Abstract
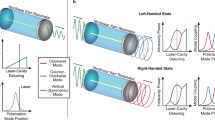
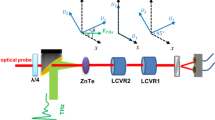
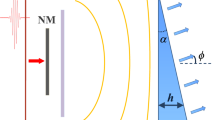
Polarization shaping of terahertz pulses enables us to manipulate the temporal evolution of the amplitude and direction of electric-field vectors in a prescribed manner. Such arbitrary control of terahertz waves has great potential in expanding the scope of terahertz spectroscopy, the manipulation of terahertz nonlinear phenomena and coherent control. This is analogous to the use of pulse-shaping techniques for optical frequencies that involve light's polarization states as a controllable degree of freedom. Here, we propose and demonstrate a method for generating a prescribed terahertz polarization-shaped waveform by the optical rectification of a laser pulse whose instantaneous polarization state and intensity are controlled by an optical pulse shaper. We have developed a deterministic procedure to derive input parameters for the pulse shaper that are adequate to generate the desired terahertz polarization-shaped waveform, with the benefit of simple polarization selection rules for the rectification process of light waves propagating along the three-fold axis of a nonlinear optical crystal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brixner, T. et al. Quantum control by ultrafast polarization shaping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 208301 (2004).
Suzuki, T., Minemoto, S., Kanai, T. & Sakai, H. Optimal control of multiphoton ionization processes in aligned I2 molecules with time-dependent polarization pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 133005 (2004).
Weise, F., Weber, S. M., Plewicki, M. & Lindinger, A. Application of phase, amplitude, and polarization shaped pulses for optimal control on molecules. Chem. Phys. 332, 313–317 (2007).
Corkum, P. B., Burnett, N. H. & Ivanov, M. Y. Subfemtosecond pulses. Opt. Lett. 19, 1870–1872 (1994).
Oron, D., Silberberg, Y., Dudovich, N. & Villeneuve, D. M. Efficient polarization gating of high-order harmonic generation by polarization-shaped ultrashort pulses. Phys. Rev. A 72, 063816 (2006).
Wefers, M. M., Kawashima, H. & Nelson, K. A. Automated multidimensional coherent optical spectroscopy with multiple phase-related femtosecond pulses. J. Chem. Phys. 102, 9133 (1995).
Brixner, T. et al. Two-dimensional spectroscopy of electronic couplings in photosynthesis. Nature 434, 625–628 (2005).
Gundogdu, K., Stone, K. W., Turner, D. B. & Nelson, K. A. Multidimensional coherent spectroscopy made easy. Chem. Phys. 341, 89–94 (2007).
Shao, J. & Hänggi, P. Control of molecular chirality. J. Chem. Phys. 107, 9935 (1997).
Fujimura, Y., González, L., Hoki, K., Manz, J. & Ohtsuki, Y. Selective preparation of enantiomers by laser pulses: quantum model simulation for H2POSH. Chem. Phys. Lett. 306, 1–8 (1999).
Hoki, K., Kröner, D. & Manz, J. Selective preparation of enantiomers from a racemate by laser pulses: model simulation for oriented atropisomers with coupled rotations and torsions. Chem. Phys. 267, 59–79 (2001).
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
Cao, J. C. Interband impact ionization and nonlinear absorption of terahertz radiation in semiconductor heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 237401 (2003).
Jewariya, M., Nagai, M. & Tanaka, K. Ladder climbing on the anharmonic intermolecular potential in an amino acid microcrystal via an intense monocycle terahertz pulse. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 203003 (2010).
Liu, M. et al. Terahertz-field-induced insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide metamaterial. Nature 487, 345–348 (2012).
Zaks, B., Liu, R. B. & Sherwin, M. S. Experimental observation of electron–hole recollisions. Nature 483, 580–583 (2012).
Lee, Y-S., Amer, N. & Hurlbut, W. C. Terahertz pulse shaping via optical rectification in poled lithium niobate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 170–172 (2003).
Liu, Y., Park, S-G. & Weiner, A. M. Terahertz waveform synthesis via optical pulse shaping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2, 709–719 (1996).
Sohn, J. Y., Ahn, Y. H., Park, D. J., Oh, E. & Kim, D. S. Tunable terahertz generation using femtosecond pulse shaping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 13–15 (2002).
Stepanov, A. G., Hebling, J. & Kuhl, J. Generation, tuning, and shaping of narrow-band, picosecond THz pulses by two-beam excitation. Opt. Express 12, 4650–4658 (2004).
Danielson, J. R., Amer, N. & Lee, Y-S. Generation of arbitrary terahertz wave forms in fanned-out periodically poled lithium niobate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 211118 (2006).
Dai, J., Karpowicz, N. & Zhang, X-C. Coherent polarization control of terahertz waves generated from two-color laser-induced gas plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 023001 (2009).
Lee, K., Yi, M., Song, J. D. & Ahn, J. Polarization shaping of few-cycle terahertz waves. Opt. Express 20, 12463–12472 (2012).
Xu, J. et al. Terahertz circular dichroism spectroscopy: a potential approach to the in situ detection of life's metabolic and genetic machinery. Astrobiology 3, 489–504 (2003).
Shan, J., Dadap, J. I. & Heinz, T. F. Circularly polarized light in the single-cycle limit: the nature of highly polychromatic radiation of defined polarization. Opt. Express 17, 7431–7439 (2009).
Amer, N., Hurlbut, W. C., Norton, B. J., Lee, Y-S. & Norris, T. B. Generation of terahertz pulses with arbitrary elliptical polarization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 221111 (2005).
