Abstract
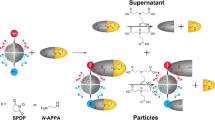
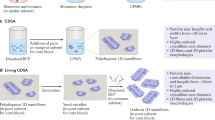
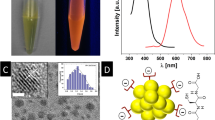
Quantum dots (QDs) need to be attached to other chemical species if they are to be used as biomarkers, therapeutic agents or sensors. These materials also need to disperse well in water and have well-defined functional groups on their surfaces. QDs are most often synthesized in the presence of ligands such as trioctylphosphine oxide, which render the nanoparticle surfaces hydrophobic. We present a complete protocol for the synthesis and water solubilization of hydrophobic CdSe/ZnS QDs using designer amphiphilic polymeric coatings. The method is based on functionalization of an anhydride polymer backbone with nucleophilic agents. Small functional groups, bulky cyclic compounds and polymeric chains can be integrated into the coating prior to solubilization. We describe the preparation of acetylene- and azide-functionalized QDs for 'click' chemistry. The method is universal and applicable to any type of nanoparticle stabilized with hydrophobic ligands able to interact with the alkyl chains in the coating in water.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jańczewski, D., Tomczak, N., Khin, Y.W., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Designer multi-functional comb-polymers for surface engineering of quantum dots on the nanoscale. Eur. Polym. J. 45, 3–9 (2009).
Medintz, I.L., Uyeda, H.T., Goldman, E.R. & Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labeling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 4, 435–446 (2005).
Alivisatos, A.P., Gu, W. & Larabell, C. Quantum dots as cellular probes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 55–76 (2005).
Tomczak, N., Jańczewski, D., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Designer polymer-quantum dot architectures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 34, 393–478 (2009).
Resch-Genger, U., Grabolle, M., Cavaliere-Jaricot, S., Nitschke, R. & Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 5, 763–775 (2008).
Michalet, X. et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307, 538–544 (2005).
Kim, S. et al. Near-infrared fluorescent type II quantum dots for sentinel lymph node mapping. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 93–97 (2004).
Wu, X. et al. Immunofluorescent labeling of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 41–46 (2003).
Pathak, S., Choi, S.-K., Arnheim, N. & Thompson, M.E. Hydroxylated quantum dots as luminescent probes for in situ hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 4103–4104 (2001).
Liu, W. et al. Compact biocompatible quantum dots functionalized for cellular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 1274–1284 (2008).
Aldana, J., Wang, Y.A. & Peng, X. Photochemical instability of CdSe nanocrystals coated by hydrophilic thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 8844–8850 (2001).
Wang, Q. et al. A facile one-step functionalization of quantum dots with preserved photoluminescence for bioconjugation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 6380–6381 (2007).
Chan, W.C.W. & Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281, 2016–2018 (1998).
Derfus, A.M., Chan, W.C.W. & Bhatia, S.N. Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. Nano Lett. 4, 11–18 (2004).
Susumu, K., Mei, B.C. & Mattoussi, H. Multifunctional ligands based on dihydrolipoic acid and polyethylene glycol to promote biocompatibility of quantum dots. Nat. Protoc. 4, 424–436 (2009).
Mei, B.C., Susumu, K., Medintz, I.L. & Mattoussi, H. Polyethylene glycol-based bidentate ligands to enhance quantum dot and gold nanoparticle stability in biological media. Nat. Protoc. 4, 412–423 (2009).
Bruchez, M. Jr ., Moronne, M., Gin, P., Weis, S. & Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281, 2013–2016 (1998).
Selvan, S.T., Patra, P.K., Ang, C.Y. & Ying, J.Y. Synthesis of silica-coated semiconductor and magnetic quantum dots and their use in the imaging of live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 2448–2452 (2007).
Kim, S.-W., Kim, S., Tracy, J.B., Jasanoff, A. & Bawendi, M.G. Phosphine oxide polymer for water-soluble nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 4556–4557 (2005).
Nann, T. Phase transfer of CdSe@ZnS quantum dots using amphiphilic hyperbranched polyethylenimine. Chem. Commun. 1735–1736 (2005).
Nikolic, M.S. et al. Tailor-made ligands for biocompatible nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 6577–6580 (2006).
Osaki, F., Kanamori, T., Sando, S., Sera, T. & Aoyama, Y. A quantum dot conjugated sugar ball and its cellular uptake. On the size effects of endocytosis in the subviral region. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 6520–6521 (2004).
Fan, H. et al. Surfactant-assisted synthesis of water-soluble and biocompatible semiconductor quantum dot micelles. Nano Lett. 5, 645–648 (2005).
Dubertret, B., Skourides, P., Norris, D.J., Noireaux, A.H. & Libchaber, A. In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phopholipid micelles. Science 298, 1759–1762 (2002).
Carion, O., Mahler, B., Pons, T. & Dubertret, B. Synthesis, encapsulation, purification and coupling of single quantum dots in phospholipid micelles for their use in cellular and in vivo imaging. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2383–2390 (2007).
Pellegrino, T. et al. Hydrophobic nanocrystals coated with and amphiphilic polymer shell: a general route to water soluble nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 4, 703–707 (2004).
Lee, H.A. et al. Biodistribution of quantum dot nanoparticles in perfused skin: evidence of coating dependency and periodicity in arterial extraction. Nano Lett. 7, 2865–2870 (2007).
