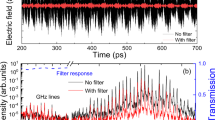
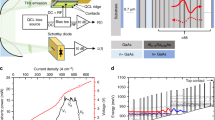
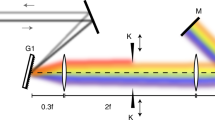
Abstract
Quantum cascade lasers are compact devices based on mature compound semiconductors such as GaAs that take advantage of highly developed optoelectronic fabrication techniques to integrate linear and nonlinear functions. This Review discusses terahertz-wave engineering using quantum cascade lasers with a particular focus on techniques that have been implemented to control their spectral and output beam properties. After briefly introducing the types of active regions and surveying present maximum operating temperatures, we review several photonic structures used for frequency and beam engineering, ranging from distributed feedback lasers to photonic crystals. We then describe techniques that allow the upconversion of terahertz quantum cascade laser radiation in the near-infrared region using nonlinear intracavity mixing. Finally, we review frequency stabilization of terahertz quantum cascade lasers with a special emphasis on phase locking to near-infrared frequency combs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Faist, J. et al. Quantum cascade laser. Science 264, 553–556 (1994).
Faist, J., Capasso, F., Sirtori, C., Sivco, D. & Cho, A. Y. in Intersubband Transitions in Quantum Wells: Physics and Device Applications II Vol. 66 (eds Liu, H. C. & Capasso, F.) 1–83 (Academic, 2000).
Yao, Y., Hoffman, A. J. & Gmachl, C. F. Mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers. Nature Photon. 6, 432–439 (2012).
Kohler, R. et al. Terahertz semiconductor-heterostructure laser. Nature 417, 156–159 (2002).
Williams, B. S. Terahertz quantum-cascade lasers, Nature Photon. 1, 517–525 (2007).
Coldren, L. A., Corzine, S. W. & Mašanović, M. L. Diode Lasers and Photonic Integrated Circuits. 2nd edn (Wiley, 2012).
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
Sirtori, C. Applied physics: bridge for the terahertz gap. Nature 417, 132–133 (2002).
Xu, G. et al. Efficient power extraction in surface-emitting semiconductor lasers using graded photonic heterostructures. Nat. Commun. 3, 952 (2012).
Barbieri, S. et al. Phase-locking of a 2.7-THz quantum cascade laser to a mode-locked erbium-doped fibre laser. Nature Photon. 4, 636–640 (2010).
Qin, Q., Williams, B. S., Kumar, S., Reno, J. L. & Hu, Q. Tuning a terahertz wire laser. Nature Photon. 3, 732–737 (2009).
Amanti, M. I., Fischer, M., Scalari, G., Beck, M. & Faist, J. Low-divergence single-mode terahertz quantum cascade laser. Nature Photon. 3, 586–590 (2009).
Miyai, E. et al. Photonics: lasers producing tailored beams. Nature 441, 946 (2006).
Vlasov, Y. A., O'Boyle, M., Hamann, H. F. & McNab, S. J. Active control of slow light on a chip with photonic crystal waveguides. Nature 438, 65–69 (2005).
Lourtioz, J. M. et al. Photonic Crystals: Towards Nanoscale Photonic Devices, 2nd edn (Springer, 2008).
Mahler, L. et al. Single-mode operation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers with distributed feedback resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 5446–5448 (2004).
Mahler, L. et al. High-performance operation of single-mode terahertz quantum cascade lasers with metallic gratings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 181101 (2005).
Mujagi, E. et al. Vertically emitting terahertz quantum cascade ring lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 011120 (2009).
Kumar, S. et al. Surface-emitting distributed feedback terahertz quantum-cascade lasers in metal-metal waveguides. Opt. Express 15, 113–128 (2007).
Fan, J. A. et al. Surface emitting terahertz quantum cascade laser with a double-metal waveguide. Opt. Express 14, 11672–11680 (2006).
Mahler, L. et al. High-power surface emission from terahertz distributed feedback lasers with a dual-slit unit cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 191109 (2010).
Vitiello, M. S. & Tredicucci, A. Tunable emission in THz quantum cascade lasers. IEEE Trans. THz Sci. Technol. 1, 76–84 (2011).
Dhillon, S. S. et al. Terahertz transfer onto a telecom optical carrier. Nature Photon. 1, 411–415 (2007).
