Abstract
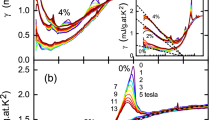
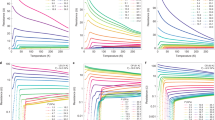
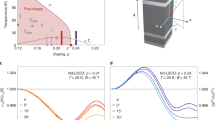
The underlying physics of the magnetic-field induced resistive state in lightly doped high-temperature cuprate superconductorsremains a mystery. One interpretation is that the application of magnetic field destroys the d-wave superconducting gap, uncovering a Fermi surface that behaves as a Fermi liquid. Another view is that an applied magnetic field destroys long-range superconducting phase coherence, but the superconducting gap amplitude survives. By measuring the specific heat of YBa2Cu3O6.56 we determine the quasiparticle density of states from the superconducting state well into the magnetic-field induced resistive state. At very high magnetic fields the specific heat exhibits both the conventional temperature dependence and quantum oscillations expected for a Fermi liquid. On the other hand, the magnetic-field dependence of the quasiparticle density of states follows  behaviour that persists smoothly through the zero-resistance transition, giving evidence of a developed d-wave superconducting gap over the entire magnetic field range measured.
behaviour that persists smoothly through the zero-resistance transition, giving evidence of a developed d-wave superconducting gap over the entire magnetic field range measured.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doiron-Leyraud, N. et al. Quantum oscillations and the Fermi surface in an underdoped high-Tc superconductor. Nature 447, 565–568 (2007).
Leboeuf, D. et al. Electron pockets in the Fermi surface of hole-doped high-Tc superconductors. Nature 450, 533–536 (2007).
Sebastian, S. E. et al. A multi-component Fermi surface in the vortex state of an underdoped high-Tc superconductor. Nature 454, 200–203 (2008).
Yelland, E. A. et al. Quantum oscillations in the underdoped cuprate YBa2Cu4O8 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 047003 (2008).
Bangura, A. F. et al. Small Fermi surface pockets in underdoped high temperature superconductors: Observation of Shubnikov–de Haas oscillations in YBa2Cu4O8 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 047004 (2008).
Audouard, A. et al. Multiple quantum oscillations in the de Haas–van Alphen spectra of the underdoped high-temperature superconductor YBa2Cu3O6.5 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 157003 (2009).
Singleton, J. et al. Magnetic quantum oscillations in YBa2Cu3O6.61 and YBa2Cu3O6.69 in fields of up to 85 T: Patching the hole in the roof of the superconducting dome. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 086403 (2010).
Wang, Y. et al. High field phase diagram of cuprates derived from the Nernst effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 257003 (2002).
Boebinger, G. S. et al. Insulator-to-metal crossover in the normal state of La2−xSrxCuO4 near optimum doping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 5417–5420 (1996).
Li, L., Checkelsky, J. G., Komiya, S., Ando, Y. & Ong, N. P. Low-temperature vortex liquid in La2−xSrxCuO4 . Nature Phys. 3, 311–314 (2007).
Cyr-Choiniere, O. et al. Enhancement of the Nernst effect by stripe order in a high-Tc superconductor. Nature 458, 743–745 (2009).
Moler, K. A. et al. Magnetic field dependence of the density of states of YBa2Cu3O6.95 as determined from the specific heat. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 2744–2747 (1994).
Revaz, B. et al. d-wave scaling relations in the mixed-state specific heat of YBa2Cu3O7 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3364–3367 (1998).
Wright, D. A. et al. Low-temperature specific heat of YBa2Cu3O7−δ, 0≤δ≤0.2: Evidence for d-wave pairing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 1550–1553 (1999).
Wang, Y., Revaz, B., Erb, A. & Junod, A. Direct observation and anisotropy of the contribution of gap nodes in the low-temperature specific heat of YBa2Cu3O7 . Phys. Rev. B 63, 094508 (2001).
Volovik, G. E. Superconductivity with lines of gap nodes: Density of states in the vortex. JETP Lett. 58, 457–461 (1993).