Di Corato, R. et al. Water solubilization of hydrophobic nanocrystals by means of poly(maleic anhydride-alt-1-octadecene). J. Mater. Chem. 18, 1991–1996 (2008).
Luccardini, C., Tribet, C., Vial, F., Marchi-Artzner, V. & Dahan, M. Size, charge, and interactions with giant lipid vesicles of quantum dots coated with an amphiphilic macromolecule. Langmuir 22, 2304–2310 (2006).
Gao, X.G., Cui, Y., levenson, R.M., Chung, L.W.K. & Nie, S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 8, 969–976 (2004).
Lees, E.E., Nguyen, T.-L., Clayton, A.H.A. & Mulvaney, P. The preparation of colloidally stable, water-soluble, biocompatible, semiconductor nanocrystals with a small hydrodynamic diameter. ACS Nano 3, 1121–1128 (2009).
Ballou, B., Lagerholm, B.C., Ernst, L.A., Bruchez, M.P. & Waggoner, A.S. Noninvasive imaging of quantum dots in mice. Bioconjugate Chem. 15, 79–86 (2004).
Larson, D.R. et al. Water-soluble quantum dots for multiphoton fluorescence imaging in vivo. Science 300, 1434–1436 (2003).
So, M.-K., Xu, C., Loening, A.M., Gambhir, S.S. & Rao, J. Self-illuminating quantum dot conjugates for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 339–343 (2006).
Clapp, A.R., Goldman, E.R. & Mattoussi, H. Capping of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots with DHLA and subsequent conjugation with proteins. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1258–1266 (2006).
Shen, H., Jawaid, A.M. & Snee, P.T. Poly(ehylene glycol) carbodiimide coupling reagents for the biological functionalization of water-soluble nanoparticles. ACS Nano 3, 915–923 (2009).
Yu, W.W. et al. Forming biocompatible and nonaggregated nanocrystals in water using amphiphilic polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 2871–2879 (2007).
Lin, C.-A. et al. Design of an amphiphilic polymer for nanoparticle coating and functionalization. Small 4, 334–341 (2008).
Yakovlev, A.V. et al. Wrapping nanocrystals with an amphiphilic polymer preloaded with fixed amounts of fluorophore generates FRET-based nanoprobes with a controlled donor/acceptor ratio. Langmuir 25, 3232–3239 (2009).
Fernandez-Arguelles, M.T. et al. Synthesis and characterization of polymer-coated quantum dots with integrated acceptor dyes as FRET-based nanoprobes. Nano Lett. 7, 2613–2617 (2007).
Jańczewski, D., Tomczak, N., Khin, Y.W., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Amphiphilic polymer and process of forming the same. World Intellectual Property Organization, Patent no. 2009/038544 (2009).
Tagit, O., Ja´czewski, D., Tomczak, N., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Thermoresponsive quantum dot/PNIPAM assemblies. Eur. Polym. J. 46, 1397–1403 (2010).
Ja´czewski, D., Tomczak, N., Liu, S.H., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Covalent assembly of functional inorganic nanoparticles by 'click' chemistry in water. Chem. Commun. 46, 3217–3404 (2010).
Jańczewski, D., Tomczak, N., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Stimulus responsive PNIPAM/QD hybrid microspheres by copolymerization with surface engineered QDs. Macromolecules 42, 1801–1804 (2009).
Jańczewski, D., Tomczak, N., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Introduction of quantum dots into PNIPAM microspheres by precipitation polymerization above LCST. Eur. Polym. J. 45, 1912–1917 (2009).
Ja´czewski, D. et al. Fabrication and responsive behaviour of quantum dot/PNIPAM micropatterns obtained by template copolymerization in water. J. Mat. Chem. 21, 6487–6490 (2011).
Tomczak, N., Jańczewski, D., Han, M.Y. & Vancso, G.J. Book chapter: Surface engineering of quantum dots with designer ligands. In Surface Design: Applications in Bioscience and Nanotechnology (eds. Förch, R., Schönherr, H. & Jenkins, A.T.A.) Ch. 4.3 341–361 (Wiley, 2009).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering of A*STAR, Singapore, for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed extensively to the work presented in this paper. D.J. and N.T. designed the experiments, tested the protocols, carried out the synthetic procedures and edited the paper. M.-Y.H. and G.J.V. designed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Photograph taken during step 5 of the quantum dot synthesis. (JPG 2455 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Diagram showing the quantum dot synthesis setup. (PDF 131 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jańczewski, D., Tomczak, N., Han, MY. et al. Synthesis of functionalized amphiphilic polymers for coating quantum dots. Nat Protoc 6, 1546–1553 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.381
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.381
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis of surface-modified quantum dots
Russian Chemical Bulletin (2020)
-
Photoswitchable semiconductor nanocrystals with self-regulating photochromic Förster resonance energy transfer acceptors
Nature Communications (2015)
-
The relationships between rheological rules and cohesive energy of amphiphilic polymers with different hydrophobic groups
Journal of Polymer Research (2015)
-
An amphiphilic chitosan derivative modified by deoxycholic acid: preparation, physicochemical characterization, and application
Journal of Materials Science (2015)
-
Formation of self-assembled quantum dot–chlorin e6 complex: influence of nanoparticles phospholipid coating
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.