53, 179–183 (2007).
Palmer, L. B. Oral clearance and pathogenic oropharyngeal colonization in the elderly. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164, 464–468 (2001).
Suominen, M. et al. Malnutrition and associated factors among aged residents in all nursing homes in Helsinki. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 59, 578–583 (2005).
Serra-Prat, M. et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia as a risk factor for malnutrition and lower respiratory tract infection in independently living older persons: a population-based prospective study. Age Ageing 41, 376–381 (2012).
Finestone, H. M., Foley, N. C., Woodbury, M. G. & Greene-Finestone, L. Quantifying fluid intake in dysphagic stroke patients: a preliminary comparison of oral and nonoral strategies. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 82, 1744–1746 (2001).
Foley, N. C., Martin, R. E., Salter, K. L. & Teasell, R. W. A review of the relationship between dysphagia and malnutrition following stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 41, 707–713 (2009).
Sellars, C. et al. Risk factors for chest infection in acute stroke: a prospective cohort study. Stroke 38, 2284–2291 (2007).
Furman, E. F. Undernutrition in older adults across the continuum of care: nutritional assessment, barriers, and interventions. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 32, 22–27 (2006).
Eslick, G. D. & Talley, N. J. Dysphagia: epidemiology, risk factors and impact on quality of life—a population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 27, 971–979 (2008).
Brunnström, H. R. & Englund, E. M. Cause of death in patients with dementia disorders. Eur. J. Neurol. 16, 488–492 (2009).
Zuliani, G. et al. Discharge diagnosis and comorbidity profile in hospitalized older patients with dementia. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 27, 313–320 (2012).
Dusick, A. Investigation and management of dysphagia. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 10, 255–264 (2003).
Prasse, J. E. & Kikano, G. E. An overview of pediatric dysphagia. Clin. Pediatr. (Phila.) 48, 247–251 (2009).
Abadie, V. & Couly, G. Congenital feeding and swallowing disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 113, 1539–1549 (2013).
Arvedson, J. C. Management of pediatric dysphagia. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 31, 453–476 (1998).
Ekberg, O., Hamdy, S., Woisard, V., Wuttge-Hannig, A. & Ortega, P. Social and psychological burden of dysphagia: its impact on diagnosis and treatment. Dysphagia 17, 139–146 (2002).
Shaker, R. et al. Manual of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques for Disorders of Deglutition (Springer, 2013).
Leonard, R. & Kendall, K. Dysphagia Assessment and Treatment Planning (Plural Publishing Inc., 2013).
McCullough, G. H. & Martino, R. in Manual of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques for Disorders of Deglutition (eds Shaker, R. et al.) 11–30 (Springer, 2013).
Hinchy, J. A. et al. Formal dysphagia screening protocols prevent pneumonia. Stroke 36, 1972–1976 (2005).
Kertscher, B., Speyer, R., Palmieri, M. & Plant, C. Bedside screening to detect oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with neurological disorders: an updated systematic review. Dysphagia 29, 204–212 (2014).
Park, Y. H., Bang, H. L., Han, H. R. & Chang, H. K. Dysphagia screening measures for use in nursing homes: a systematic review. J. Kor. Acad. Nurs. 45, 1–13 (2015).
Martino, R. et al. The Toronto Bedside Swallowing Screening Test (TOR-BSST): development and validation of a dysphagia screening tool for patients with stroke. Stroke 40, 555–561 (2009).
Clavé, P. et al. Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. Clin. Nutr. 27, 806–815 (2008).
Perry, L. Screening swallowing function of patients with acute stroke. Part one: identification, implementation and initial evaluation of a screening tool for use by nurses. J. Clin. Nurs. 10, 463–473 (2001).
Perry, L. Screening swallowing function of patients with acute stroke. Part two: detailed evaluation of the tool used by nurses. J. Clin. Nurs. 10, 474–481 (2001).
Trapl, M. et al. Dysphagia bedside screening for acute-stroke patients: the Gugging Swallowing Screen. Stroke 38, 2948–2952 (2007).
Logemann, J. Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders (Pro-Ed, 1997).
Belafsky, P. C. et al. Validity and reliability of the Eating Assessment Tool (EAT-10). Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 117, 919–924 (2008).
Hughes, T. A. & Wiles, C. M. Neurogenic dysphagia: the role of the neurologist. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 64, 569–572 (1998).
Sapir, S., Ramig, L. & Fox, C. Speech and swallowing disorders in Parkinson disease. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 16, 205–210 (2008).
Adams, V., Mathisen, B., Baines, S., Lazarus, C. & Callister, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 28, 350–369 (2013).
McCormack, J., Casey, V., Conway, R., Saunders, J. & Perry, A. OroPress a new wireless tool for measuring oro-lingual pressures: a pilot study in healthy adults. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 12, 32 (2015).
Schroeder, M. F., Daniels, S. K., McClain, M., Corey, D. M. & Foundas, A. L. Clinical and cognitive predictors of swallowing recovery in stroke. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 43, 301–310 (2006).
