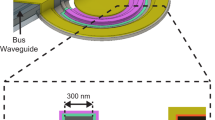
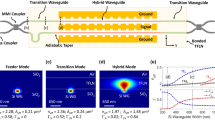
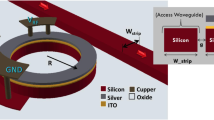
Abstract
Optical technology is poised to revolutionize short-reach interconnects. The leading candidate technology is silicon photonics, and the workhorse of such an interconnect is the optical modulator. Modulators have been improved dramatically in recent years, with a notable increase in bandwidth from the megahertz to the multigigahertz regime in just over half a decade. However, the demands of optical interconnects are significant, and many questions remain unanswered as to whether silicon can meet the required performance metrics. Minimizing metrics such as the device footprint and energy requirement per bit, while also maximizing bandwidth and modulation depth, is non-trivial. All of this must be achieved within an acceptable thermal tolerance and optical spectral width using CMOS-compatible fabrication processes. This Review discusses the techniques that have been (and will continue to be) used to implement silicon optical modulators, as well as providing an outlook for these devices and the candidate solutions of the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 August 2010
Ref. 86 was incorrectly cited in both the title and the last data row of Table 1. The correct citation is ref. 24, and this has been corrected for all versions of the article.
References
http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/∼awm22/publications/miller2009motivating.pdf
Miller, D. A. B. Rationale and challenges for optical interconnects to electronic chips. Proc. IEEE 88, 728–749 (2000).
Miller, D. Device requirements for optical interconnects to silicon chips. Proc. IEEE 97, 1166–1185 (2009).
Pepeljugoski, P. K. et al. Low power and high density optical interconnects for future supercomputers. Optical Fiber Communication Conf. paper OThX2 (2010).
Lee, B. G., Biberman, A., Chan, J. & Bergman, K. High-performance modulators and switches for silicon photonic networks-on-chip. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 16, 6–22 (2010).
Pollock, C. & Lipson, M. Integrated Photonics Ch. 12, 301–334 (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003).
Soref, R. & Bennett, B. Electrooptical effects in silicon. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 23, 123–129 (1987).
Reed, G. T. & Knights, A. P. Silicon Photonics: An Introduction Ch. 4, 97–103 (Wiley, 2004).
Cocorullo, G. & Rendina, I. Thermo-optical modulation at 1.5 μm in silicon etalon. Electron. Lett. 28, 83–85 (1992).
Reed, G. T. Silicon Photonics: The State of the Art Ch. 4, 95–145 (Wiley, 2008).
Liu, J. et al. Waveguide-integrated, ultralow-energy GeSi electro-absorption modulators. Nature Photon. 2, 433–437 (2008).
Kuo, Y.-H. et al. Strong quantum-confined Stark effect in germanium quantum-well structures on silicon. Nature 437, 1334–1336 (2005).
Roth, J. E. et al. Optical modulator on silicon employing germanium quantum wells. Opt. Express 15, 5851–5859 (2007).
Roth, J. E. et al. C-band side-entry Ge quantum-well electroabsorption modulator on SOI operating at 1 V swing. Electron. Lett. 44, 49–50 (2008).
Krishnamoorthy, A. V. et al. Potentials of group IV photonics interconnects for 'red-shift' computing applications. Proc. 4th IEEE Int. Conf. Group IV Photonics 1–3 (2007).
Barwicz, T. et al. Silicon photonics for compact, energy-efficient interconnects. J. Opt. Netw. 6, 63–73 (2007).
Yoo, S. J. B. Future prospects of silicon photonics in next generation communication and computing systems. Electron. Lett. 45, 584–588 (2009).
Alduino, A. & Paniccia, M. Wiring electronics with light. Nature Photon. 1, 153–155 (2007).
Green, W. M., Rooks, M. J., Sekaric, L. & Vlasov, Y. A. Ultra-compact, low RF power, 10 Gb/s silicon Mach–Zehnder modulator. Opt. Express 15, 17106–17113 (2007).
Helman, N. C. et al. Misalignment-tolerant surface-normal low-voltage modulator for optical interconnects. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 11, 338–342 (2005).
Xu, Q., Schmidt, B., Pradhan, S. & Lipson, M. Micrometre-scale silicon electro-optic modulator. Nature 435, 325–327 (2005).
Gardes, F. Y. et al. High-speed modulation of a compact silicon ring resonator based on a reverse-biased pn diode. Opt. Express 17, 21986–21991 (2009).
Dong, P. et al. Low Vpp, ultralow-energy, compact, high-speed silicon electro-optic modulator. Opt. Express 17, 22484–22490 (2009).