Madeo, J. et al. All-optical wavelength shifting in a semiconductor laser using resonant nonlinearities. Nature Photon. 6, 519–524 (2012).
Williams, B. S., Kumar, S., Callebaut, H., Hu, Q. & Reno, J. L. THz quantum cascade laser at λ ≈ 10μm using metal waveguide for mode confinement. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2124–2126 (2003).
Maineult, W. et al. Microwave modulation of terahertz quantum cascade lasers: a transmission-line approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 021108 (2010).
Gellie, P. et al. Injection locking of terahertz quantum cascade lasers up to 35GHz using RF amplitude modulation. Opt. Express 18, 20799–20816 (2010).
Barbieri, S. et al. Coherent sampling of active mode-locked terahertz quantum cascade lasers and frequency synthesis. Nature Photon. 5, 306–313 (2011).
Freeman, J. R. et al. Direct intensity sampling of a modelocked terahertz quantum cascade laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 181115 (2012).
Consolino, L. et al. Phase-locking to a free-space terahertz comb for metrological-grade terahertz lasers. Nat. Commun. 3, 1040 (2012).
Yokoyama, S., Nakamura, R., Nose, M., Araki, T. & Yasui, T. Terahertz spectrum analyzer based on a terahertz frequency comb. Opt. Express 16, 13052–13061 (2008).
Rochat, M. et al. Low-threshold terahertz quantum-cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1381–1383 (2002).
Scalari, G. et al. Far-infrared (λ = 87 μm) bound-to-continuum quantum-cascade lasers operating up to 90 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3165–3167 (2003).
Barbieri, S. et al. 2.9 THz quantum cascade lasers operating up to 70 K in continuous wave. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1674–1677 (2004).
Kohler, R. et al. Terahertz quantum-cascade lasers based on an interlaced photon-phonon cascade. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1266–1268 (2004).
Scalari, G., Hoyler, N., Giovannini, M. & Faist, J. Terahertz bound-to-continuum quantum cascade lasers based on optical-phonon scattering extraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 181101 (2005).
Walther, C., Scalari, G., Faist, J., Beere, H. & Ritchie, D. Low frequency terahertz quantum cascade laser operating from 1.6 to 1.8 THz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 231121 (2006).
Bai, Y., Bandyopadhyay, N., Tsao, S., Slivken, S. & Razeghi, M. Room temperature quantum cascade lasers with 27% wall plug efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 181102 (2011).
Lu, Q. Y., Bai, Y., Bandyopadhyay, N., Slivken S. & Razeghi, M. 2.4 W room temperature continuous wave operation of distributed feedback quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 181106 (2011).
Bismuto, A., Beck, M. & Faist, J. High power Sb-free quantum cascade laser emitting at 3.3 μm above 350 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 191104 (2011).
Scalari, G., Terazzi, R., Giovannini, M., Hoyler, N. & Faist, J. Population inversion by resonant tunneling in quantum wells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 032103 (2007).
Wacker, A. Extraction-controlled quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 081105 (2010).
Vitiello, M. S., Scamarcio, G., Spagnolo, V., Dhillon, S. S. & Sirtori, C. Terahertz quantum cascade lasers with large wall-plug efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 191115 (2007).
Williams, B. S, Kumar, S., Hu, Q. & Reno, J. L. Operation of terahertz quantum-cascade lasers at 164 K in pulsed mode and at 117 K in continuous-wave mode. Opt. Express 13, 3331–3339 (2005).
Fathololoumi, S. et al. Terahertz quantum cascade lasers operating up to ∼200 K with optimized oscillator strength and improved injection tunneling. Opt. Express 20, 3866–3876 (2012).
Kumar, S., Chan, C. W. I., Hu, Q. & Reno, J. L. A 1.8-THz quantum cascade laser operating significantly above the temperature of ω/kB . Nature Phys. 7, 166–171 (2011).
Wade, A. et al. Magnetic-field-assisted terahertz quantum cascade laser operating up to 225 K. Nature Photon. 3, 41–45 (2009).
Sirtori, C. Quantum cascade lasers: breaking energy bands. Nature Photon. 3, 13–15 (2009).
Chassagneux, Y. et al. Limiting factors to the temperature performance of THz quantum cascade lasers based on the resonant-phonon depopulation scheme. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Tech. 2, 83–92 (2012).
Belkin, M. A. et al. Terahertz quantum-cascade-laser source based on intracavity difference-frequency generation. Nature Photon. 1, 288–292 (2007).
