Abstract
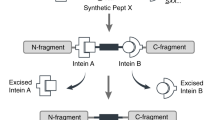
Segmental isotopic labeling is a powerful labeling technique for reducing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal overlap, which is associated with larger proteins by incorporating stable isotopes into only one region of a protein for NMR detections. Segmental isotopic labeling can not only reduce complexities of NMR spectra but also retain possibilities to carry out sequential resonance assignments by triple-resonance NMR experiments. We described in vivo (i.e., in Escherichia coli) and in vitro protocols for segmental isotopic labeling of multi-domain and fusion proteins via protein trans-splicing (PTS) using split DnaE intein without any refolding steps or α-thioester modification. The advantage of PTS approach is that it can be carried out in vivo by time-delayed dual-expression system with two controllable promoters. A segmentally isotope-labeled protein can be expressed in Escherichia coli within 1 d once required vectors are constructed. The total preparation time of a segmentally labeled sample can be as short as 7–13 d depending on the protocol used.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riek, R., Pervushin, K. & Wüthrich, K. TROSY and CRINEPT: NMR with large molecular and supramolecular structures in solution. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 462–468 (2000).
Wider, G. & Wüthrich, K. NMR spectroscopy of large molecules and multimolecular assemblies in solution. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9, 594–601 (1999).
Ohki, S. & Kainosho, M. Stable isotope-labeling methods for protein NMR spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 53, 208–226 (2008).
Kainosho, M. & Tsuji, T. Assignment of the three methionyl carbonyl carbon resonances in Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor by a carbon-13 and nitrogen-15 double-labeling technique. A new strategy for structural studies of proteins in solution. Biochemistry 21, 6273–6279 (1982).
Bax, A. Multidimensional nuclear-magnetic-resonance methods for protein studies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4, 738–744 (1994).
Yamazaki, T. et al. Segmental isotope labeling for protein NMR using peptide splicing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 5591–5592 (1998).
Xu, R., Ayers, B., Cowburn, D. & Muir, T.W. Chemical ligation of folded recombinant proteins: segmental isotopic labeling of domains for NMR studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 388–393 (1999).
Iwai, H. & Züger, S. Protein ligation: applications in NMR studies of proteins. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 24, 129–146 (2007).
Otomo, T., Teruya, K., Uegaki, K., Yamazaki, T. & Kyogoku, Y. Improved segmental isotope labeling of proteins and application to a larger protein. J. Biomol. NMR 14, 105–114 (1999).
Yagi, H., Tsujimoto, T., Yamazaki, T., Yoshida, M. & Akutsu, H. Conformational change of H+-ATPase beta monomer revealed on segmental isotope labeling NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 16632–16638 (2004).
Muona, M., Aranko, A.S. & Iwai, H. Segmental isotopic labelling of a multi-domain protein by protein ligation using protein trans-splicing. Chembiochem 9, 2958–2961 (2008).
Züger, S. & Iwai, H. Intein-based biosynthetic incorporation of unlabeled protein tags into isotopically labeled proteins for NMR studies. Nat. Biotech. 23, 736–740 (2005).
Wu, H., Hu, Z.M. & Liu, X.Q. Protein trans-splicing by a split intein encoded in a split DnaE gene of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9226–9231 (1998).
Paulus, H. Protein splicing and related forms of protein autoprocessing. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 69, 447–496 (2000).
Evans, T.C. Jr., Benner, J. & Xu, M.Q. Semisynthesis of cytotoxic proteins using a modified protein-splicing element. Protein Sci. 7, 2256–64 (1998).
Skrisovska, L. & Allain, F.H. Improved segmental isotope labeling methods for the NMR study of multidomain or large proteins: application to the RRMs of Npl3p and hnRNP L. J. Mol. Biol. 375, 151–164 (2008).
Iwai, H., Züger, S., Jin, J. & Tam, P.H. Highly efficient protein trans-splicing by a naturally occurring split DnaE intein from Nostoc punctiforme . FEBS Lett. 580, 1853–1858 (2006).
Zettler, J., Schütz, V. & Mootz, H.D. The naturally split NpuDnaE intein exhibits an extraordinarily high rate in the protein trans-splicing reaction. FEBS Lett. 583, 909–914 (2009).