You, J.-B., Park, M., Park, J.-W. & Kim, G. 12.5 Gbps optical modulation of silicon racetrack resonator based on carrier-depletion in asymmetric p-n diode. Opt. Express 16, 18340–18344 (2008).
Watts, M. R., Trotter, D. C., Young, R. W. & Lentine, A. L. Ultralow power silicon microdisk modulators and switches. Proc. 5th IEEE Int. Conf. Group IV Photonics 4–6 (2008).
Vlasov, Y. Silicon photonics for next generation computing systems. Proc. 34th European Conf. Optical Communications paper Tu.1.A.1 (2008).
Gondarenko, A., Levy, J. S. & Lipson, M. High confinement micron-scale silicon nitride high Q ring resonator. Opt. Express 17, 11366–11370 (2009).
Holzwarth, C. W. et al. Accurate resonant frequency spacing of microring filters without postfabrication trimming. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 24, 3244–3247 (2006).
Teng, J. et al. Athermal silicon-on-insulator ring resonators by overlaying a polymer cladding on narrowed waveguides. Opt. Express 17, 14627–14633 (2009).
Ye, W. N., Michel, J. & Kimerling, L. C. Athermal high-index-contrast waveguide design. IEEE Photon. Tech. Lett. 20, 885–887 (2008).
Xu, Q., Fattal, D. & Beausoleil, R. G. Silicon microring resonators with 1.5-μm radius. Opt. Express 16, 4309–4315 (2008).
Xiao, S., Khan, M. H., Shen, H. & Qi, M. A highly compact third-order silicon microring add-drop filter with a very large free spectral range, a flat passband and a low delay dispersion. Opt. Express 15, 14765–14771 (2007).
Xia, F., Rooks, M., Sekaric, L. & Vlasov, Y. Ultra-compact high order ring resonator filters using submicron silicon photonic wires for on-chip optical interconnects. Opt. Express 15, 11934–11941 (2007).
Manipatruni, S. et al. Wide temperature range operation of micrometer-scale silicon electro-optic modulators. Opt. Lett. 33, 2185–2187 (2008).
Lee, J.-M. et al. Controlling temperature dependence of silicon waveguide using slot structure. Opt. Express 16, 1645–1652 (2008).
Vlasov, Y., Green, W. M. J. & Xia, F. High-throughput silicon nanophotonic wavelength-insensitive switch for on-chip optical networks. Nature Photon. 2, 242–246 (2008).
Guha, B., Kyotoku, B. B. C. & Lipson, M. CMOS-compatible athermal silicon microring resonators. Opt. Express 18, 3487–3493 (2010).
Liao, L. et al. 40 Gbit/s silicon optical modulator for high-speed applications. Electron. Lett. 43, 1196–1197 (2007).
Soref, R. A. & Bennett, B. R. Kramers–Kronig analysis of electro-optical switching in silicon. Proc. SPIE Integrated Optical Circuit Engineering IV 704, 32–37 (1987).
Lorenzo, J. P. & Soref, R. A. 1. 3 μm electro-optic silicon switch. Appl. Phys. Lett. 51, 6–8 (1987).
Friedman, L., Soref, R. A. & Lorenzo, J. P. Silicon double-injection electro-optic modulator with junction gate control. J. Appl. Phys. 63, 1831–1839 (1988).
Treyz, G. V. Silicon Mach–Zehnder waveguide interferometers operating at 1.3 μm. Electron. Lett. 27, 118–120 (1991).
Treyz, G. V., May, P. G. & Halbout, J.-M. Silicon optical modulators at 1.3-μm based on free-carrier absorption. IEEE Electr. Device Lett. 12, 276–278 (1991).
Jackson, S. M. et al. A novel optical phase modulator design suitable for phased arrays. J. Lightwave Technol. 16, 2016–2019 (1998).
Jackson, S. M. et al. Optical beamsteering using integrated optical modulators. J. Lightwave Technol. 15, 2259–2263 (1997).
Fischer, U., Schuppert, B. & Petermann, K. Integrated optical switches in silicon based on SiGe-waveguides. IEEE Photon. Tech. Lett. 5, 785–787 (1993).
Tang, C. K., Reed, G. T., Wilson, A. J. & Rickman, A. G. Low-loss, single-model optical phase modulator in SIMOX material. J. Lightwave Technol. 12, 1394–1400 (1994).
Tang, C. K., Reed, G. T., Wilson, A. J. & Rickman, A. G. Simulation of a low loss optical modulator for fabrication in SIMOX material. Proc. Symp. Mater. Res. Soc. 298, 247–252 (1993).
Tang, C. K. & Reed, G. T. Highly efficient optical phase modulator in SOI waveguides. Electron. Lett. 31, 451–452 (1995).