Shimano, R., Nishimura, H. & Sato, T. Frequency tunable circular polarization control of terahertz radiation. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 21, L676–L678 (2005).
Wen, H. & Lindenberg, A. M. Coherent terahertz polarization control through manipulation of electron trajectories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 023902 (2009).
Kanda, N., Higuchi, T., Shimizu, H., Konishi, K., Yoshioka, K. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M. The vectorial control of magnetization by light. Nat. Commun. 2, 362 (2011).
Brixner, T. & Gerber, G. Femtosecond polarization pulse shaping. Opt. Lett. 26, 557–559 (2001).
Polachek, L., Oron, D. & Silberberg, Y. Full control of the spectral polarization of ultrashort pulses. Opt. Lett. 31, 631–633 (2006).
Plewicki, M., Weise, F., Weber, S. M. & Lindinger, A. Phase, amplitude, and polarization shaping with a pulse shaper in a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Appl. Opt. 45, 8354–8359 (2006).
Ninck, M., Galler, A., Feurer, T. & Brixner, T. Programmable common-path vector field synthesizer for femtosecond pulses. Opt. Lett. 32, 3379–3381 (2007).
Sato, M., Suzuki, T. & Misawa, K. Interferometric polarization pulse shaper stabilized by an external laser diode for arbitrary vector field shaping. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 123107 (2009).
Selle, R. et al. Generation of polarization-shaped ultraviolet femtosecond pulses. Opt. Lett. 33, 803–805 (2008).
Seidel, M. T., Zhang, Z., Yan, S. & Tan, H-S. Ultraviolet polarization pulse shaping using sum-frequency generation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28, 1146–1151 (2011).
Seidel, M. T., Yan, S. & Tan, H-S. Mid-infrared polarization pulse shaping by parametric transfer. Opt. Lett. 35, 478–480 (2010).
Higuchi, T., Kanda, N., Tamaru, H. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M. Selection rules for light-induced magnetization of a crystal with threefold symmetry: the case of antiferromagnetic NiO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 047401 (2011).
Bass, M., Franken, P. A. & Ward, J. F. Optical rectification. Phys. Rev. 138, A534–A542 (1965).
Tanabe, T., Suto, K., Nishizawa, J., Sato, K. & Kimura, T. Tunable terahertz wave generation in the 3- to 7-THz region from GaP. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 237–239 (2003).
Chen, Q., Tani, M., Jiang, Z. & Zhang X-C . Electro-optic transceivers for terahertz-wave applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 18, 823–831 (2001).
Casalbuoni, S., Schlarb, H., Schmidt, B., Schmüser, P., Steffen, B. & Winter, A. Numerical studies on the electro-optic detection of femtosecond electron bunches. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 11, 072802 (2008).
Higuchi, T., Tamaru, H. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M. Selection rules for angular momentum transfer via impulsive stimulated Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. A 87, 013808 (2013).
Weiner, A. M. Ultrafast Optics 112–118 (Wiley, 2009).
Cundiff, S. T. & Weiner, A. M. Optical arbitrary waveform generation. Nature Photon. 4, 760–766 (2010).
Baltuška, A., Fuji, T. & Kobayashi, T. Controlling the carrier-envelope phase of ultrashort light pulses with optical parametric amplifiers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 133901 (2002).
Weiner, A. M. Femtosecond pulse shaping using spatial light modulators. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 1929–1960 (2000).
Hoffmann, M. C., Yeh, K-L., Hebling, J. & Nelson, K. A. Efficient terahertz generation by optical rectification at 1035 nm. Opt. Express 15, 11706–11713 (2007).
Stobrawa, G. et al. A new high-resolution femtosecond pulse shaper. Appl. Phys. B 72, 627–630 (2001).
Kanda, N., Konishi, K. & Kuwata-Gonokami, M. Terahertz wave polarization rotation with double layered metal grating of complementary chiral patterns. Opt. Express 15, 11117–11125 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) in innovative area ‘Optical Science of Dynamically Correlated Electrons (DYCE, no. 2003)’ (20104002) and in priority area ‘Strong Photon–Molecule Coupling Fields (no. 470)’ (21020011) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT), by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) through its Funding Program for World-Leading Innovative R&D on Science and Technology (FIRST), the Photon Frontier Network Program (MEXT), and by the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology (MEXT). M.S., T.H. and N.K. acknowledge support from JSPS Research Fellowships. The authors thank Y. Svirko for his critical reading and suggestions about the manuscript, and thank the reviewers for providing comments that helped in improving the discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.S. and T.H. contributed equally to the work. All authors contributed to the design, data analysis and preparation of the manuscript. M.S. and N.K. performed all experiments at the University of Tokyo. M.S. and K.M. designed and developed the optical polarization shaper. T.H. and M.K-G. provided the theory for designing pulse shapes and terahertz generation. K.K. and T.S. gave technical support. K.Y. and M.K-G. provided experimental support. K.M. and M.K-G. planned and supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 872 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, M., Higuchi, T., Kanda, N. et al. Terahertz polarization pulse shaping with arbitrary field control. Nature Photon 7, 724–731 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.213
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.213
This article is cited by
-
A novel scheme for ultrashort terahertz pulse generation over a gapless wide spectral range: Raman-resonance-enhanced four-wave mixing
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Terahertz waveform synthesis in integrated thin-film lithium niobate platform
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Spintronic terahertz emission with manipulated polarization (STEMP)
Frontiers of Optoelectronics (2022)
-
Terahertz pulse shaping using diffractive surfaces
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Stokes–Mueller method for comprehensive characterization of coherent terahertz waves
Scientific Reports (2020)