Crary, M. A., Mann, G. D. & Groher, M. E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 86, 1516–1520 (2005).
Mann, G. MASA: the Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability (Singular, 2002).
Martino, R., Pron, G. & Diamant, N. E. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: surveying practice patterns of the speech-language pathologist. Dysphagia 19, 165–176 (2004).
DePippo, K. L., Holas, M. A. & Reding, M. J. Validation of the 3-oz water swallow test for aspiration following stroke. Arch. Neurol. 49, 1259–1261 (1992).
McCullough, G. H. et al. Inter- and intrajudge reliability for videofluoroscopic swallowing evaluation measures. Dysphagia 16, 110–118 (2001).
Daniels, S. K., Ballo, L. A., Mahoney, M. C. & Foundas, A. L. Clinical predictors of dysphagia and aspiration risk: outcome measures in acute stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 81, 1030–1033 (2000).
Lee, J. Y., Kim, D. K., Seo, K. M. & Kang, S. H. Usefulness of the simplified cough test in evaluating cough reflex sensitivity as a screening test for silent aspiration. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 38, 476–484 (2014).
Troche, M. S., Brandimore, A. E., Okun, M. S., Davenport, P. W. & Hegland, K. W. Decreased cough sensitivity and aspiration in Parkinson disease. Chest 146, 1294–1299 (2014).
Sejdic, E., Dudik, J. M., Kurosu, A., Jestrovic, I. & Coyle, J. L. Understanding differences between healthy swallows and penetration-aspiration swallows via compressive sensing of tri-axial swallowing accelerometry signals. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9190, 91090M (2014).
Jestrovic, I., Dudik, J. M., Luan, B., Coyle, J. L. & Sejdic, E. The effects of increased fluid viscosity on swallowing sounds in healthy adults. Biomed. Eng. Online 12, 90 (2013).
Sejdic, E., Steele, C. M. & Chau, T. Classification of penetration — aspiration versus healthy swallows using dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signals in dysphagic subjects. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60, 1859–1866 (2013).
Lee, J., Steele, C. M. & Chau, T. Classification of healthy and abnormal swallows based on accelerometry and nasal airflow signals. Artif. Intell. Med. 52, 17–25 (2011).
Hammoudi, K., Boiron, M., Hernandez, N., Bobillier, C. & Morinière, S. Acoustic study of pharyngeal swallowing as a function of the volume and consistency of the bolus. Dysphagia 29, 468–474 (2014).
Bergström, L., Svensson, P. & Hartelius, L. Cervical auscultation as an adjunct to the clinical swallow examination: a comparison with fibre-optic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 16, 517–528 (2014).
Crary, M. A., Sura, L. & Carnaby, G. Validation and demonstration of an isolated acoustic recording technique to estimate spontaneous swallow frequency. Dysphagia 28, 86–94 (2013).
Youmans, S. R. & Stierwalt, J. A. Normal swallowing acoustics across age, gender, bolus viscosity, and bolus volume. Dysphagia 26, 374–384 (2011).
Regan, J., Walshe, M., Timon, C. & McMahon, B. P. Endoflip® evaluation of pharyngo-oesophageal segment tone and swallowing in a clinical population: a total laryngectomy case series. Clin. Otolaryngol. 40, 121–129 (2015).
Regan, J., Walshe, M., Rommel, N., Tack, J. & McMahon, B. P. New measures of upper esophageal sphincter distensibility and opening patterns during swallowing in healthy subjects using EndoFLIP®. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e25–e34 (2013).
Regan, J., Walshe, M., Rommel, N. & McMahon, B. P. A new evaluation of the upper esophageal sphincter using the functional lumen imaging probe: a preliminary report. Dis. Esophagus 26, 117–123 (2013).
Cook, I. J. Oropharyngeal dysphagia. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 38, 411–431 (2009).
Rosenbek, J. C. et al. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 11, 93–98 (1996).
Jaffer, N. M., Ng, E., Au, F. W. & Steele, C. M. Fluoroscopic evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: anatomic, technical, and common etiologic factors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 204, 49–58 (2015).
Yamamoto, H., Furuya, J., Tamada, Y. & Kondo, H. Impacts of wearing complete dentures on bolus transport during feeding in elderly edentulous. J. Oral Rehabil. 40, 923–931 (2013).
Molfenter, S. M. & Steele, C. M. Variation in temporal measures of swallowing: sex and volume effects. Dysphagia 28, 226–233 (2013).
Humbert, I. A. et al. Human hyolaryngeal movements show adaptive motor learning during swallowing. Dysphagia 28, 139–145 (2013).
Steele, C. M. et al. The relationship between hyoid and laryngeal displacement and swallowing impairment. Clin. Otolaryngol. 36, 30–36 (2011).
Rofes, L. et al. Pathophysiology of oropharyngeal dysphagia in the frail elderly. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22, 851–858 (2010).
Allen, J. E., White, C. J., Leonard, R. J. & Belafsky, P. C. Prevalence of penetration and aspiration on videofluoroscopy in normal individuals without dysphagia. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 142, 208–213 (2010).
