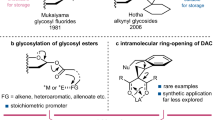
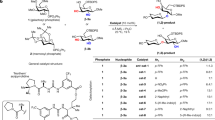
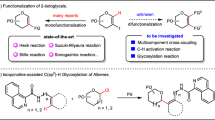
Abstract
Chemoenzymatic synthesis, which combines the flexibility of chemical synthesis and the high selectivity of enzymatic synthesis, is a powerful approach to obtain complex carbohydrates. It is a preferred method for synthesizing sialic acid-containing structures, including those with diverse naturally occurring and non-natural sialic acid forms, different sialyl linkages and different glycans that link to the sialic acid. Starting from N-acetylmannosamine, mannose or their chemically or enzymatically modified derivatives, sialic acid aldolase-catalyzed condensation reaction leads to the formation of sialic acids and their derivatives. These compounds are subsequently activated by a CMP-sialic acid synthetase and transferred to a wide range of suitable acceptors by a suitable sialyltransferase for the formation of sialosides containing natural and non-natural functionalities. The three-enzyme coupled synthesis of sialosides can be carried out in one pot without the isolation of intermediates. The time for synthesis is 4–18 h. Purification and characterization of the product can be completed within 2–3 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angata, T. & Varki, A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem. Rev. 102, 439–469 (2002).
Schauer, R. Achievements and challenges of sialic acid research. Glycoconj. J. 17, 485–499 (2000).
Yu, H. et al. Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of naturally occurring and non-natural alpha-2,6-linked sialosides: a P. damsela alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase with extremely flexible donor-substrate specificity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 45, 3938–3944 (2006).
Butor, C., Diaz, S. & Varki, A. High level O-acetylation of sialic acids on N-linked oligosaccharides of rat liver membranes. Differential subcellular distribution of 7- and 9-O-acetyl groups and of enzymes involved in their regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 10197–10206 (1993).
Shi, W.X., Chammas, R. & Varki, A. Linkage-specific action of endogenous sialic acid O-acetyltransferase in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 15130–15138 (1996).
Varki, A. Diversity in the sialic acids. Glycobiology 2, 25–40 (1992).
Schauer, R. & Kamerling, J.P. Chemistry, biochemistry and biology of sialic acids. In Glycoproteins II (eds. Montreuil, J., Vliegenthart, J.F.G. & Schachter, H.) 243–402 (Elsevier, Amsterdam).
Lewis, A.L., Nizet, V. & Varki, A. Discovery and characterization of sialic acid O-acetylation in group B Streptococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 11123–11128 (2004).
Chappell, M.D. & Halcomb, R.L. Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of oligosaccharides that contain functionalized sialic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 3393–3394 (1997).
Boons, G.J. & Demchenko, A.V. Recent advances in o-sialylation. Chem. Rev. 100, 4539–4566 (2000).
Kiefel, M.J. & von Itzstein, M. Recent advances in the synthesis of sialic acid derivatives and sialylmimetics as biological probes. Chem. Rev. 102, 471–490 (2002).
Izumi, M. & Wong, C.H. Microbial sialyltransferases for carbohydrate synthesis. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 13, 345–360 (2001).
Joziasse, D.H. et al. Branch specificity of bovine colostrum CMP-sialic acid: Gal beta 1-4GlcNAc-R alpha 2-6-sialyltransferase. Sialylation of bi-, tri-, and tetraantennary oligosaccharides and glycopeptides of the N-acetyllactosamine type. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 2025–2033 (1987).
Thiem, J. & Treder, W. Synthesis of the trisaccharide Neu-5-Ac-α(2 → 6)Gal-β(1 → )GlcNAc by the use of immobilized enzymes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 25, 1096–1097 (1986).
Blixt, O., Allin, K., Pereira, L., Datta, A. & Paulson, J.C. Efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of O-linked sialyl oligosaccharides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 5739–5746 (2002).
Wong, C.H., Halcomb, R.L., Ichikawa, Y. & Kajimoto, T. Enzymes in organic synthesis: application to the problems of carbohydrate recognition (Part 2). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 521–546 (1995).
Kajihara, Y. et al. A novel alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase: transfer of sialic acid to fucosyl and sialyl trisaccharides. J. Org. Chem. 61, 8632–8635 (1996).
Fitz, W. & Wong, C.H. Oligosaccharide synthesis by enzymatic glycosidation. In Preparative Carbohydrate Chemistry (ed. Hanessian, S.) 485–504 (Marcel Dekker, New York).
Ichikawa, Y., Wang, R. & Wong, C.H. Regeneration of sugar nucleotide for enzymatic oligosaccharide synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 247, 107–127 (1996).
Yu, H. et al. A multifunctional Pasteurella multocida sialyltransferase: a powerful tool for the synthesis of sialoside libraries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 17618–17619 (2005).
Yu, H., Yu, H., Karpel, R. & Chen, X. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of CMP-sialic acid derivatives by a one-pot two-enzyme system: comparison of substrate flexibility of three microbial CMP-sialic acid synthetases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 6427–6435 (2004).
Herrler, G. et al. A synthetic sialic acid analogue is recognized by influenza C virus as a receptor determinant but is resistant to the receptor-destroying enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 12501–12505 (1992).
Blixt, O. & Paulson, J.C. Biocatalytic preparation of N-glycolylneuraminic acid, deaminoneuraminic acid (KDN) and 9-azido-9-deoxysialic acid oligosaccharides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 345, 687–690 (2003).
Wong, C.-H. Chemoenzymatic synthesis: application to the study of carbohydrate recognition. Acta Chem. Scand. 50, 211–218 (1996).
Saxon, E. & Bertozzi, C.R. Cell surface engineering by a modified Staudinger reaction. Science 287, 2007–2010 (2000).
Kolb, H.C., Finn, M.G. & Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 40, 2004–2021 (2001).
Fazio, F., Bryan, M.C., Blixt, O., Paulson, J.C. & Wong, C.H. Synthesis of sugar arrays in microtiter plate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 14397–14402 (2002).
Wu, X., Ling, C.C. & Bundle, D.R. A new homobifunctional p-nitro phenyl ester coupling reagent for the preparation of neoglycoproteins. Org. Lett. 6, 4407–4410 (2004).
Ding, Y., Alkan, S.S., Baschang, G. & Defaye, J. Synthesis of the HSA-conjugate of the S-linked thiomimetic of the branched tetrasaccharide repeating unit of the immunostimulant polysaccharide, schizophyllan. Evaluation as potential immunomodulator. Carbohydr. Res. 328, 71–76 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Mizutani Foundation for Glycoscience, NIH R01GM076360, and start-up funds from the Regents of the University of California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Chokhawala, H., Huang, S. et al. One-pot three-enzyme chemoenzymatic approach to the synthesis of sialosides containing natural and non-natural functionalities. Nat Protoc 1, 2485–2492 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.401
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.401
This article is cited by
-
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of genetically-encoded multivalent liquid N-glycan arrays
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Small tools for sweet challenges: advances in microfluidic technologies for glycan synthesis
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2022)
-
Enzymatic synthesis of lactosylated and sialylated derivatives of epothilone A
Glycoconjugate Journal (2016)
-
Sialic acid metabolism and sialyltransferases: natural functions and applications
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2012)
-
Pasteurella multocida CMP-sialic acid synthetase and mutants of Neisseria meningitidis CMP-sialic acid synthetase with improved substrate promiscuity
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.