Abstract
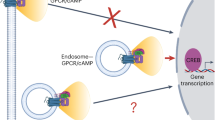
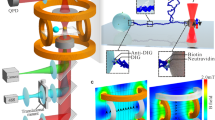
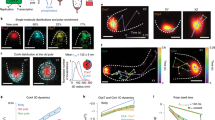
Many cell functions rely on the coordinated activity of signalling pathways at a subcellular scale1,2. However, there are few tools capable of probing and perturbing signalling networks with a spatial resolution matching the intracellular dimensions of their activity patterns. Here we present a generic magnetogenetic approach based on the self-assembly of signalling complexes on the surface of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles inside living cells. The nanoparticles act as nanoscopic hot spots that can be displaced by magnetic forces and trigger signal transduction pathways that bring about a cell response. We applied this strategy to Rho-GTPases, a set of molecular switches known to regulate cell morphology via complex spatiotemporal patterns of activity3,4. We demonstrate that the nanoparticle-mediated activation of signalling pathways leads to local remodelling of the actin cytoskeleton and to morphological changes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott, J. D. & Pawson, T. Cell signalling in space and time: where proteins come together and when they're apart. Science 326, 1220–1224 (2009).
Dehmelt, L. & Bastiaens, P. I. Spatial organization of intracellular communication: insights from imaging. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 440–452 (2010).
Machacek, M. et al. Coordination of Rho GTPase activities during cell protrusion. Nature 461, 99–103 (2009).
Pertz, O. Spatio-temporal Rho GTPase signalling—where are we now? J. Cell Sci. 123, 1841–1850 (2010).
Vartak, N. & Bastiaens, P. Spatial cycles in G-protein crowd control. EMBO J. 29, 2689–2699 (2010).
Mayer, G. & Heckel, A. Biologically active molecules with a ‘light switch'. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 4900–4921 (2006).
Umeda, N., Ueno, T., Pohlmeyer, C., Nagano, T. & Inoue, T. A photocleavable rapamycin conjugate for spatiotemporal control of small GTPase activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 12–14 (2011).
Wu, Y. I. et al. A genetically encoded photoactivatable Rac controls the motility of living cells. Nature 461, 104–108 (2009).
Levskaya, A., Weiner, O. D., Lim, W. A. & Voigt, C. A. Spatiotemporal control of cell signalling using a light-switchable protein interaction. Nature 461, 997–1001 (2009).
Jun, Y. W., Seo, J. W. & Cheon, J. Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 179–189 (2008).
Desprat, N., Supatto, W., Pouille, P. A., Beaurepaire, E. & Farge, E. Tissue deformation modulates twist expression to determine anterior midgut differentiation in Drosophila embryos. Dev. Cell 15, 470–477 (2008).
Weber, G. F., Bjerke, M. A. & DeSimone, D. W. A mechanoresponsive cadherin–keratin complex directs polarized protrusive behavior and collective cell migration. Dev. Cell 22, 104–115 (2012).
Mannix, R. J. et al. Nanomagnetic actuation of receptor-mediated signal transduction. Nature Nanotech. 3, 36–40 (2008).
Cho, M. H. et al. A magnetic switch for the control of cell death signalling in in vitro and in vivo systems. Nature Mater. 11, 1038–1043 (2012).
Steketee, M. B. et al. Nanoparticle-mediated signalling endosome localization regulates growth cone motility and neurite growth. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 19042–19047 (2011).
Huang, H., Delikanli, S., Zeng, H., Ferkey, D. M. & Pralle, A. Remote control of ion channels and neurons through magnetic-field heating of nanoparticles. Nature Nanotech. 5, 602–606 (2010).
De Vries, A. H., Krenn, B. E., van Driel, R., Subramaniam, V. & Kanger, J. S. Direct observation of nanomechanical properties of chromatin in living cells. Nano Lett. 7, 1424–1427 (2007).
Bausch, A. R., Moller, W. & Sackmann, E. Measurement of local viscoelasticity and forces in living cells by magnetic tweezers. Biophys. J. 76, 573–579 (1999).