Maffei, C. et al. Videofluoroscopic evaluation of mastication and swallowing in individuals with TMD. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 78, 24–28 (2012).
Leder, S. B., Burrell, M. I. & Van Daele, D. J. Epiglottis is not essential for successful swallowing in humans. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 119, 795–798 (2010).
Kang, B. S. et al. Influence of aging on movement of the hyoid bone and epiglottis during normal swallowing: a motion analysis. Gerontology 56, 474–482 (2010).
Stokely, S. L., Molfenter, S. M. & Steele, C. M. Effects of barium concentration on oropharyngeal swallow timing measures. Dysphagia 29, 78–82 (2014).
Nagy, A. et al. Timing differences between cued and noncued swallows in healthy young adults. Dysphagia 28, 428–434 (2013).
Kim, H. M., Choi, K. H. & Kim, T. W. Patients' radiation dose during videofluoroscopic swallowing studies according to underlying characteristics. Dysphagia 28, 153–158 (2013).
Chau, K. H. & Kung, C. M. Patient dose during videofluoroscopy swallowing studies in a Hong Kong public hospital. Dysphagia 24, 387–390 (2009).
Kurosu, A. & Logemann, J. A. Gender effects on airway closure in head and neck cancer patients. Dysphagia 26, 18–26 (2011).
Umemoto, G. et al. Dysphagia in Duchenne muscular dystrophy versus myotonic dystrophy type 1. Muscle Nerve 46, 490–495 (2012).
Almirall, J. et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a risk factor for community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly. Eur. Respir. J. 41, 923–928 (2013).
Warabi, T. et al. Effects of stroke-induced damage to swallow-related areas in the brain on swallowing mechanics of elderly patients. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 8, 234–242 (2008).
Ford, S., Gollins, S., Hobson, P. & Vyas, S. Structural displacements during the swallow in patients with early laryngeal cancers and other early primary cancers of the head and neck. Dysphagia 24, 127–136 (2009).
Narajos, N., Samejima, Y., Kumai, Y. & Yumoto, E. Postdeglutitive residue in idiopathic unilateral vocal fold paralysis: a quantitative videofluoroscopic study. Laryngoscope 123, 2776–2779 (2013).
Langdon, P. C., Mulcahy, K., Shepherd, K. L., Low, V. H. & Mastaglia, F. L. Pharyngeal dysphagia in inflammatory muscle diseases resulting from impaired suprahyoid musculature. Dysphagia 27, 408–417 (2012).
dos Santos, C. M., Cassiani, R. A. & Dantas, R. O. Videofluoroscopic evaluation of swallowing in Chagas' disease. Dysphagia 26, 361–365 (2011).
Troche, M. S., Huebner, I., Rosenbek, J. C., Okun, M. S. & Sapienza, C. M. Respiratory-swallowing coordination and swallowing safety in patients with Parkinson's disease. Dysphagia 26, 218–224 (2011).
Hunter, K. U. et al. Aspiration pneumonia chemo-intensity-modulated radiation therapy of oropharyngeal carcinoma and its clinical and dysphagia-related predictors. Head Neck 36, 120–125 (2014).
Cvejic, L. et al. Laryngeal penetration and aspiration in individuals with stable COPD. Respirology 16, 269–275 (2011).
Gluck, I. et al. Evaluating and reporting dysphagia in trials of chemoirradiation for head-and-neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 77, 727–733 (2010).
Falsetti, P. et al. Oropharyngeal dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and clinical predictors in patients admitted to a neurorehabilitation unit. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 18, 329–335 (2009).
Terré, R. & Mearin, F. Resolution of tracheal aspiration after the acute phase of stroke-related oropharyngeal dysphagia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 104, 923–932 (2009).
Aung, M. S., Goulermas, J. Y., Hamdy, S. & Power, M. Spatiotemporal visualizations for the measurement of oropharyngeal transit time from videofluoroscopy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57, 432–441 (2010).
Power, M. L. et al. Predicting aspiration after hemispheric stroke from timing measures of oropharyngeal bolus flow and laryngeal closure. Dysphagia 24, 257–264 (2009).
Aung, M. S., Goulermas, J. Y., Stanschus, S., Hamdy, S. & Power, M. Automated anatomical demarcation using an active shape model for videofluoroscopic analysis in swallowing. Med. Eng. Phys. 32, 1170–1179 (2010).
Leonard, R., Rees, C. J., Belafsky, P. & Allen, J. Fluoroscopic surrogate for pharyngeal strength: the pharyngeal constriction ratio (PCR). Dysphagia 26, 13–17 (2011).
Lafer, M. et al. Temporal measurements of deglutition in dynamic magnetic resonance imaging versus videofluoroscopy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 122, 748–753 (2013).
Waito, A., Bailey, G. L., Molfenter, S. M., Zoratto, D. C. & Steele, C. M. Voice-quality abnormalities as a sign of dysphagia: validation against acoustic and videofluoroscopic data. Dysphagia 26, 125–134 (2011).