Simon, S. H. & Lee, P. A. Scaling of the quasiparticle spectrum for d-wave superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1548–1551 (1997).
Franz, M. & Tešanovć, Z. Self-consistent electronic structure of a d x 2 − y 2 and a d x 2 − y 2 +id xy vortex. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4763–4766 (1998).
Mel’nikov, A. S. Quantization of the quasiparticle spectrum in the mixed state of d-wave superconductors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11, 4219–4229 (1999).
Vekhter, I., Hirschfeld, P. J. & Nicol, E. J. Thermodynamics of d-wave superconductors in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. B 64, 064513 (2001).
Sebastian, S. E. et al. Metal–insulator quantum critical point beneath the high Tc superconducting dome. Proc. Natl Acad Sci. USA 107, 6175–6179 (2010).
Jaudet, C. et al. Quantum oscillations in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6.5 . Physica B 404, 354–356 (2009).
Sutherland, M. et al. Thermal conductivity across the phase diagram of cuprates: Low-energy quasiparticles and doping dependence of the superconducting gap. Phys. Rev. B 67, 174520 (2003).
Shoenberg, D. Magnetic Oscillations in Metals (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1984).
Ramshaw, B. J. et al. Angle-dependence of quantum oscillations in YBa2Cu3O6.59 shows free spin behaviour of quasiparticles. Nature Phys. published online 10.1038/nphys1873, (19 December 2010).
Fisher, R. A., Gordon, J. E. & Phillips, N. in Handbook of High-Temperature Superconductivity (eds Schrieffer, J. R. & Brooks, J. S.) Ch. 9, 326–397 (Springer, 2007).
Bangura, A. F. et al. Fermi surface and electronic homogeneity of the overdoped cuprate superconductor Tl2Ba2CuO6+δ as revealed by quantum oscillations. Phys. Rev. B 82, 140501 (2010).
Wade, J. M., Loram, J. W., Mirza, K. A., Cooper, J. R. & Tallon, J. L. Electronic specific heat of Tl2Ba2CuO6+δ from 2 K to 300 K for 0≤δ≤0.1. J. Supercond. 7, 261–264 (1994).
Harrison, N. et al. de Haas–van Alphen effect in the vortex state of Nb3Sn. Phys. Rev. B 50, 4208–4211 (1994).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge discussions with N. Harrison, P. Hirschfeld, S. Kivelson, P. A. Lee, R. McDonald, S. Sachdev, J. Singleton, Z. Tesanovic, T. Senthil, and C. M. Varma. S.C.R. acknowledges financial support from ICAM. W.N.H., R.L., and D.A.B. are supported by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research. O.V. was supported in part by the NSF CAREER award under Grant No. DMR-0955561. The National High Magnetic Field Laboratory is supported by the State of Florida and the National Science Foundation’s Division of Materials Research through DMR-0654118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.C.R., G.S.B., J.B.B., A.M., F.F.B. and J.B.K. developed the specific heat equipment and collected the data. D.A.B., W.N.H. and R.L. grew the sample and contributed to interpretation of the results. O.V., S.C.R., G.S.B., A.M. and J.B.K. contributed to the data analysis and interpretation and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1632 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riggs, S., Vafek, O., Kemper, J. et al. Heat capacity through the magnetic-field-induced resistive transition in an underdoped high-temperature superconductor. Nature Phys 7, 332–335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1921
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1921
This article is cited by
-
Unveiling the double-peak structure of quantum oscillations in the specific heat
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Fermi surface transformation at the pseudogap critical point of a cuprate superconductor
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Hard antinodal gap revealed by quantum oscillations in the pseudogap regime of underdoped high-Tc superconductors
Nature Physics (2020)
-
Stabilization of three-dimensional charge order in YBa2Cu3O6+x via epitaxial growth
Nature Communications (2018)
-
On the Origin of a Small Hole Pocket in the Fermi Surface of Underdoped YBa2Cu3O y
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2018)