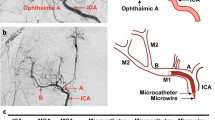
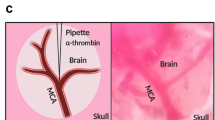
Abstract
Animal models of focal cerebral ischemia are well accepted for investigating the pathogenesis and potential treatment strategies for human stroke. Occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) with an endovascular filament is a widely used model to induce focal cerebral ischemia. However, this model is not amenable to thrombolytic therapies. As thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) is a standard of care within 4.5 h of human stroke onset, suitable animal models that mimic cellular and molecular mechanisms of thrombosis and thrombolysis of stroke are required. By occluding the MCA with a fibrin-rich allogeneic clot, we previously developed an embolic model of MCA occlusion in the rat, which recapitulates the key components of thrombotic development and of thrombolytic therapy of rtPA observed from human ischemic stroke. Here we describe in detail the surgical procedures of our model, including preparing emboli from rat donors. These procedures can be typically completed within ∼30 min, and they are highly adaptable to other strains of rats, as well as mice, in both sexes. Thus, this model provides a powerful tool for translational stroke research.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hacke, W. et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 1317–1329 (2008).
Adeoye, O., Hornung, R., Khatri, P. & Kleindorfer, D. Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator use for ischemic stroke in the United States: a doubling of treatment rates over the course of 5 years. Stroke 42, 1952–1955 (2011).
Kleindorfer, D., Lindsell, C.J., Brass, L., Koroshetz, W. & Broderick, J.P. National US estimates of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator use: ICD-9 codes substantially underestimate. Stroke 39, 924–928 (2008).
Fonarow, G.C. et al. Timeliness of tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy in acute ischemic stroke: patient characteristics, hospital factors, and outcomes associated with door-to-needle times within 60 minutes. Circulation 123, 750–758 (2011).
Bogousslavsky, J., Van Melle, G. & Regli, F. The Lausanne Stroke Registry: analysis of 1,000 consecutive patients with first stroke. Stroke 19, 1083–1092 (1988).
Dalal, P.M., Shah, P.M., Sheth, S.C. & Deshpande, C.K. Cerebral embolism. Angiographic observations on spontaneous clot lysis. Lancet 1, 61–64 (1965).
Longa, E.Z., Weinstein, P.R., Carlson, S. & Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20, 84–91 (1989).
Schmid-Elsaesser, R., Zausinger, S., Hungerhuber, E., Baethmann, A. & Reulen, H.J. A critical reevaluation of the intraluminal thread model of focal cerebral ischemia: evidence of inadvertent premature reperfusion and subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats by laser-Doppler flowmetry. Stroke 29, 2162–2170 (1998).
Ginsberg, M.D. Current status of neuroprotection for cerebral ischemia: synoptic overview. Stroke 40, S111–114 (2009).
Feuerstein, G.Z. et al. Missing steps in the STAIR case: a translational medicine perspective on the development of NXY-059 for treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 28, 217–219 (2008).
O'Collins, V.E. et al. 1,026 experimental treatments in acute stroke. Ann. Neurol. 59, 467–477 (2006).
Lo, E.H. A new penumbra: transitioning from injury into repair after stroke. Nat. Med. 14, 497–500 (2008).
Lo, E.H. Experimental models, neurovascular mechanisms and translational issues in stroke research. Br. J. Pharmacol. 153 (suppl. 1): S396–S405 (2008).
Zhang, R.L., Chopp, M., Zhang, Z.G., Jiang, Q. & Ewing, J.R. A rat model of focal embolic cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 766, 83–92 (1997).
Zhang, Z.G. et al. Cerebral microvascular obstruction by fibrin is associated with upregulation of PAI-1 acutely after onset of focal embolic ischemia in rats. J. Neurosci. 19, 10898–10907 (1999).
Zhang, Z.G. et al. Dynamic platelet accumulation at the site of the occluded middle cerebral artery and in downstream microvessels is associated with loss of microvascular integrity after embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion. Brain Res. 912, 181–194 (2001).
Ding, G. et al. MRI of combination treatment of embolic stroke in rat with rtPA and atorvastatin. J. Neurol. Sci. 246, 139–147 (2006).
Zhang, R.L., Zhang, Z.G., Chopp, M. & Zivin, J.A. Thrombolysis with tissue plasminogen activator alters adhesion molecule expression in the ischemic rat brain. Stroke 30, 624–629 (1999).
Zhang, L. et al. Effects of a selective CD11b/CD18 antagonist and recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator treatment alone and in combination in a rat embolic model of stroke. Stroke 34, 1790–1795 (2003).