Lu, Q. Y., Bandyopadhyay, N., Slivken, S., Bai, Y. & Razeghi, M. Room temperature single-mode terahertz sources based on intracavity difference-frequency generation in quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 131106 (2011).
Vijayraghavan, K. et al. Terahertz sources based on Čerenkov difference-frequency generation in quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 251104 (2012).
Kohen, S., Williams, B. S. & Hu, Q. Electromagnetic modeling of terahertz quantum cascade laser waveguides and resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 053106 (2005).
Qin, Q., Reno, J. L. & Hu, Q. MEMS-based tunable terahertz wire-laser over 330 GHz. Opt. Lett. 36, 692–694 (2011).
Hugi, A. et al. External cavity quantum cascade laser tunable from 7.6 to 11.4 μm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 061103 (2009).
Lee, A. W. M., Williams, B. S., Kumar, S., Hu, Q. & Reno, J. L. Tunable terahertz quantum cascade lasers with external gratings. Opt. Lett. 35, 910–912 (2010).
Rungsawang, R. et al. Gain enhancement in a terahertz quantum cascade laser with parylene antireflection coatings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 101102 (2011).
Orlova, E. E. et al. Antenna model for wire lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 173904 (2006).
Balanis, C. A., Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 2nd edn (Wiley, 1996).
Amanti, M. I., Fischer, M., Walther, C., Scalari, G. & Faist, J. Horn antennas for terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Electron. Lett. 43, 573–574 (2007).
Maineult, W. et al. Metal-metal terahertz quantum cascade laser with micro-transverse-electromagnetic-horn antenna. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 183508 (2008).
Sirigu, L. et al. Terahertz quantum cascade lasers based on two-dimensional photonic crystal resonators. Opt. Express 16, 5206 (2008).
Amanti, M. I., Scalari, G., Castellano, F., Beck, M. & Faist, J. Low divergence terahertz photonic-wire laser. Opt. Express 18, 6390–6395 (2010).
Kao, T.-Y., Hu, Q. & Reno, J. L. Perfectly phase-matched third-order distributed feedback terahertz quantum-cascade lasers. Opt. Lett. 37, 2070–2072 (2012).
Kloosterman, J. L. et al. Hot electron bolometer heterodyne receiver with a 4.7-THz quantum cascade laser as a local oscillator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 011123 (2013).
Painter, O. et al. Two-dimensional photonic band-gap defect mode laser. Science 284, 1819–1821 (1999).
Miyai, E. & Noda, S Phase-shift effect on a two-dimensional surface-emitting photonic-crystal laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 111113 (2005).
Srinivasan, K. et al. Experimental demonstration of a high quality factor photonic crystal microcavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 1915–1917 (2003).
Li, S., Witjaksono, G., Macomber, S. & Botez, D. Analysis of surface-emitting second-order distributed feedback lasers with central grating phaseshift. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 9, 1153–1165 (2003).
Colombelli, R. et al. Quantum cascade surface-emitting photonic-crystal laser. Science 302, 1374–1377 (2003).
Dunbar, L. A. et al. Design, fabrication and optical characterization of quantum cascade lasers at terahertz frequencies using photonic crystal reflectors. Opt. Express 13, 8960–8968 (2005).
Chassagneux, Y. et al. Electrically pumped photonic-crystal terahertz lasers controlled by boundary conditions. Nature 457, 174–178 (2009).
Sevin, G. et al. Optimized surface-emitting photonic-crystal terahertz quantum cascade lasers with reduced resonator dimensions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 131101 (2010).
Chassagneux, Y. et al. Graded photonic crystal terahertz quantum cascade lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 031104 (2010).
Nguyen, D.-T., Simoens, F., Ouvrier-Buffet, J.-L., Meilhan, J. & Coutaz, J.-L. Broadband THz uncooled antenna-coupled microbolometer array—electromagnetic design, simulations and measurements, IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Tech. 2, 299–305 (2012).
Kasraian, M. & Botez, D. Metal-grating-outcoupled, surface-emitting distributed-feedback diode lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 2795–2797 (1996).
Xu, G. et al. Stable single-mode operation of surface-emitting THz lasers with graded photonic heterostructure resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 231105 (2013).
Campi, D. & Coriasso, C. Wavelength conversion technologies. Photon. Network Commun. 2, 85–95 (2000).
