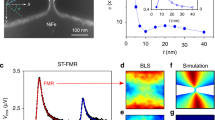
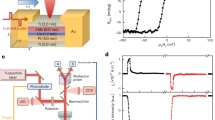
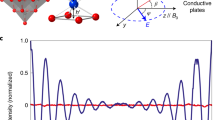
Abstract
Electrons and other fundamental particles have an intrinsic angular momentum called spin. A change in the spin state of such a particle is therefore equivalent to a mechanical torque. This spin-induced torque is central to our understanding of experiments1,2 ranging from the measurement of the angular momentum of photons3 and the g-factor of metals4,5,6,7 to magnetic resonance8 and magnetization reversal in magnetic multilayers8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15. When a spin-polarized current passes through a metallic nanowire in which one half is ferromagnetic and the other half is nonmagnetic, the spins of the itinerant electrons are ‘flipped’ at the interface between the two regions to produces a torque. Here, we report direct measurement of this mechanical torque in an integrated nanoscale torsion oscillator, and measurements of the itinerant electron spin polarization that could yield new information on the itinerancy of the d-band electrons. The unprecedented torque sensitivity of 1 × 10−22 N-m Hz−1/2 may have applications in spintronics and precision measurements of charge–parity-violating forces16,17, and might also enable experiments on the untwisting of DNA18 and torque-generating molecules19,20.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richardson, O. W. A mechanical effect accompanying magnetization. Phys. Rev. 26, 248–253 (1908).
Einstein, A. & de Hass, W. J. Experimenteller Nachweis der ampere'schen molekularstroeme. Verhandlungen der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft 17, 152–170 (1915).
Beth, R. A. Mechanical detection and measurement of the angular momentum of light. Phys. Rev. 50, 115–125 (1936).
Barnett, S. J. New researches in gyromagnetism. Phys. Rev. 66, 224–225 (1944).
Kittel, C. On the gyromagnetic ratio and spectroscopic splitting factor of ferromagnetic substances. Phys. Rev. 76, 743–748 (1949).
Scott, G. G. A precise mechanical measurement of the gyromagnetic ratio of iron. Phys. Rev. 82, 542–547 (1952).
Wallis, T. M., Moreland, J. & Kabos, P. Einstein-de Haas effect in a NiFe film deposited on a microcantilever. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 122502 (2006).
Ascoli, C. et al. Micromechanical detection of magnetic resonance by angular momentum absorption. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 3920–3922 (1996).
Slonczewski, J. C. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, L1–L7 (1996).
Berger, L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9353–9358 (1996).
Sun, J. Z. Current-driven magnetic switching in manganite trilayer junctions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 202, 157–162 (1999).
Myers, E. B., Ralph, D. C., Katine, J. A., Louie, R. N. & Buhrman, R. A. Current-induced switching of domains in magnetic multilayer devices. Science 285, 867–870 (1999).
Tsoi, M. et al. Generation and detection of phase-coherent current-driven magnons in magnetic multilayers. Nature 406, 46–48 (2000).
Wegrowe, J.-E. et al. Exchange torque and spin transfer between spin-polarized current and ferromagnetic layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3775–3777 (2002).
Stiles, M. D. & Zangwill, A. Anatomy of spin-transfer torque. Phys. Rev. B 65, 014407 (2002).
Pospelov, M. & Romanis, M. Lorentz invariance on trial. Physics Today 40, 40–46 (July 2004).
Heckel, B. R. et al. New CP-violation and preferred-frame tests with polarized electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 021603 (2006).
Bryant, Z. et al. Structural transitions and elasticity from torque measurements on DNA, Nature 424, 338–341 (2003).
Noji, H., Yasuda, R., Yoshida, M. & Kinosita, K. Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature 386, 299–302 (1997).
Ryu, W. S., Berry, R. M. & Berg, H. C. Torque-generating units of the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli have a high duty ratio. Nature 403, 444–447 (2000).
Johnson, M. & Silsbee, R. H. Thermodynamic analysis of interfacial transport and of the thermomagnetoelectric system. Phys. Rev. B 35, 4959–4972 (1987).
Johnson, M. & Silsbee, R. H. Coupling of electronic charge and spin at a ferromagnetic–paramagnetic metal interface. Phys. Rev. B 37, 5312–5325 (1988).
Fabian, J. & Das Sarma, S. Spin relaxation of conduction electrons. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 17, 1708–1715 (1999).
Mohanty, P., Zolfagharkhani, G., Kettemann, S. & Fulde, P. Spin-mechanical torsion device for detection and control of spin by nanomechanical torque. Phys. Rev. B 70, 195301 (2004).
Kovalev, A. A., Bauer, G. E. W. & Brataas, A. Current-driven ferromagnetic resonance, mechanical torques and rotary motion in magnetic nanostructures. Phys. Rev. B 75, 014430 (2007).
Fulde, P. & Kettemann, S. Spin-flip torsion balance. Ann. Phys. 7, 214–216 (1998).
Upadhyay, S. K., Palanisami, A., Louie, R. N. & Buhrman, R. A. Probing ferromagnets with Andreev reflection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3247–3250 (1998).
Soulen, R. J. et al. Measuring the spin polarization of a metal with a superconducting point contact. Science 282, 85–88 (1998).
Volpe, G. & Petrov, D. Torque detection using brownian fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 210603 (2006).
Weiss, P. Magnetic overthrow. Science News 169, 11–13 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This work was primarily supported by the National Science Foundation (Division of Material Research (DMR)-0346707) under the NSF-European Community (EC) Cooperative Activity in Materials Research (Material World Network). S.K. acknowledges support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (Sonderforschungsbereich (SFB)668 B3 and DFG SFB508 B9). P.D. acknowledges support from the Condensed Matter Theory visitors program at Boston University, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique/Direction des Relations Internationales (CNRS/DREI) (contract no. 4024) and Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR)-PNANO Quspin. The authors thank M. Johnson, I. Zutic, T. Wehling, J. Wei, L. Saminadayar, C. Bäuerle and C. Chamon for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 173 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zolfagharkhani, G., Gaidarzhy, A., Degiovanni, P. et al. Nanomechanical detection of itinerant electron spin flip. Nature Nanotech 3, 720–723 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.311
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.311
This article is cited by
-
Giant spin hydrodynamic generation in laminar flow
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Spin Seebeck mechanical force
Nature Communications (2019)
-
A new twist on phonons
Nature Physics (2018)
-
Spin conversion on the nanoscale
Nature Physics (2017)
-
High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
Nature Communications (2015)