Zhang, R.L., Chopp, M., Zhang, Z.G. & Divine, G. Early (1 h) administration of tissue plasminogen activator reduces infarct volume without increasing hemorrhagic transformation after focal cerebral embolization in rats. J. Neurol. Sci. 160, 1–8 (1998).
Marder, V.J. et al. Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 37, 2086–2093 (2006).
Singh, P., Doostkam, S., Reinhard, M., Ivanovas, V. & Taschner, C.A. Immunohistochemical analysis of thrombi retrieved during treatment of acute ischemic stroke: does stent-retriever cause intimal damage? Stroke 44, 1720–1722 (2013).
Cheng, T. et al. Activated protein C inhibits tissue plasminogen activator-induced brain hemorrhage. Nat. Med. 12, 1278–1285 (2006).
Zhang, L. et al. Functional recovery in aged and young rats after embolic stroke: treatment with a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor. Stroke 36, 847–852 (2005).
Zhang, L. et al. Adjuvant treatment with a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor increases the therapeutic window for low-dose tissue plasminogen activator administration in a rat model of embolic stroke. Circulation 107, 2837–2843 (2003).
Zhang, Z. et al. Adjuvant treatment with neuroserpin increases the therapeutic window for tissue-type plasminogen activator administration in a rat model of embolic stroke. Circulation 106, 740–745 (2002).
Wilhelm-Schwenkmezger, T. et al. Therapeutic application of 20-kHz transcranial ultrasound in an embolic middle cerebral artery occlusion model in rats: safety concerns. Stroke 38, 1031–1035 (2007).
Hobohm, C. et al. Long-lasting neuronal loss following experimental focal cerebral ischemia is not affected by combined administration of tissue plasminogen activator and hyperbaric oxygen. Brain Res. 1417, 115–126 (2011).
Guluma, K.Z. & Lapchak, P.A. Comparison of the post-embolization effects of tissue-plasminogen activator and simvastatin on neurological outcome in a clinically relevant rat model of acute ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 1354, 206–216 (2010).
Tanaka, Y., Marumo, T., Omura, T. & Yoshida, S. Serum S100B indicates successful combination treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and MK-801 in a rat model of embolic stroke. Brain Res. 1154, 194–199 (2007).
Zhang, Z.G. et al. A model of mini-embolic stroke offers measurements of the neurovascular unit response in the living mouse. Stroke 36, 2701–2704 (2005).
Undas, A. & Ariens, R.A. Fibrin clot structure and function: a role in the pathophysiology of arterial and venous thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31, e88–99 (2011).
Wohner, N. et al. Lytic resistance of fibrin containing red blood cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31, 2306–2313 (2011).
Zhang, Z., Chopp, M., Zhang, R.L. & Goussev, A. A mouse model of embolic focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 1081–1088 (1997).
Del Sette, M., Angeli, S., Stara, I., Finocchi, C. & Gandolfo, C. Microembolic signals with serial transcranial Doppler monitoring in acute focal ischemic deficit. A local phenomenon? Stroke 28, 1311–1313 (1997).
Idicula, T.T., Naess, H. & Thomassen, L. Microemboli-monitoring during the acute phase of ischemic stroke: is it worth the time? BMC Neurol. 10, 79 (2010).
Koennecke, H.C. et al. Frequency and determinants of microembolic signals on transcranial Doppler in unselected patients with acute carotid territory ischemia. A prospective study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 8, 107–112 (1998).
Poppert, H., Sadikovic, S., Sander, K., Wolf, O. & Sander, D. Embolic signals in unselected stroke patients: prevalence and diagnostic benefit. Stroke 37, 2039–2043 (2006).
Chen, J. et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke 32, 2682–2688 (2001).
Hernandez, T.D. & Schallert, T. Seizures and recovery from experimental brain damage. Exp. Neurol. 102, 318–324 (1988).
Bouet, V. et al. The adhesive removal test: a sensitive method to assess sensorimotor deficits in mice. Nat. Protoc. 4, 1560–1564 (2009).
Schallert, T. et al. Tactile extinction: distinguishing between sensorimotor and motor asymmetries in rats with unilateral nigrostriatal damage. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 16, 455–462 (1982).
Zhang, L. et al. Tadalafil, a long-acting type 5 phosphodiesterase isoenzyme inhibitor, improves neurological functional recovery in a rat model of embolic stroke. Brain Res. 1118, 192–198 (2006).
Jiang, Q. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging indexes of therapeutic efficacy of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment of rat at 1 and 4 hours after embolic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 20, 21–27 (2000).
Jiang, Q. et al. Diffusion-, T2-, and perfusion-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of middle cerebral artery embolic stroke and recombinant tissue plasminogen activator intervention in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 758–767 (1998).
Zhang, L. et al. Combination treatment with N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline and tissue plasminogen activator provides potent neuroprotection in rats after stroke. Stroke 45, 1108–1114 (2014).
