Abstract
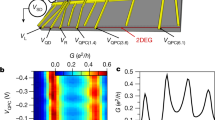
In the spin Hall effect, a current passed through a spin–orbit coupled electron gas induces a spin accumulation of inverse sign on either side of the sample. A number of possible mechanisms have been described, extrinsic as well as intrinsic ones, and they may occur in the ballistic as well as the diffusive transport regime. A central problem for experimentalists in studying the effect is the very small signals that result from the spin accumulation. Electrical measurements on metals have yielded reliable signatures of the spin Hall effect, but in semiconductors the spin accumulation could only be detected by optical techniques. Here we report experimental evidence for electrical manipulation and detection of the ballistic intrinsic spin Hall effect (ISHE) in semiconductors. We perform a non-local electrical measurement in nanoscale H-shaped structures built on high-mobility HgTe/(Hg, Cd)Te quantum wells. When the samples are tuned into the p-regime, we observe a large non-local resistance signal due to the ISHE, several orders of magnitude larger than in metals. In the n-regime, where the spin–orbit splitting is reduced, the signal is at least one order of magnitude smaller and vanishes for narrower quantum wells. We verify our experimental observations by quantum transport calculations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awschalom, D. D. & Flatté, M. E. Challenges for semiconductor spintronics. Nature Phys. 3, 153–159 (2007).
Dyakonov, M. I. & Perel, V. I. Current-induced spin orientation of electrons in semiconductors. Phys. Lett. A 35, 459–460 (1971).
Hirsch, J. E. Spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1834–1837 (1999).
Hankiewicz, E. M. & Vignale, G. Coulomb corrections to the extrinsic spin-Hall effect of a two-dimensional electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 73, 115339 (2006).
Engel, H-A., Rashba, E. I. & Halperin, B. I. Handbook of Magnetism and Advanced Magnetic Materials (John Wiley, 2007).
Murakami, S., Nagaosa, N. & Zhang, S-C. Dissipationless quantum spin current at room temperature. Science 301, 1348–1351 (2003).
Sinova, J. et al. Universal intrinsic spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 126603 (2004).
Kato, Y. K., Myers, R. C., Gossard, A. C. & Awschalom, D. D. Observation of the spin Hall effect in semiconductors. Science 306, 1910–1913 (2004).
Wunderlich, J., Kaestner, B., Sinova, J. & Jungwirth, T. Experimental observation of the spin-Hall effect in a two-dimensional spin–orbit coupled semiconductor system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 047204 (2005).
Sih, V. et al. Spatial imaging of the spin Hall effect and current-induced polarization in two-dimensional electron gases. Nature Phys. 1, 31–35 (2005).
Valenzuela, S. O. & Tinkham, M. Direct electronic measurement of the spin Hall effect. Nature 442, 176–179 (2006).
Saitoh, E., Ueda, M., Miyajima, H. & Tatara, G. Conversion of spin current into charge current at room temperature: Inverse spin-Hall effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 182509 (2006).
Kimura, T., Otani, Y., Sato, T., Takahashi, S. & Maekawa, S. Room-temperature reversible spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 156601 (2007).
Seki, T. et al. Giant spin Hall effect in perpendicularly spin-polarized FePt/Au devices. Nature Matter. 7, 125–129 (2008).
Weng, K., Chandrasekhar, N., Miniatura, C. & Englert, B-G. in Electron Transport in Nanosystems (eds Bonca, J. & Kruchinin, S.) 49–58 (Springer, 2008).
Hankiewicz, E. M., Molenkamp, L. W., Jungwirth, T. & Sinova, J. Manifestation of the spin Hall effect through charge-transport in the mesoscopic regime. Phys. Rev. B 70, 241301 (2004).
Nikolić, B. K., Souma, S., Zârbo, L. & Sinova, J. Nonequilibrium spin Hall accumulation in ballistic semiconductor nanostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 046601 (2005).
König, M. et al. Quantum spin Hall insulator state in HgTe quantum wells. Science 318, 766–770 (2007).
Gui, Y. et al. Giant spin–orbit splitting in a HgTe quantum well. Phys. Rev. B 70, 115328 (2004).
Hinz, J. et al. Gate control of the giant Rashba effect in HgTe quantum wells. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 21, 501–506 (2006).
Novik, E. et al. Band structure of semimagnetic HgMnTe quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 72, 35321 (2005).
Hankiewicz, E. M. et al. Charge Hall effect driven by spin-dependent chemical potential gradients and Onsager relations in mesoscopic systems. Phys. Rev. B 72, 155305 (2005).
Roth, A. et al. Nonlocal transport in the quantum spin Hall state. Science 325, 294–297 (2009).
Zhou, B., Lu, H-Z., Chu, R-L., Shen, S-Q. & Niu, Q. Finite size effects on helical edge states in a quantum spin-Hall system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 246807 (2008).
Yang, W., Chang, K. & Zhang, S-C. Intrinsic spin Hall effect induced by quantum phase transition in HgCdTe quantum wells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 056602 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Schneider and N. Eikenberg for assistance in the experiments, and C. Gould, S-C. Zhang and X-L. Qi for stimulating discussions. We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the German–Israeli Foundation (I-881-138.7/2005), DFG under grants AS 327/2-1 and HA5893/1-1, ONR under grant ONR-N000140610122, NSF under grant DMR-0547875, and SWAN-NRI. We thank the Leibniz Rechenzentrum Münich for providing computer resources. J.S. is a Cottrell Scholar of the Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Device fabrication: C.B., A.R., M.K.; experiments and data analysis: C.B., A.R., M.K., H.B., L.W.M.; theory: E.G.N., E.M.H., W.H., J.S.; writing: C.B., H.B., E.M.H., J.S., L.W.M.; project planning: H.B., L.W.M.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 324 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brüne, C., Roth, A., Novik, E. et al. Evidence for the ballistic intrinsic spin Hall effect in HgTe nanostructures. Nature Phys 6, 448–454 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1655
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys1655
This article is cited by
-
Non-identical moiré twins in bilayer graphene
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Spin Precession and Spin‐Charge Conversion in a Strong Rashba Channel at Room Temperature
Electronic Materials Letters (2021)
-
Two-Dimensional Time-Reversal-Invariant Topological Insulators via Fredholm Theory
Mathematical Physics, Analysis and Geometry (2020)
-
Gapless Andreev bound states in the quantum spin Hall insulator HgTe
Nature Nanotechnology (2017)
-
Room-temperature chiral charge pumping in Dirac semimetals
Nature Communications (2017)