Abstract
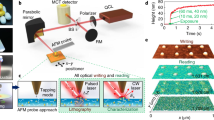
Nanophotonic devices are designed to generate, guide or detect light using structures with nanoscale dimensions that are closely tied to their functionality1,2,3,4. However, the integration of photonic nanostructures with electronic circuitry5 remains one of the most challenging aspects of device development. Here we report the development of rewritable nanoscale photodetectors created at the interface between LaAlO3 and SrTiO3. Nanowire junctions with characteristic dimensions of 2–3 nm are created using a reversible conductive atomic force microscope writing technique6,7. These nanoscale devices exhibit remarkably high gain for their size, in part because of the large electric fields produced in the gap region. The photoconductive response is electric field-tunable and spans the visible-to-near-infrared regime. The ability to integrate rewritable nanoscale photodetectors with nanowires and transistors in a single material platform foreshadows new families of integrated optoelectronic devices and applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J., Gudiksen, M. S., Duan, X., Cui, Y. & Lieber, C. M. Highly polarized photoluminescence and photodetection from single indium phosphide nanowires. Science 293, 1455–1457 (2001).
Sirbuly, D. J., Law, M., Yan, H. & Yang, P. Semiconductor nanowires for subwavelength photonics integration. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 15190–15213 (2005).
Agarwal, R. & Lieber, C. M. Semiconductor nanowires: optics and optoelectronics. Appl. Phys. A 85, 209–215 (2006).
Tian, B. et al. Coaxial silicon nanowires as solar cells and nanoelectronic power sources. Nature 449, 885–889 (2007).
Fan, Z., Ho, J. C., Jacobson, Z. A., Razavi, H. & Javey, A. Large-scale, heterogeneous integration of nanowire arrays for image sensor circuitry. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 11066–11070 (2008).
Cen, C. et al. Nanoscale control of an interfacial metal–insulator transition at room temperature. Nature Mater. 7, 298–302 (2008).
Cen, C., Thiel, S., Mannhart, J. & Levy, J. Oxide nanoelectronics on demand. Science 323, 1026–1030 (2009).
Ohtomo, A. & Hwang, H. Y. A high-mobility electron gas at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterointerface. Nature 427, 423–426 (2004).
Mannhart, J., Blank, D., Hwang, H., Millis, A. & Triscone, J.-M. Two-dimensional electron gases at oxide interfaces. MRS Bull. 33, 1027–1034 (2008).
Thiel, S., Hammerl, G., Schmehl, A., Schneider, C. W. & Mannhart, J. Tunable quasi-two-dimensional electron gases in oxide heterostructures. Science 313, 1942–1945 (2006).
Bogorin, D. F. et al. Nanoscale rectification at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 013102 (2010).
Kawasaki, M. et al. Atomic control of the SrTiO3 crystal surface. Science 266, 1540–1542 (1994).
Balasubramanian, K., Burghard, M., Kern, K., Scolari, M. & Mews, A. Photocurrent imaging of charge transport barriers in carbon nanotube devices. Nano Lett. 5, 507–510 (2005).
Xia, F. et al. Photocurrent imaging and efficient photon detection in a graphene transistor. Nano Lett. 9, 1039–1044 (2009).
Dudley, J. M., Genty, G. & Coen, S. Supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fiber. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1135–1184 (2006).
Stöckmann, F. Superlinear photoconductivity. Phys. Status Solidi 34, 751–757 (1969).
Prezioso, S. et al. Superlinear photovoltaic effect in Si nanocrystals based metal–insulator–semiconductor devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 062108 (2009).
van Benthem, K., Elsasser, C. & French, R. H. Bulk electronic structure of SrTiO3: experiment and theory. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 6156–6164 (2001).
Grabner, L. Photoluminescence in SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. 177, 1315–1323 (1969).
Leonelli, R. & Brebner, J. L. Time-resolved spectroscopy of the visible emission band in strontium titanate. Phys. Rev. B 33, 8649–8656 (1986).
Okamura, H. et al. Photogenerated carriers in SrTiO3 probed by mid-infrared absorption. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 75, 023703 (2006).
Kareev, M. et al. Atomic control and characterization of surface defect states of TiO2 terminated SrTiO3 single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 061909 (2008).
Zhang, J., Walsh, S., Brooks, C., Schlom, D. G. & Brillson, L. J. Depth-resolved cathodoluminescence spectroscopy study of defects in SrTiO3 . J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 26, 1466–1471 (2008).
Herranz, G. et al. High mobility in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures: origin, dimensionality, and perspectives. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 216803 (2007).
Kalabukhov, A. et al. Effect of oxygen vacancies in the SrTiO3 substrate on the electrical properties of the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Phys. Rev. B 75, 121404 (2007).
Basletic, M. et al. Mapping the spatial distribution of charge carriers in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures. Nature Mater. 7, 621–625 (2008).
Seo, S. S. A. et al. Multiple conducting carriers generated in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 082107 (2009).
Shibuya, K., Ohnishi, T., Sato, T. & Lippmaa, M. Metal–insulator transition in SrTiO3 induced by field effect. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 083713 (2007).
Feng, T. Anomalous photoelectronic processes in SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. B 25, 627–642 (1982).
Cui, Y., Wei, Q., Park, H. & Lieber, C. M. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 293, 1289–1292 (2001).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (W911N3-09-10258) (J.L.), the Fine Foundation (J.L.) and the National Science Foundation through grants DMR-0704022 (J.L.) and DMR-0906443 (C.-B.E).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.I. and J.L. conceived the study. C.W.B., C.M.F. and C.-B.E. supplied materials. P.I., Y.M., D.F.B. and C.C. performed c-AFM lithography. P.I. and Y.M. performed the optical experiments and analysed data. C.C. performed finite element analysis. P.I. and J.L. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irvin, P., Ma, Y., Bogorin, D. et al. Rewritable nanoscale oxide photodetector. Nature Photon 4, 849–852 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.238
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2010.238
This article is cited by
-
A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Transition from a uni- to a bimodal interfacial charge distribution in \(\hbox {LaAlO}_3\)/\(\hbox {SrTiO}_3\) upon cooling
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Band offset determination of p-NiO/n-TiO2 heterojunctions for applications in high-performance UV photodetectors
Journal of Materials Science (2020)
-
Over 100-THz bandwidth selective difference frequency generation at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanojunctions
Light: Science & Applications (2019)
-
Optimized Growth of Gallium Oxide Thin Films Using Different Synthesis Processes
Journal of Electronic Materials (2019)