Hendricks, A. G., Holzbaur, E. L. & Goldman, Y. E. Force measurements on cargoes in living cells reveal collective dynamics of microtubule motors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 18447–18452 (2012).
Wirtz, D. Particle-tracking microrheology of living cells: principles and applications. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 38, 301–326 (2009).
Los, G. V. et al. HaloTag: a novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 3, 373–382 (2008).
Lisse, D., Wilkens, V., You, C., Busch, K. & Piehler, J. Selective targeting of fluorescent nanoparticles to proteins inside live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 9352–9355 (2011).
Etienne-Manneville, S. & Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420, 629–635 (2002).
Rohatgi, R. et al. The interaction between N-WASP and the Arp2/3 complex links Cdc42-dependent signals to actin assembly. Cell 97, 221–231 (1999).
Rudolph, M. G. et al. Thermodynamics of Ras/effector and Cdc42/effector interactions probed by isothermal titration calorimetry. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 23914–23921 (2001).
Van der Gucht, J., Paluch, E., Plastino, J. & Sykes, C. Stress release drives symmetry breaking for actin-based movement. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7847–7852 (2005).
Michiels, F. et al. Regulated membrane localization of Tiam1, mediated by the NH2-terminal pleckstrin homology domain, is required for Rac-dependent membrane ruffling and C-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation. J. Cell Biol. 137, 387–398 (1997).
Aoki, K. & Matsuda, M. Visualization of small GTPase activity with fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors. Nature Protoc. 4, 1623–1631 (2009).
Riedl, J. et al. Lifeact: a versatile marker to visualize F-actin. Nature Methods 5, 605–607 (2008).
Hahne, P., Sechi, A., Benesch, S. & Small, J. V. Scar/WAVE is localised at the tips of protruding lamellipodia in living cells. FEBS Lett. 492, 215–220 (2001).
Tseng, P., Judy, J. W. & Di Carlo, D. Magnetic nanoparticle-mediated massively parallel mechanical modulation of single-cell behavior. Nature Methods 9, 1113–1119 (2012).
Serge, A., Bertaux, N., Rigneault, H. & Marguet, D. Dynamic multiple-target tracing to probe spatiotemporal cartography of cell membranes. Nature Methods 5, 687–694 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank B. Mueller and M. Warntjen for their contributions to the initial stage of this project, O. Chen and M. Bawendi for useful discussions on magnetic nanoparticles, D. Lévy for his help with electron microscopy and P.F. Lenne for a critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program (grant no. RGP0005/2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.E., D.L.,Y.B., J.P., M.C. and M.D. conceived the project and designed the experiments. F.E., D.L. and M.C. acquired and analysed the data. F.E., J.P., M.C. and M.D. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2303 kb)
Supplementary movie S1
Supplementary movie S1 (AVI 3804 kb)
Supplementary movie S2
Supplementary movie S2 (AVI 7666 kb)
Supplementary movie S3
Supplementary movie S3 (AVI 440 kb)
Supplementary movie S4
Supplementary movie S4 (AVI 6459 kb)
Supplementary movie S5
Supplementary movie S5 (AVI 3483 kb)
Supplementary movie S6
Supplementary movie S6 (AVI 7734 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etoc, F., Lisse, D., Bellaiche, Y. et al. Subcellular control of Rac-GTPase signalling by magnetogenetic manipulation inside living cells. Nature Nanotech 8, 193–198 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2013.23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2013.23
This article is cited by
-
A comprehensive approach to characterize navigation instruments for magnetic guidance in biological systems
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Acoustic and Magnetic Stimuli-Based Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Platform for Tissue Engineering
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2023)
-
Kinetics of phagosome maturation is coupled to their intracellular motility
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Transient cell stiffening triggered by magnetic nanoparticle exposure
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2021)
-
Magnetic spatiotemporal control of SOS1 coupled nanoparticles for guided neurite growth in dopaminergic single cells
Scientific Reports (2020)