Omari, T. I. et al. Reproducibility and agreement of pharyngeal automated impedance manometry with videofluoroscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9, 862–867 (2011).
Schultheiss, C., Schauer, T., Nahrstaedt, H. & Seidl, R. O. Evaluation of an EMG bioimpedance measurement system for recording and analysing the pharyngeal phase of swallowing. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 270, 2149–2156 (2013).
Shem, K. L. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of bedside swallow evaluation versus videofluoroscopy to assess dysphagia in individuals with tetraplegia. PMR 4, 283–289 (2012).
Singh, V. et al. Investigation of aspiration: milk nasendoscopy versus videofluoroscopy. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 266, 543–545 (2009).
Stroud, A. E., Lawrie, B. W. & Wiles, C. M. Inter- and intra-rater reliability of cervical auscultation to detect aspiration in patients with dysphagia. Clin. Rehabil. 16, 640–645 (2002).
Colodny, N. Interjudge and intrajudge reliabilities in fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES®) using the penetration-aspiration scale: a replication study. Dysphagia 17, 308–315 (2002).
Huang, Y. H. et al. The value of pharyngeal scintigraphy in predicting videofluoroscopic findings. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 92, 1075–1083 (2013).
Kim, S. J., Han, T. R. & Kwon, T. K. Kinematic analysis of hyolaryngeal complex movement in patients with dysphagia development after pneumonectomy. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 58, 108–112 (2010).
Rofes, L., Arreola, V., Mukherjee, R., Swanson, J. & Clavé, P. The effects of a xanthan gum-based thickener on the swallowing function of patients with dysphagia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 39, 1169–1179 (2014).
Zu, Y. et al. Evaluation of swallow function after tongue cancer treatment using real-time magnetic resonance imaging: a pilot study. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 139, 1312–1319 (2013).
Mannelli, G., Parrinello, G. & Gallo, O. Hypopharyngeal mucosal flap reconstruction in endoscopic supraglottic laryngectomy. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 34, 523–526 (2013).
Archontaki, M. et al. Functional results of speech and swallowing after oral microvascular free flap reconstruction. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 267, 1771–1777 (2010).
Cola, P. C. et al. The influence of sour taste and cold temperature in pharyngeal transit duration in patients with stroke. Arq. Gastroenterol. 47, 18–21 (2010).
Regan, J., Walshe, M. & Tobin, W. O. Immediate effects of thermal-tactile stimulation on timing of swallow in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Dysphagia 25, 207–215 (2010).
Tei, K. et al. Does swallowing function recover in the long term in patients with surgically treated tongue carcinomas? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 70, 2680–2686 (2012).
Terré, R. & Mearin, F. Effectiveness of chin-down posture to prevent tracheal aspiration in dysphagia secondary to acquired brain injury. A videofluoroscopy study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 24, 414–419 (2012).
Sdravou, K., Walshe, M. & Dagdilelis, L. Effects of carbonated liquids on oropharyngeal swallowing measures in people with neurogenic dysphagia. Dysphagia 27, 240–250 (2012).
van der Kruis, J. G., Baijens, L. W., Speyer, R. & Zwijnenberg, I. Biomechanical analysis of hyoid bone displacement in videofluoroscopy: a systematic review of intervention effects. Dysphagia 26, 171–182 (2011).
Ozgursoy, O. B. & Salassa, J. R. Manofluorographic and functional outcomes after endoscopic laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for cricopharyngeal bar. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 142, 735–740 (2010).
Baylow, H. E., Goldfarb, R., Taveira, C. H. & Steinberg, R. S. Accuracy of clinical judgment of the chin-down posture for dysphagia during the clinical/bedside assessment as corroborated by videofluoroscopy in adults with acute stroke. Dysphagia 24, 423–433 (2009).
Langmore, S. E. et al. Predictors of aspiration pneumonia: how important is dysphagia? Dysphagia 13, 69–81 (1998).
Baijens, L., Barikroo, A. & Pilz, W. Intrarater and interrater reliability for measurements in videofluoroscopy of swallowing. Eur. J. Radiol. 82, 1683–1695 (2013).
Nativ-Zeltzer, N., Kahrilas, P. J. & Logemann, J. A. Manofluorography in the evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia 27, 151–161 (2012).
Langmore, S. E. & Aviv, J. E. Endoscopic Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders (Thieme, 2000).
Hiss, S. G. & Postma, G. N. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Laryngoscope 113, 1386–1393 (2003).
Langmore, S. E., Schatz, K. & Olsen, N. Fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing safety: a new procedure. Dysphagia 2, 216–219 (1988).
Butler, S. G., Markley, L., Sanders, B. & Stuart, A. Reliability of the penetration aspiration scale with flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 124, 480–483 (2015).
Kaneoka, A. S. et al. The Boston residue and clearance scale: preliminary reliability and validity testing. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 65, 312–317 (2013).