Černe, J. et al. Near-infrared sideband generation induced by intense far-infrared radiation in GaAs quantum wells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 3543–3545 (1997).
Phillips, C., Su, M. Y., Sherwin, M. S., Ko, J. & Coldren, L. Generation of first-order terahertz optical sidebands in asymmetric coupled quantum wells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 2728–2730 (1999).
Carter, S. G. et al. Terahertz-optical mixing in undoped and doped GaAs quantum wells: from excitonic to electronic intersubband transitions. Phys. Rev. B 72, 155309 (2005).
Yariv, A. Quantum Electronics. 3rd edn (Wiley, 1989).
Rosencher, E. & Bois, Ph. Model system for optical nonlinearities: asymmetric quantum wells. Phys. Rev. B 44, 011315 (1991).
Sirtori, C., Capasso, F., Faist, J., Pfeiffer, L. N. & West, K. W. Far-infrared generation of doubly resonant difference frequency mixing in a coupled quantum well two-dimensional electron gas system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 65, 445–447 (1994).
Berger, V. & Sirtori, C. Nonlinear phase matching in THz semiconductor waveguides. Semicond. Sci. Tech. 19, 964–970 (2004).
Rafailov, E. U. et al. Second-harmonic generation from a first-order quasi-phase-matched GaAs/AlGaAs waveguide crystal. Opt. Lett. 26, 1984–1986 (2001).
Vodopyanov, K. L. Optical THz-wave generation with periodically-inverted GaAs. Laser & Photon. Rev. 2, 11–25 (2008).
Ravaro, M. et al. Measurement of the intrinsic linewidth of terahertz quantum cascade lasers using a near-infrared frequency comb. Opt. Express 20, 25654–25661 (2012).
Vitiello, M. S. et al. Quantum-limited frequency fluctuations in a terahertz laser. Nature Photon. 6, 525–528 (2012).
Hübers, H.-W. et al. High-resolution gas phase spectroscopy with a distributed feedback terahertz quantum cascade laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 061115 (2006).
Ren, Y. et al. High-resolution heterodyne spectroscopy using a tunable quantum cascade laser around 3.5 THz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 231109 (2011).
Riehle, F. Frequency Standards. (Wiley, 2006).
Betz, A. L. et al. Frequency and phase-lock control of a 3 THz quantum cascade laser. Opt. Lett. 30, 1837–1839 (2005).
Richter, H. et al. Submegahertz frequency stabilization of a terahertz quantum cascade laser to a molecular absorption line. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 071112 (2010).
Ren, Y. et al. Frequency locking of single-mode 3.5-THz quantum cascade lasers using a gas cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 041111 (2012).
Rabanus, D. et al. Phase locking of a 1.5THz quantum cascade laser and use as a local oscillator in a heterodyne HEB receiver. Opt. Express 17, 1159–1168 (2009).
Khosropanah, P. et al. Phase locking of a 2.7 THz quantum cascade laser to a microwave reference. Opt. Lett. 34, 2958–2960 (2009).
VDI Virginia Diodes, Inc.; available at http://vadiodes.com.
Ravaro, M. et al. Phase-locking of a 2.5 THz quantum cascade laser to a frequency comb using a GaAs photomixer. Opt. Lett. 36, 3969–3971 (2011).
Ravaro, M. et al. Continuous-wave coherent imaging with terahertz quantum cascade lasers using electro-optic harmonic sampling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 091107 (2013).
Ravaro, M. et al. Stabilization and mode locking of terahertz quantum cascade lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 19, 8501011 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge several helpful discussions with S. Dhillon and G. Xu. C.S. gratefully acknowledges support from the Institut Universitaire de France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirtori, C., Barbieri, S. & Colombelli, R. Wave engineering with THz quantum cascade lasers. Nature Photon 7, 691–701 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.208
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.208
This article is cited by
-
Terahertz radiation generation from metallic electronic structure manipulated by inhomogeneous DC-fields
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Highly efficient THz four-wave mixing in doped silicon
Light: Science & Applications (2021)
-
Highly efficient surface-emitting semiconductor lasers exploiting quasi-crystalline distributed feedback photonic patterns
Light: Science & Applications (2020)
-
Electrically pumped topological laser with valley edge modes
Nature (2020)
-
Programmable terahertz chip-scale sensing interface with direct digital reconfiguration at sub-wavelength scales
Nature Communications (2019)