Abstract
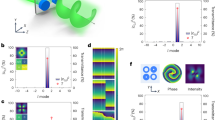
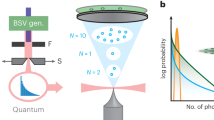
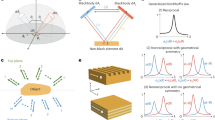
Recent theoretical work on random lasing predicts that the occurrence of narrow lasing spikes can be caused by both localized and extended modes of light1,2,3. Typical random lasing spikes have been observed in powders of zinc oxide nanoparticles4, but identifying the possible degrees of localization of such modes has until now been an open issue5. In this Letter we present an experimental procedure that directly extracts the area of localization of the modes. This method relies on the investigation of micro-structured fields of zinc oxide powder, which also allows direct correlation to the local structural properties of the ensemble of subwavelength particles by scanning electron microscopy. We find that lasing from both localized and extended modes can be observed simultaneously. Our observation also corroborates the prediction that localized modes have a lower loss rate than that of extended modes5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vanneste, C. & Sebbah, P. Selective excitation of localized modes in active random media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 183903 (2001).
Mujumdar, S., Ricci, M., Torre, R. & Wiersma, D. S. Amplified extended modes in random lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 053903 (2004).
Vanneste, C., Sebbah, P. & Cao, H. Lasing with resonant feedback in weakly scattering random systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 143902 (2007).
Cao, H. et al. Random laser action in semiconductor powder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 2278–2281 (1999).
Wiersma, D. S. The physics and applications of random lasers. Nature Phys. 4, 359–367 (2008).
Wiersma, D. S., Bartolini, P., Lagendijk, A. & Righini, R. Localization of light in a disordered medium. Nature 390, 671–673 (1997).
John, S. Strong localization of photons in certain disordered dielectric superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2486–2489 (1987).
Cao, H. in Waves Random Media 13, R1–R39 (2003).
Klingshirn, C. ZnO: From basics towards applications. Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 244, 3027–3073 (2007).
Markushev, V. M., Ryzhkov, M. V. & Briskina, C. M. Characteristic properties of ZnO random laser pumped by nanosecond pulses. Appl. Phys. B 84, 333–337 (2006).
Anderson, P. W. Absence of diffusion in certain random lattices. Phys. Rev. 109, 1492–1505 (1958).
Türeci, H. E., Ge, L., Rotter, S. & Stone, A. D. Strong interactions in multimode random lasers. Science 320, 643–646 (2008).
van der Molen, K. L., Tjerkstra, R. W., Mosk, A. P. & Lagendijk, A. Spatial extent of random laser modes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 143901 (2007).
Fallert, J. et al. Lasing dynamics in single ZnO nanorods. Opt. Express 16, 1125–1131 (2008).
Anglos, D. et al. Random laser action in organic–inorganic nanocomposites. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21, 208–213 (2004).
Aegerter, C. M., Störzer, M., Fiebig, S., Bührer, W. & Maret, G. Observation of Anderson localization of light in three dimensions. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 24, 23–27 (2007).
Apalkov, V. M., Raikh, M. E. & Shapiro, B. Random resonators and prelocalized modes in disordered dielectric films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 016802 (2002).
Fallert, J. et al. Lasing in single ZnO nanorods after fs- and ns-pulsed excitation. Phys. Stat. Sol. (c) 6, 449–452 (2009).
Fallert, J. et al. Random lasing in ZnO nanocrystals. J. Luminescence in the press (2009).
Fallert, J. et al. Surface-state related luminescence in ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 073506 (2007).
Hauser, M. et al. Absolute external luminescence quantum efficiency of zinc oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 211105 (2008).
Wu, X. H. et al. Random lasing in closely packed resonant scatterers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21, 159–167 (2004).
John, S. Electromagnetic absorption in a disordered medium near a photon mobility edge. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 2169–2172 (1984).
Yoshikawa, H. & Adachi, S. Optical constants of ZnO. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 6237–6243 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG) in the framework of project KL345/23-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to this paper and agree to its contents.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallert, J., Dietz, R., Sartor, J. et al. Co-existence of strongly and weakly localized random laser modes. Nature Photon 3, 279–282 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.67
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2009.67
This article is cited by
-
Random lasing and amplified spontaneous emission from silk inverse opals: Optical gain enhancement via protein scatterers
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Determining random lasing action
Nature Reviews Physics (2019)
-
Random lasing in an Anderson localizing optical fiber
Light: Science & Applications (2017)
-
Temporal profiles for measuring threshold of random lasers pumped by ns pulses
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Lasing from ZnO Nanocrystals in ZnO-ZnS Microbelts
Journal of Electronic Materials (2017)