Brady, S. & Donzelli, J. The modified barium swallow and the functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 46, 1009–1022 (2013).
Langmore, S. E. Evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: which diagnostic tool is superior? Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 11, 485–489 (2003).
Baijens, L. W., Speyer, R., Pilz, W. & Roodenburg, N. FEES protocol derived estimates of sensitivity: aspiration in dysphagic patients. Dysphagia 29, 583–590 (2014).
Dziewas, R. et al. Towards a basic endoscopic assessment of swallowing in acute stroke—development and evaluation of a simple dysphagia score. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 26, 41–47 (2008).
Aviv, J. E., Murry, T., Zschommler, A., Cohen, M. & Gartner, C. Flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing: patient characteristics and analysis of safety in 1,340 consecutive examinations. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 114, 173–176 (2005).
Aviv, J. E., Martin, J. H., Keen, M. S., Debell, M. & Blitzer, A. Air pulse quantification of supraglottic and pharyngeal sensation: a new technique. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 102, 777–780 (1993).
Aviv, J. E. et al. Laryngopharyngeal sensory discrimination testing and the laryngeal adductor reflex. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 108, 725–730 (1999).
Leder, S. B., Acton, L. M., Lisitano, H. L. & Murray, J. T. Fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) with and without blue-dyed food. Dysphagia 20, 157–162 (2005).
Badenduck, L. A. et al. Fiber-optic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing to assess swallowing outcomes as a function of head position in a normal population. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 43, 9 (2014).
Butler, S. G. et al. Effects of liquid type, delivery method, and bolus volume on penetration-aspiration scores in healthy older adults during flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 120, 288–295 (2011).
Schultheiss, C., Nusser-Müller-Busch, R. & Seidl, R. O. The semisolid bolus swallow test for clinical diagnosis of oropharyngeal dysphagia: a prospective randomised study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 268, 1837–1844 (2011).
Kelly, A. M., Leslie, P., Beale, T., Payten, C. & Drinnan, M. J. Fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing and videofluoroscopy: does examination type influence perception of pharyngeal residue severity? Clin. Otolaryngol. 31, 425–432 (2006).
Thottam, P. J., Silva, R. C., McLevy, J. D., Simons, J. P. & Mehta, D. K. Use of fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) in the management of psychogenic dysphagia in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 79, 108–110 (2015).
Butler, S. G., Stuart, A., Markley, L. & Rees, C. Penetration and aspiration in healthy older adults as assessed during endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 118, 190–198 (2009).
Osborn, A. J. et al. Swallowing function after laryngeal cleft repair: more than just fixing the cleft. Laryngoscope 124, 1965–1969 (2014).
Leder, S. B., Joe, J. K., Hill, S. E. & Traube, M. Effect of tracheotomy tube occlusion on upper esophageal sphincter and pharyngeal pressures in aspirating and nonaspirating patients. Dysphagia 16, 79–82 (2001).
McGowan, S. L., Gleeson, M., Smith, M., Hirsch, N. & Shuldham, C. M. A pilot study of fibreoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in patients with cuffed tracheostomies in neurological intensive care. Neurocrit. Care 6, 90–93 (2007).
Clayton, N. A., Carnaby, G. D., Peters, M. J. & Ing, A. J. Impaired laryngopharyngeal sensitivity in patients with COPD: the association with swallow function. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 16, 615–623 (2014).
Patterson, M. et al. Functional swallowing outcomes in nasopharyngeal cancer treated with IMRT at 6 to 42 months post-radiotherapy. Dysphagia 29, 663–670 (2014).
Leder, S. B. & Espinosa, J. F. Aspiration risk after acute stroke: comparison of clinical examination and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing. Dysphagia 17, 214–218 (2002).
Somasundaram, S. et al. Dysphagia risk assessment in acute left-hemispheric middle cerebral artery stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 37, 217–222 (2014).
Warnecke, T. et al. Assessment of aspiration risk in acute ischaemic stroke — evaluation of the simple swallowing provocation test. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 312–314 (2008).
Warnecke, T. et al. Endoscopic characteristics and levodopa responsiveness of swallowing function in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov. Disord. 25, 1239–1245 (2010).
Brady, S. L., Pape, T. L., Darragh, M., Escobar, N. G. & Rao, N. Feasibility of instrumental swallowing assessments in patients with prolonged disordered consciousness while undergoing inpatient rehabilitation. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 24, 384–391 (2009).
Lim, S. H. et al. Accuracy of bedside clinical methods compared with fiberoptic endoscopic examination of swallowing (FEES) in determining the risk of aspiration in acute stroke patients. Dysphagia 16, 1–6 (2001).
Kelly, A. M., Drinnan, M. J. & Leslie, P. Assessing penetration and aspiration: how do videofluoroscopy and fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing compare? Laryngoscope 117, 1723–1727 (2007).
Olthoff, A., Zhang, S., Schweizer, R. & Frahm, J. On the physiology of normal swallowing as revealed by magnetic resonance imaging in real time. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 493174 (2014).