Ding, G. et al. MRI evaluation of BBB disruption after adjuvant AcSDKP treatment of stroke with tPA in rat. Neuroscience 271, 1–8 (2014).
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z.G. & Chopp, M. The neurovascular unit and combination treatment strategies for stroke. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 33, 415–422 (2012).
Zhang, L. et al. Combination treatment with VELCADE and low-dose tissue plasminogen activator provides potent neuroprotection in aged rats after embolic focal ischemia. Stroke 41, 1001–1007 (2010).
Jia, L., Chopp, M., Zhang, L., Lu, M. & Zhang, Z. Erythropoietin in combination of tissue plasminogen activator exacerbates brain hemorrhage when treatment is initiated 6 hours after stroke. Stroke 41, 2071–2076 (2010).
Zhang, L. et al. Treatment of embolic stroke in rats with bortezomib and recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator. Thromb. Haemost. 95, 166–173 (2006).
Zhang, L. et al. Multitargeted effects of statin-enhanced thrombolytic therapy for stroke with recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator in the rat. Circulation 112, 3486–3494 (2005).
Ding, G. et al. Analysis of combined treatment of embolic stroke in rat with r-tPA and a GPIIb/IIIa inhibitor. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25, 87–97 (2005).
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z.G., Zhang, C., Zhang, R.L. & Chopp, M. Intravenous administration of a GPIIb/IIIa receptor antagonist extends the therapeutic window of intra-arterial tenecteplase-tissue plasminogen activator in a rat stroke model. Stroke 35, 2890–2895 (2004).
Jiang, Q. et al. MRI evaluation of treatment of embolic stroke in rat with intra-arterial and intravenous rt-PA. J. Neurol. Sci. 224, 57–67 (2004).
Ding, G. et al. Multiparametric ISODATA analysis of embolic stroke and rt-PA intervention in rat. J. Neurol. Sci. 223, 135–143 (2004).
Morris, D.C. et al. Extension of the therapeutic window for recombinant tissue plasminogen activator with argatroban in a rat model of embolic stroke. Stroke 32, 2635–2640 (2001).
Zhang, R.L. et al. Postischemic intracarotid treatment with TNK-tPA reduces infarct volume and improves neurological deficits in embolic stroke in the unanesthetized rat. Brain Res. 878, 64–71 (2000).
Nakayama, H., Dietrich, W.D., Watson, B.D., Busto, R. & Ginsberg, M.D. Photothrombotic occlusion of rat middle cerebral artery: histopathological and hemodynamic sequelae of acute recanalization. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 8, 357–366 (1988).
Watson, B.D., Dietrich, W.D., Busto, R., Wachtel, M.S. & Ginsberg, M.D. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann. Neurol. 17, 497–504 (1985).
Zivin, J.A. et al. A model for quantitative evaluation of embolic stroke therapy. Brain Res. 435, 305–309 (1987).
Gerriets, T. et al. The macrosphere model: evaluation of a new stroke model for permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 122, 201–211 (2003).
Kudo, M., Aoyama, A., Ichimori, S. & Fukunaga, N. An animal model of cerebral infarction. Homologous blood clot emboli in rats. Stroke 13, 505–508 (1982).
Overgaard, K. et al. A rat model of reproducible cerebral infarction using thrombotic blood clot emboli. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 12, 484–490 (1992).
Benes, V., Zabramski, J.M., Boston, M., Puca, A. & Spetzler, R.F. Effect of intra-arterial tissue plasminogen activator and urokinase on autologous arterial emboli in the cerebral circulation of rabbits [corrected]. Stroke 21, 1594–1599 (1990).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by US National Institutes of Health grants R01NS079612 (Z.G.Z.) and R01AG037506 (M.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.L.Z., Z.G.Z. and M.C. conceptualized experiments. R.L.Z., L.Z. and Z.G.Z. performed the surgeries and histological analysis. Q.J. and G.D. performed MRI experiments and analyzed MRI data. L.Z., Z.G.Z. and M.C. wrote the manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Zhang, R., Jiang, Q. et al. Focal embolic cerebral ischemia in the rat. Nat Protoc 10, 539–547 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.036
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.036
This article is cited by
-
A clinically relevant model of focal embolic cerebral ischemia by thrombus and thrombolysis in rhesus monkeys
Nature Protocols (2022)
-
Rodent Models of Vascular Cognitive Impairment
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2021)
-
The interrelationship between cerebral ischemic stroke and glioma: a comprehensive study of recent reports
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2019)
-
Preclinical Validation of the Therapeutic Potential of Glasgow Oxygen Level Dependent (GOLD) Technology: a Theranostic for Acute Stroke
Translational Stroke Research (2019)
-
Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Models in Nonhuman Primates
Neurotherapeutics (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.