Cutolo, A., Iodice, M., Spirito, P. & Zeni, L. Silicon electro-optic modulator based on a three terminal device integrated in a low-loss single-mode SOI waveguide. J. Lightwave Technol. 15, 505–518 (1997).
Cutolo, A., Iodice, M., Irace, A., Spirito, P. & Zeni, L. An electrically controlled Bragg reflector integrated in a rib silicon on insulator waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 199–201 (1997).
Sciuto, A., Libertino, S., Alessandria, A., Coffa, S. & Coppola, G. Design, fabrication, and testing of an integrated Si-based light modulator. J. Lightwave Technol. 21, 228–235 (2003).
Hewitt, P. D. & Reed, G. T. Improving the response of optical phase modulators in SOI by computer simulation. J. Lightwave Technol. 18, 443–450 (2000).
Hewitt, P. D. & Reed, G. T. Multi micron dimension optical p-i-n modulators in silicon-on-insulator. Proc. SPIE 3630, 237–243 (1999).
Winney, T. et al. Single-chip variable optical attenuator and multiplexer subsystem integration. Optical Fiber Communication Conf. paper TuK4 (2002).
Dainesi, P. et al. CMOS compatible fully integrated Mach-Zehnder interferometer in SOI technology. IEEE Photon. Tech. Lett. 12, 660–662 (2000).
Png, C. E., Chan, S. P., Lim, S. T. & Reed, G. T. Optical phase modulators for MHz and GHz modulation in silicon-on-insulator (SOI). J. Lightwave Technol. 22, 1573–1582 (2004).
Barrios, C. A., Almeida, V. R., Panepucci, R. & Lipson, M. Electrooptic modulation of silicon-on-insulator submicrometer-size waveguide devices. J. Lightwave Technol. 21, 2332–2339 (2003).
Liu, A. et al. A high-speed silicon optical modulator based on a metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitor. Nature 427, 615–618 (2004).
Liao, L. et al. High speed silicon Mach-Zehnder modulator. Opt. Express 13, 3129–3135 (2005).
Kajikawa, K., Tabei, T. & Sunami, H. An infrared silicon optical modulator of metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitor based on accumulation-carrier absorption. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 04C107 (2009).
http://www.ofcnfoec.org/conference_program/2009/images/09-DAndrea.pdf
Gardes, F. Y., Reed, G. T., Emerson, N. G. & Png, C. E. A sub-micron depletion-type photonic modulator in silicon on insulator. Opt. Express 13, 8845–8854 (2005).
Liu, A. et al. High-speed optical modulation based on carrier depletion in a silicon waveguide. Opt. Express 15, 660–668 (2007).
Marris-Morini, D. et al. Optical modulation by carrier depletion in a silicon PIN diode. Opt. Express 14, 10838–10843, (2006).
Gunn, C. CMOS photonics for high-speed interconnects. IEEE Micro 26, 58–66 (2006).
Park, J. W., You, J.-B., Kim, I. G. & Kim, G. High-modulation efficiency silicon Mach–Zehnder optical modulator based on carrier depletion in a PN Diode. Opt. Express 17, 15520–15524 (2009).
Narasimha, A. et al. An ultra low power CMOS photonics technology platform for H/S optoelectronic transceivers at less than $1 per Gbps. Optical Fiber Communication Conf. paper OMV4 (2010).
Liow, T.-Y. et al. Silicon modulators and germanium photodetectors on SOI: Monolithic integration, compatibility, and performance optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 16, 307–315 (2010).
Feng, N. N. et al. High speed carrier-depletion modulators with 1.4V-cm VπL integrated on 0.25μm silicon-on-insulator waveguides. Opt. Express 18, 7994–7999 (2010).
Gill, D. M. et al. Internal bandwidth equalization in a CMOS-compatible Si-ring modulator. IEEE Photon. Tech. Lett. 21, 200–202 (2009).
Spector, S. J. et al. High-speed silicon electro-optical modulator that can be operated in carrier depletion or carrier injection mode. Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics paper CFH4 (2008).
Manipatruni, S., Qianfan, X., Schmidt, B., Shakya, J. & Lipson, M. High speed carrier injection 18 Gb/s silicon micro-ring electro-optic modulator. IEEE Proc. Lasers and Electro-Optics Soc. 537–538 (2007).
Png, C. E. Silicon-on-insulator phase modulators. PhD thesis, Univ. Surrey (2004).
Soljacic, M. et al. Photonic-crystal slow-light enhancement of nonlinear phase sensitivity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19, 2052–2059 (2002).
Jiang, Y., Jiang, W., Gu, L., Chen, X. & Chen, R. T. 80-micron interaction length silicon photonic crystal waveguide modulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 221105 (2005).