Rommel, N. & Omari, T. Manual of High Resolution Esophageal Manometry (UNI-MED, 2014).
Ghosh, S. K., Pandolfino, J. E., Zhang, Q., Jarosz, A. & Kahrilas, P. J. Deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter relaxation: a study of 75 volunteer subjects using solid-state high-resolution manometry. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 291, G525–G531 (2006).
Dire, C., Shi, G., Manka, M. & Kahrilas, P. J. Manometric characteristics of the upper esophageal sphincter recorded with a microsleeve. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 96, 1383–1389 (2001).
Kahrilas, P. J., Logemann, J. A., Krugler, C. & Flanagan, E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am. J. Physiol. 260, G450–G456 (1991).
Kahrilas, P. J., Dodds, W. J., Dent, J., Logemann, J. A. & Shaker, R. Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterology 95, 52–62 (1988).
Kahrilas, P. J., Dent, J., Dodds, W. J., Hogan, W. J. & Arndorfer, R. C. A method for continuous monitoring of upper esophageal sphincter pressure. Dig. Dis. Sci. 32, 121–128 (1987).
Pouderoux, P. & Kahrilas, P. J. Function of upper esophageal sphincter during swallowing: the grabbing effect. Am. J. Physiol. 272, G1057–G1063 (1997).
Lee, C. T., Chang, F. Y., Yeh, C. L. & Lee, S. D. Radial asymmetry characterized the upper esophageal sphincter pressures. Chin. J. Physiol. 37, 225–228 (1994).
Silva, L. C. et al. Anatomophysiology of the pharyngo-upper esophageal area in light of high-resolution manometry. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 17, 2033–2038 (2013).
Lee, T. H. et al. High-resolution impedance manometry facilitates assessment of pharyngeal residue and oropharyngeal dysphagic mechanisms. Dis. Esophagus 27, 220–229 (2014).
Kessing, B. F., Bredenoord, A. J. & Smout, A. J. Mechanisms of gastric and supragastric belching: a study using concurrent high-resolution manometry and impedance monitoring. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 24, e573–e579 (2012).
Amaris, M., Dua, K. S., Naini, S. R., Samuel, E. & Shaker, R. Characterization of the upper esophageal sphincter response during cough. Chest 142, 1229–1236 (2012).
Hernandez, L. V., Dua, K. S., Surapaneni, S. N., Rittman, T. & Shaker, R. Anatomic-manometric correlation of the upper esophageal sphincter: a concurrent US and manometry study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 72, 587–592 (2010).
Babaei, A. et al. Response of the upper esophageal sphincter to esophageal distension is affected by posture, velocity, volume, and composition of the infusate. Gastroenterology 142, 734–743.e7 (2012).
Castell, J. A., Dalton, C. B. & Castell, D. O. Effects of body position and bolus consistency on the manometric parameters and coordination of the upper esophageal sphincter and pharynx. Dysphagia 5, 179–186 (1990).
Dejaeger, E., Pelemans, W., Ponette, E. & Vantrappen, G. Effect of body position on deglutition. Dig. Dis. Sci. 39, 762–765 (1994).
Balou, M. et al. Manometric measures of head rotation and chin tuck in healthy participants. Dysphagia 29, 25–32 (2014).
Castell, J. A., Castell, D. O., Schultz, A. R. & Georgeson, S. Effect of head position on the dynamics of the upper esophageal sphincter and pharynx. Dysphagia 8, 1–6 (1993).
Takasaki, K., Umeki, H., Kumagami, H. & Takahashi, H. Influence of head rotation on upper esophageal sphincter pressure evaluated by high-resolution manometry system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 142, 214–217 (2010).
Dantas, R. O. et al. Effect of swallowed bolus variables on oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. Am. J. Physiol. 258, G675–G681 (1990).
Lin, T. et al. Effect of bolus volume on pharyngeal swallowing assessed by high-resolution manometry. Physiol. Behav. 128, 46–51 (2014).
Hoffman, M. R., Ciucci, M. R., Mielens, J. D., Jiang, J. J. & McCulloch, T. M. Pharyngeal swallow adaptations to bolus volume measured with high-resolution manometry. Laryngoscope 120, 2367–2373 (2010).
Omari, T. I., Dejaeger, E., Tack, J., Van Beckevoort, D. & Rommel, N. Effect of bolus volume and viscosity on pharyngeal automated impedance manometry variables derived for broad dysphagia patients. Dysphagia 28, 146–152 (2013).
Doeltgen, S. H., Macrae, P. & Huckabee, M. L. Pharyngeal pressure generation during tongue-hold swallows across age groups. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 20, 124–130 (2011).
Ren, J. et al. Deterioration of the pharyngo-UES contractile reflex in the elderly. Laryngoscope 110, 1563–1566 (2000).
Yokoyama, M., Mitomi, N., Tetsuka, K., Tayama, N. & Niimi, S. Role of laryngeal movement and effect of aging on swallowing pressure in the pharynx and upper esophageal sphincter. Laryngoscope 110, 434–439 (2000).