Nallamsetty, S. & Waugh, D.S. Solubility-enhancing proteins MBP and NusA play a passive role in the folding of their fusion partners. Protein Expr. Purif. 45, 175–182 (2006).
Zhou, P., Lugovskoy, A.A. & Wagner, G. A solubility enhancement tag (SET) for NMR studies of poorly behaving proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 20, 11–14 (2001).
Serber, Z. & Dötsch, V. In-cell NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 40, 14317–14323 (2001).
Aranko, A.S., Züger, S., Buchinger, E. & Iwaï, H. In vivo and in vitro protein ligation by naturally occurring and engineered split DnaE inteins. PLoS ONE 4, e5185 (2009).
Guzman, L.M., Belin, D., Carson, M.J. & Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 177, 4121–4130 (1995).
Dillon, P.J. & Rosen, C.A. A rapid method for the construction of synthetic genes using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques 9, 298–300 (1990).
Han, J.C. & Han, G.Y. A procedure for quantitative determination of tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine, an odorless reducing agent more stable and effective than dithiothreitol. Anal. Biochem. 220, 5–10 (1994).
Getz, E.B., Xiao, M., Chakrabarty, T., Cooke, R. & Selvin, P.R. A comparison between the sulfhydryl reductants tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine and dithiothreitol for use in protein biochemistry. Anal. Biochem. 273, 73–80 (1999).
Nishihara, K., Kanemori, M., Kitagawa, M., Yanagi, H. & Yura, T. Chaperone coexpression plasmids: differential and synergistic roles of DnaK-DnaJ-GrpE and GroEL-GroES in assisting folding of an allergen of Japanese cedar pollen, Cryj2, in Escherichia coli . Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 1694–1699 (1998).
Studier, F.W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J. Mol. Biol. 219, 37–44 (1991).
Zhang, X. & Studier, F.W. Mechanism of inhibition of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase by T7 lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 269, 10–27 (1997).
Brinkmann, U., Mattes, R.E. & Buckel, P. High-level expression of recombinant genes in Escherichia coli is dependent on the availability of the DnaY gene product. Gene 85, 109–114 (1989).
Oeemig, J.S., Aranko, A.S., Djupsjöbacka, J., Heinämäki, K. & Iwaï, H. Solution structure of DnaE intein from Nostoc punctiforme: structural basis for the design of a new split intein suitable for site-specific chemical modification. FEBS Lett. 583, 1451–1456 (2009).
Aachmann, F.L., Svanem, B.I., Güntert, P., Petersen, S.B., Valla, S. & Wimmer, R. NMR structure of the R-module: a parallel beta-roll subunit from an Azotobacter vinelandii mannuronan C-5 epimerase. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 7350–6 (2006).
Busche, A.E.L., Aranko, A.S., Talebzadeh-Farooji, M., Bernhard, F., Dötsch, V. & Iwaï, H. Segmental isotopic labelling of a central domain in a multi-domain protein by the use of only one robust DnaE intein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 6128–6131 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Wimmer, F.L. Aachmann and E. Buchinger for providing the plasmids for the AlgE4 experiments and S. Züger for Figure 1 . This work is supported by the grants from the Academy of Finland (118385), Sigrid Jusélius Foundation and the Biocentrum Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.I. conceived and designed the experiments. M.M., A.S.A. and H.I. performed the experiments. M.M., A.S.A., V.R. and H.I. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muona, M., Aranko, A., Raulinaitis, V. et al. Segmental isotopic labeling of multi-domain and fusion proteins by protein trans-splicing in vivo and in vitro. Nat Protoc 5, 574–587 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.240
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.240
This article is cited by
-
Nature-inspired protein ligation and its applications
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2023)
-
Synthetic circuits based on split Cas9 to detect cellular events
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Deciphering protein post-translational modifications using chemical biology tools
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2020)
-
Phosphorylation-induced conformation of β2-adrenoceptor related to arrestin recruitment revealed by NMR
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Accessing Structure, Dynamics and Function of Biological Macromolecules by NMR Through Advances in Isotope Labeling
Journal of the Indian Institute of Science (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.