Gu, L., Jiang, W., Chen, X., Wang, L. & Chen, R. T. High speed silicon photonic crystal waveguide modulator for low voltage operation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 071105 (2007).
Tanabe, T., Nishiguchi, K., Kuramochi, E. & Notomi, M. Low power and fast electro-optic silicon modulator with lateral p-i-n embedded photonic crystal nanocavity. Opt. Express 17, 22505–22513 (2009).
Chen, X., Chen, Y. S., Zhao, Y., Jiang, W. & Chen, R. T. Capacitor-embedded 0.54 pJ/bit silicon-slot photonic crystal waveguide modulator. Opt. Lett. 34, 602–604 (2009).
Li, J., White, T. P., O'Faolain, L., Gomez-Iglesias, A. & Krauss, T. F. Systematic design of flat band slow light in photonic crystal waveguides. Opt. Express 16, 6227–6232 (2008).
Brimont, A., Sanchis, P. & Marti, J. Strong electro-optical modulation enhancement in a slow wave corrugated waveguide. Opt. Express 17, 9204–9211 (2009).
Chen, L., Preston, K., Manipatruni, S. & Lipson, M. Integrated GHz silicon photonic interconnect with micrometer-scale modulators and detectors. Opt. Express 17, 15248–15256 (2009).
Batten, C. et al. Building manycore processor-to-DRAM networks with monolithic silicon photonics. 16th IEEE Symp. High Performance Interconnects 21–30 (2008).
Stojanovic, V., Joshi, A., Batten, C., Yong-jin, K. & Asanovic, K. Manycore processor networks with monolithic integrated CMOS photonics. Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics/Int. Quantum Electronics Conf. paper CTuC3 (2009).
Zheng, X. et al. Ultra-low-energy all-CMOS modulator integrated with driver. Opt. Express 18, 3059–3070 (2010).
Liu, L. et al. Carrier-injection-based electro-optic modulator on silicon-on-insulator with a heterogeneously integrated III–V microdisk cavity. Opt. Lett. 33, 2518–2520 (2008).
Kuo, Y.-H., Chen, H.-W. & Bowers, J. E. High speed hybrid silicon evanescent electroabsorption modulator. Opt. Express 16, 9936–9941 (2008).
Chen, H.-W., Kuo, Y. H. & Bowers, J. E. 25Gb/s hybrid silicon switch using a capacitively loaded traveling wave electrode. Opt. Express 18, 1070–1075 (2010).
Hochberg, M. et al. Terahertz all-optical modulation in a silicon-polymer hybrid system. Nature Mater. 5, 703–709 (2006).
Rong, Y. et al. Quantum-confined Stark effect in Ge/SiGe quantum wells on Si. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 16, 85–92 (2010).
Liu, J. et al. Design of monolithically integrated GeSi electro-absorption modulators and photodetectors on an SOI platform. Opt. Express 15, 623–628 (2007).
Preston, K., Manipatruni, S., Gondarenko, A., Poitras, C. B. & Lipson, M. Deposited silicon high-speed integrated electro-optic modulator. Opt. Express 17, 5118–5124 (2009).
Della Corte, F. G., Rao, S., Nigro, M. A., Suriano, F. & Summonte, C. Electro-optically induced absorption in α-Si:H/α-SiCN waveguiding multistacks. Opt. Express 16, 7540–7550 (2008).
Jacobsen, R. S. et al. Strained silicon as a new electro-optic material. Nature 441, 199–202 (2006).
Hon, N. K., Tsia, K. K., Solli, D. R., Jalali, B. & Khurgin, J. B. Stress-induced χ(2) in silicon — comparison between theoretical and experimental values. Proc. 6th IEEE Int. Conf. Group IV Photonics 232–234 (2009).
Xu, Q., Manipatruni, S., Schmidt, B., Shakya, J. & Lipson, M. 12.5 Gbit/s carrier-injection-based silicon micro-ring silicon modulators. Opt. Express 15, 430–436 (2007).
Liao, L. High speed silicon-on-insulator modulators based on the free carrier plasma dispersion effect. PhD thesis, Univ. Surrey (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, G., Mashanovich, G., Gardes, F. et al. Silicon optical modulators. Nature Photon 4, 518–526 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.179
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.179
This article is cited by
-
Ultra-compact exciton polariton modulator based on van der Waals semiconductors
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A 5 × 200 Gbps microring modulator silicon chip empowered by two-segment Z-shape junctions
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Graphene/Al2O3/Si Schottky diode with integrated waveguide on a silicon-on-insulator wafer
Indian Journal of Physics (2024)
-
Graphene-based hybrid plasmonic optical electro-absorption modulator on InP platform
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2024)
-
Graphene oxide for photonics, electronics and optoelectronics
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2023)