Kern, M. et al. Comparison of upper esophageal sphincter opening in healthy asymptomatic young and elderly volunteers. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 108, 982–989 (1999).
Shaw, D. W. et al. Influence of normal aging on oral-pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter function during swallowing. Am. J. Physiol. 268, G389–G396 (1995).
Ren, J. et al. Effect of age and bolus variables on the coordination of the glottis and upper esophageal sphincter during swallowing. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 88, 665–669 (1993).
Robbins, J., Hamilton, J. W., Lof, G. L. & Kempster, G. B. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 103, 823–829 (1992).
Fulp, S. R., Dalton, C. B., Castell, J. A. & Castell, D. O. Aging-related alterations in human upper esophageal sphincter function. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 85, 1569–1572 (1990).
Wilson, J. A., Pryde, A., Macintyre, C. C., Maran, A. G. & Heading, R. C. The effects of age, sex, and smoking on normal pharyngoesophageal motility. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 85, 686–691 (1990).
Omari, T. I. et al. Swallowing dysfunction in healthy older people using pharyngeal pressure-flow analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26, 59–68 (2014).
Bodén, K., Hallgren, A. & Witt Hedström, H. Effects of three different swallow maneuvers analyzed by videomanometry. Acta Radiol. 47, 628–633 (2006).
Kwiatek, M. A., Mirza, F., Kahrilas, P. J. & Pandolfino, J. E. Hyperdynamic upper esophageal sphincter pressure: a manometric observation in patients reporting globus sensation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 104, 289–298 (2009).
Peng, L., Patel, A., Kushnir, V. & Gyawali, C. P. Assessment of upper esophageal sphincter function on high-resolution manometry: identification of predictors of globus symptoms. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 49, 95–100 (2015).
Choi, W. S. et al. High-resolution manometry and globus: comparison of globus, gastroesophageal reflux disease and normal controls using high-resolution manometry. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 19, 473–478 (2013).
Vakil, N. B., Kahrilas, P. J., Dodds, W. J. & Vanagunas, A. Absence of an upper esophageal sphincter response to acid reflux. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 84, 606–610 (1989).
Vardar, R., Sweis, R., Anggiansah, A., Wong, T. & Fox, M. R. Upper esophageal sphincter and esophageal motility in patients with chronic cough and reflux: assessment by high-resolution manometry. Dis. Esophagus 26, 219–225 (2013).
Szczesniak, M. M. et al. Upregulation of the esophago-UES relaxation response: a possible pathophysiological mechanism in suspected reflux laryngitis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22, 381–386 (2010).
Mathews, S. C. et al. Upper esophageal sphincter abnormalities are strongly predictive of treatment response in patients with achalasia. World J. Clin. Cases 2, 448–454 (2014).
Wauters, L. et al. Balloon dilation of the esophago-gastric junction affects lower and upper esophageal sphincter function in achalasia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26, 69–76 (2014).
Chavez, Y. H. et al. Upper esophageal sphincter abnormalities: frequent finding on high-resolution esophageal manometry and associated with poorer treatment response in achalasia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 49, 17–23 (2015).
Wilson, J. A., Pryde, A., White, A., Maher, L. & Maran, A. G. Swallowing performance in patients with vocal fold motion impairment. Dysphagia 10, 149–154 (1995).
Lan, Y. et al. The correlation between manometric and videofluoroscopic measurements of the swallowing function in brainstem stroke patients with dysphagia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 49, 24–30 (2015).
Lan, Y. et al. Biomechanical changes in the pharynx and upper esophageal sphincter after modified balloon dilatation in brainstem stroke patients with dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e821–e829 (2013).
Williams, R. B., Wallace, K. L., Ali, G. N. & Cook, I. J. Biomechanics of failed deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter relaxation in neurogenic dysphagia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 283, G16–G26 (2002).
Kuhn, M. A. & Belafsky, P. C. Management of cricopharyngeus muscle dysfunction. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 46, 1087–1099 (2013).
Jungheim, M., Janhsen, A. M., Miller, S. & Ptok, M. Impact of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on upper esophageal sphincter dynamics: a high-resolution manometry study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 124, 5–12 (2015).
Terré, R., Panadés, A. & Mearin, F. Botulinum toxin treatment for oropharyngeal dysphagia in patients with stroke. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, e896–e702 (2013).
Kelly, E. A. et al. Botulinum toxin injection for the treatment of upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 122, 100–108 (2013).
Knauer, C. M., Castell, J. A., Dalton, C. B., Nowak, L. & Castell, D. O. Pharyngeal/upper esophageal sphincter pressure dynamics in humans. Effects of pharmacologic agents and thermal stimulation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 35, 774–780 (1990).
Massey, B. T. Manual of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques for Disorders of Deglutition (Springer, 2013).
Omari, T. I. et al. A method to objectively assess swallow function in adults with suspected aspiration. Gastroenterology 140, 1454–1463 (2011).
Omari, T. I. et al. A novel method for the nonradiological assessment of ineffective swallowing. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 106, 1796–1802 (2011).
