Abstract
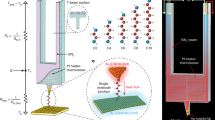
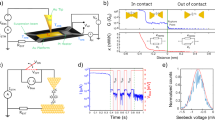
A basic aim in molecular electronics is to understand transport through a single molecule connected to two electrodes. Substantial progress towards this goal has been made over the past decade as a result of advances in both experimental techniques and theoretical methods1,2,3. Nonetheless, a fundamental and technologically important issue, current-induced local heating of molecules4,5,6,7,8, has received much less attention. Here, we report on a combined experimental and theoretical study of local heating in single molecules (6-, 8- and 10-alkanedithiol) covalently attached to two gold electrodes as a function of applied bias and molecular length. We find that the effective local temperature of the molecular junction first increases with applied bias, and then decreases after reaching a maximum. At fixed bias, the effective temperature decreases with increasing molecular length. These experimental findings are in agreement with hydrodynamic predictions, which include both electron–phonon and electron–electron interactions7,9.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindsay, S. M. & Ratner, M. A. Molecular transport junctions: Clearing mists. Adv. Mater. 19, 23–31 (2007).
Tao, N. J. Electron transport in molecular junctions. Nature Nanotechnol. 1, 173–181 (2006).
Selzer, Y. & Allara, D. L. Single-molecule electrical junctions. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 57, 593–623 (2006).
Todorov, T. N. Local heating in ballistic atomic-scale contacts. Phil. Mag. B 77, 965–973 (1998).
Segal, D. & Nitzan, A. Heating in current carrying molecular junctions. J. Chem. Phys. 117, 3915–3927 (2002).
Chen, Y. C., Zwolak, M. & Di Ventra, M. Local heating in nanoscale conductors. Nano Lett. 3, 1691–1694 (2003).
D'Agosta, R., Sai, N. & Di Ventra, M. Local electron heating in nanoscale conductors. Nano Lett. 6, 2935–2938 (2006).
Huang, Z. F., Xu, B. Q., Chen, Y. C., Di Ventra, M. & Tao, N. J. Measurement of current-induced local heating in a single molecule junction. Nano Lett. 6, 1240–1244 (2006).
D'Agosta, R. & Di Ventra, M. Hydrodynamic approach to transport and turbulence in nanoscale conductors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 18, 11059–11065 (2006).
Bechtold, T., Rudnyi, E. B. & Korvink, J. G. Dynamic electro-thermal simulation of microsystems—a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, R17–R31 (2005).
Solomon, G. C. et al. Understanding the inelastic electron-tunneling spectra of alkanedithiols on gold. J. Chem. Phys. 124, 094704 (2006).
Wang, W. Y., Lee, T., Kretzschmar, I. & Reed, M. A. Inelastic electron tunneling spectroscopy of an alkanedithiol self-assembled monolayer. Nano Lett. 4, 643–646 (2004).
Kushmerick, J. G. et al. Vibronic contributions to charge transport across molecular junctions. Nano Lett. 4, 639–642 (2004).
Kaun, C. C. & Seideman, T. Current-driven oscillations and time-dependent transport in nanojunctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 226801 (2005).
Kaun, C. C., Jorn, R. & Seideman, T. Spontaneous oscillation of current in fullerene molecular junctions. Phys. Rev. B 74, 045415 (2006).
Di Ventra, M., Pantelides, S.T. & Lang, N. D. Current-induced forces in molecular wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 046801 (2002).
Xu, B. Q., Xiao, X. Y. & Tao, N. J. Measurements of single-molecule electromechanical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 16164–16165 (2003).
Evans, E. Probing the relation between force, lifetime and chemistry in single molecular bonds. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 30, 105–128 (2001).
Tsutsui, M., Kurokawa, S. & Sakai, A. Bias-induced local heating in atom-sized metal contacts at 77 K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 133121 (2007).
Li, X. et al. Conductance of single alkanedithiols: Conduction mechanism and effect of molecule–electrode contacts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 2135–2141 (2006).
Xu, B. Q. & Tao, N. J. J. Measurement of single-molecule resistance by repeated formation of molecular junctions. Science 301, 1221–1223 (2003).
Xiao, X. Y., Nagahara, L. A., Rawlett, A. M. & Tao, N. J. Electrochemical gate-controlled conductance of single oligo(phenylene ethynylene)s. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9235–9240 (2005).
Evans, E. & Ritchie, K. Dynamic strength of molecular adhesion bonds. Biophys. J. 72, 1541–1555 (1997).
Evans, E. Energy landscapes of biomolecular adhesion and receptor anchoring at interfaces explored with dynamic force spectroscopy. Faraday Discussions 111, 1–16 (1998).
Rubio-Bollinger, G., Bahn, S. R., Agrait, N., Jacobsen, K. W. & Vieira, S. Mechanical properties and formation mechanisms of a wire of single gold atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 026101 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank the US National Science Foundation (ECS0304682, Z.F.H.), the US Department of Energy (DE-FG03-01ER45943, F.C. and Z.F.H.) and (DE-FG02-05ER46204, R.D.) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.F.H. carried out the experiment and data analysis, F.C. assisted in the experiment, R.D. and M.D.V. worked out the theory and predicted local cooling, P.B. provided important comments and N.J.T. conceived the experiment.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1-S3 (PDF 934 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Chen, F., D'agosta, R. et al. Local ionic and electron heating in single-molecule junctions. Nature Nanotech 2, 698–703 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.345
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.345