Abstract
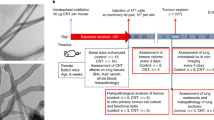
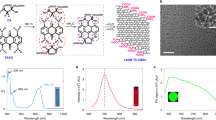
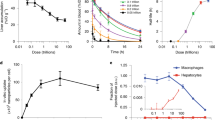
Single-walled carbon nanotubes are currently under evaluation in biomedical applications, including in vivo delivery1,2,3 of drugs4, proteins, peptides5,6,7 and nucleic acids8,9 (for gene transfer10 or gene silencing11), in vivo tumour imaging12 and tumour targeting of single-walled carbon nanotubes as an anti-neoplastic treatment5. However, concerns about the potential toxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes have been raised13,14. Here we examine the acute and chronic toxicity of functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes when injected into the bloodstream of mice. Survival, clinical and laboratory parameters reveal no evidence of toxicity over 4 months. Upon killing, careful necropsy and tissue histology show age-related changes only. Histology and Raman microscopic mapping demonstrate that functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes persisted within liver and spleen macrophages for 4 months without apparent toxicity. Although this is a preliminary study with a small group of animals, our results encourage further confirmation studies with larger groups of animals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianco, A. et al. Biomedical applications of functionalised carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 571–577 (2005).
Bianco, A., Kostarelos, K. & Prato, M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 9, 674–679 (2005).
Klumpp, C. et al. Functionalized carbon nanotubes as emerging nanovectors for the delivery of therapeutics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1758, 404–412 (2006).
Wu, W. et al. Targeted delivery of amphotericin B to cells by using functionalized carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn 44, 6358–6362 (2005).
Kam, N. W. et al. Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 11600–11605 (2005).
Kam, N. W., Liu, Z. & Dai, H. Carbon nanotubes as intracellular transporters for proteins and DNA: an investigation of the uptake mechanism and pathway. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn 45, 577–581 (2006).
Pantarotto, D. et al. Translocation of bioactive peptides across cell membranes by carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 16–17 (2004).
Pantarotto, D. et al. Functionalized carbon nanotubes for plasmid DNA gene delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn 43, 5242–5246 (2004).
Singh, R. et al. Binding and condensation of plasmid DNA onto functionalized carbon nanotubes: toward the construction of nanotube-based gene delivery vectors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 4388–4396 (2005).
Liu, Y. et al. Polyethylenimine-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes for secure noncovalent immobilization and efficient delivery of DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn 44, 4782–4785 (2005).
Kam, N. W., Liu, Z. & Dai, H. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes via cleavable disulfide bonds for efficient intracellular delivery of siRNA and potent gene silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 12492–12493 (2005).
Liu, Z. et al. In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nature Nanotech. 2, 47–52 (2007).
Lison, D. & Muller, J. Lung and systemic responses to carbon nanotubes (CNT) in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 101, 179–180 (2008).
Mitchell, L. A. et al. Pulmonary and systemic immune response to inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Toxicol. Sci. 100, 203–214 (2007).
Monteiro-Riviere, N. A. et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotube interactions with human epidermal keratinocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 155, 377–384 (2005).
Shvedova, A. A. et al. Exposure to carbon nanotube material: assessment of nanotube cytotoxicity using human keratinocyte cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 66, 1909–1926 (2003).
Cui, D. et al. Effect of single wall carbon nanotubes on human HEK293 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 155, 73–85 (2005).
Bottini, M. et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induce T lymphocyte apoptosis. Toxicol. Lett. 160, 121–126 (2006).
Kagan, V. E. et al. Direct and indirect effects of single walled carbon nanotubes on RAW 264.7 macrophages: Role of iron. Toxicol. Lett. 165, 88–100 (2006).
Tian, F. et al. Cytotoxicity of single-wall carbon nanotubes on human fibroblasts. Toxicol. In Vitro 20(7) 1202–1212 2006.
Sayes, C. M. et al. Functionalization density dependence of single-walled carbon nanotubes cytotoxicity in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 161, 135–142 (2006).
Magrez, A. et al. Cellular toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 6, 1121–1125 (2006).
Shvedova, A. A. et al. Unusual inflammatory and fibrogenic pulmonary responses to single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 289, L698–L708 (2005).
Lam, C. W. et al. Pulmonary toxicity of single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice 7 and 90 days after intratracheal instillation. Toxicol. Sci. 77, 126–134 (2004).
Warheit, D. B. et al. Comparative pulmonary toxicity assessment of single-wall carbon nanotubes in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 77, 117–125 (2004).
Radomski, A. et al. Nanoparticle-induced platelet aggregation and vascular thrombosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 146, 882–893 (2005).
Wang, H. et al. Biodistribution of carbon single-wall carbon nanotubes in mice. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4, 1019–1024 (2004).
Singh, R. et al. Tissue biodistribution and blood clearance rates of intravenously administered carbon nanotube radiotracers. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 3357–3362 (2006).
Cherukuri, P. et al. Near-infrared fluorescence microscopy of single-walled carbon nanotubes in phagocytic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 15638–15639 (2004).
Urch, B. et al. Acute blood pressure responses in healthy adults during controlled air pollution exposures. Environ. Health Perspect. 113, 1052–1055 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute Center for Cancer Nanotechnology Excellence (CCNE) U54 CA119367 (S.S.G.) and In vivo Cellular and Molecular Imaging Center (ICMIC) P50 CA114747 (S.S.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.L.S. and S.S.G. conceived and designed the experiments. M.L.S. performed the experiments. M.L.S. and S.S.G. analysed the data. N.N.R., C.R.D., N.W.S.K., P.C., Z.L., X.S. and H.D. contributed materials and analysis tools. M.L.S. and S.S.G. co-wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schipper, M., Nakayama-Ratchford, N., Davis, C. et al. A pilot toxicology study of single-walled carbon nanotubes in a small sample of mice. Nature Nanotech 3, 216–221 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.68
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.68
This article is cited by
-
Antibacterial and in vivo toxicological studies of Bi2O3/CuO/GO nanocomposite synthesized via cost effective methods
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Carbon-based heterogeneous photocatalysts for water cleaning technologies: a review
Environmental Chemistry Letters (2021)
-
Macrophage-targeted single walled carbon nanotubes stimulate phagocytosis via pH-dependent drug release
Nano Research (2021)
-
Pro-efferocytic nanoparticles are specifically taken up by lesional macrophages and prevent atherosclerosis
Nature Nanotechnology (2020)