Noll, L., Rommel, N., Davidson, G. P. & Omari, T. I. Pharyngeal flow interval: a novel impedance based parameter correlating with aspiration. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 23, 551–e206 (2011).
Ferris, L. et al. Pressure flow analysis in the assessment of preswallow pharyngeal bolus presence in dysphagia. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2015, 764709 (2015).
Omari, T. I., Dejaeger, E., Tack, J., Vanbeckevoort, D. & Rommel, N. An impedance-manometry based method for non-radiological detection of pharyngeal postswallow residue. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 24, e277–e284 (2012).
Omari, T. I. et al. Upper esophageal sphincter impedance as a marker of sphincter opening diameter. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 302, G909–G913 (2012).
Hoffman, M. R. et al. Artificial neural network classification of pharyngeal high-resolution manometry with impedance data. Laryngoscope 123, 713–720 (2013).
Omari, T. I. et al. Upper esophageal sphincter mechanical states analysis: a novel methodology to describe UES relaxation and opening. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 8, 241 (2015).
McMahon, B. et al. A new technique for evaluating sphincter function in visceral organs: application of the functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) for the evaluation of the oesophago–gastric junction. Physiol. Meas. 26, 823–836 (2005).
McMahon, B. P. et al. The functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) for evaluation of the esophagogastric junction. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292, G377–G384 (2007).
McMahon, B., Frøkjaer, J. B., Drewes, A. M. & Gregersen, H. A new measurement of oesophago-gastric junction competence. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 16, 543–546 (2004).
Kunwald, P. et al. A new distensibility technique to measure sphincter of Oddi function. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22, 978–983 (2010).
Kwiatek, M. A. et al. Mechanical properties of the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 140, 82–90 (2011).
Selley, W. G., Ellis, R. E., Flack, F. C., Bayliss, C. R. & Pearce, V. R. The synchronization of respiration and swallow sounds with videofluoroscopy during swallowing. Dysphagia 9, 162–167 (1994).
Reynolds, E. W., Vice, F. L., Bosma, J. F. & Gewolb, I. H. Cervical accelerometry in preterm infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 44, 587–592 (2002).
Sejdic, E., Steele, C. M. & Chau, T. A procedure for denoising dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signals. Physiol. Meas. 31, N1–N9 (2010).
Lee, J., Sejdic, E., Steele, C. M. & Chau, T. Effects of liquid stimuli on dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signals in a healthy population. Biomed. Eng. Online 9, 7 (2010).
Hanna, F., Molfenter, S. M., Cliffe, R. E., Chau, T. & Steele, C. M. Anthropometric and demographic correlates of dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signal characteristics: a canonical correlation analysis. Dysphagia 25, 94–103 (2010).
Dudik, J. M., Kurosu, A., Coyle, J. L. & Sejdic, E. A comparative analysis of DBSCAN, K-means, and quadratic variation algorithms for automatic identification of swallows from swallowing accelerometry signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 59, 10–18 (2015).
Lee, J., Steele, C. M. & Chau, T. Swallow segmentation with artificial neural networks and multi-sensor fusion. Med. Eng. Phys. 31, 1049–1055 (2009).
Steele, C. M., Sejdic, E. & Chau, T. Noninvasive detection of thin-liquid aspiration using dual-axis swallowing accelorometry. Dysphagia 28, 105–112 (2013).
Nikjoo, M. S., Steele, C. M., Sejdic, E. & Chau, T. Automatic discrimination between safe and unsafe swallowing using a reputation-based classifier. Biomed. Eng. Online 10, 100 (2011).
Merey, C., Kushki, A., Sejdic, E., Berall, G. & Chau, T. Quantitative classification of pediatric swallowing through accelerometry. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 9, 34 (2012).
Lee, J. et al. A radial basis classifier for the automatic detection of aspiration in children with dysphagia. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 3, 14 (2006).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank E. Michou for her advice and contributions to the manifestations section of this manuscript. We would also like to thank C. Borgers for her technical support for the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects in the production of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
N.R. has a patent on Automated Impedance Manometry technology. S.H. is a scientific officer for Phagenesis, which focuses on therapy for dysphagia, but has no competing interests related to this manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rommel, N., Hamdy, S. Oropharyngeal dysphagia: manifestations and diagnosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13, 49–59 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.199
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2015.199
This article is cited by
-
Asymptomatic Dysphagia and Aspiration in Patients with Idiopathic Bronchiectasis
Lung (2024)
-
Development of a Dutch Version of the Sydney Swallow Questionnaire: Assessing Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Severity in Dutch-Speaking Populations
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery (2024)
-
Dysphagia as a Missing Link Between Post-surgical- and Opioid-Related Pneumonia
Lung (2024)
-
Feasibility study of the Nox-T3 device to detect swallowing and respiration pattern in neurologically impaired patients in the acute phase
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Application of deep learning technology for temporal analysis of videofluoroscopic swallowing studies
Scientific Reports (2023)