Abstract
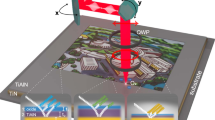
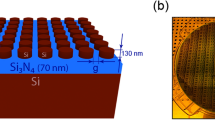
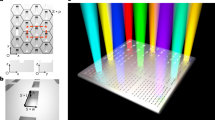
Colour generation by plasmonic nanostructures1,2 and metasurfaces3,4 has several advantages over dye technology: reduced pixel area, sub-wavelength resolution and the production of bright and non-fading colours5. However, plasmonic colour patterns need to be pre-designed and printed either by e-beam lithography (EBL)6,7,8,9,10,11 or focused ion beam (FIB)12,13,14, both expensive and not scalable processes that are not suitable for post-processing customization. Here we show a method of colour printing on nanoimprinted plasmonic metasurfaces using laser post-writing. Laser pulses induce transient local heat generation that leads to melting and reshaping of the imprinted nanostructures15. Depending on the laser pulse energy density, different surface morphologies that support different plasmonic resonances leading to different colour appearances can be created. Using this technique we can print all primary colours with a speed of 1 ns per pixel, resolution up to 127,000 dots per inch (DPI) and power consumption down to 0.3 nJ per pixel.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebbesen, T. W., Lezec, H. J., Ghaemi, H. F., Thio, T. & Wolff, P. A. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391, 667–669 (1998).
Maier, S. A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications (Springer, 2007).
Pendry, J. B., Schurig, D. & Smith, D. R. Controlling electromagnetic fields. Science 312, 1780–1782 (2006).
Leonhardt, U. Optical conformal mapping. Science 312, 1777–1780 (2006).
Dean, N. Colouring at the nanoscale. Nature Nanotechnol. 10, 15–16 (2015).
Kumar, K. et al. Printing colour at the optical diffraction limit. Nature Nanotechnol. 7, 557–561 (2012).
Wu, Y.-K., Hollowell, A. E., Zhang, C. & Guo, L. J. Angle-insensitive structural colours based on metallic nanocavities and coloured pixels beyond the diffraction limit. Sci. Rep. 3, 1194 (2013).
Roberts, A. S., Pors, A., Albrektsen, O. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Subwavelength plasmonic color printing protected for ambient use. Nano Lett. 14, 783–787 (2014).
Tan, S. J. et al. Plasmonic color palettes for photorealistic printing with aluminum nanostructures. Nano Lett. 14, 4023–4029 (2014).
Goh, X. M. et al. Three-dimensional plasmonic stereoscopic prints in full colour. Nature Commun. 5, 5361 (2014).
Ellenbogen, T., Seo, K. & Crozier, K. B. Chromatic plasmonic polarizers for active visible color filtering and polarimetry. Nano Lett. 12, 1026–1031 (2012).
Zeng, B., Gao, Y. & Bartoli, F. J. Ultrathin nanostructured metals for highly transmissive plasmonic subtractive color filters. Sci. Rep. 3, 2840 (2013).
Cheng, F., Gao, J., Luk, T. S. & Yang, X. Structural color printing based on plasmonic metasurfaces of perfect light absorption. Sci. Rep. 5, 11045 (2015).
Yokogawa, S., Burgos, S. P. & Atwater, H. A. Plasmonic color filters for cmos image sensor applications. Nano Lett. 12, 4349–4354 (2012).
Chichkov, B. N., Momma, C., Nolte, S., von Alvensleben, F. & Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 63, 109–115 (1996).
Knight, M. W. et al. Aluminum plasmonic nanoantennas. Nano Lett. 12, 6000–6004 (2012).
Olson, J. et al. Vivid, full-color aluminum plasmonic pixels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 14348–14353 (2014).
Prodan, E., Radloff, C., Halas, N. & Nordlander, P. A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302, 419–422 (2003).
Clausen, J. S. et al. Plasmonic metasurfaces for coloration of plastic consumer products. Nano Lett. 14, 4499–4504 (2014).
Wang, Y. M. et al. High aspect ratio 10-nm-scale nanoaperture arrays with template-guided metal dewetting. Sci. Rep. 5, 9654 (2015).
Chen, X., Chen, Y., Yan, M. & Qiu, M. Nanosecond photothermal effects in plasmonic nanostructures. ACS Nano 6, 2550–2557 (2012).
Zywietz, U., Evlyukhin, A. B., Reinhardt, C. & Chichkov, B. N. Laser printing of silicon nanoparticles with resonant optical electric and magnetic responses. Nature Commun. 5, 3402 (2014).
Baffou, G., Quidant, R. & Garca de Abajo, F. J. Nanoscale control of optical heating in complex plasmonic systems. ACS Nano 4, 709–716 (2010).
Zijlstra, P., Chon, J. W. M. & Gu, M. Five-dimensional optical recording mediated by surface plasmons in gold nanorods. Nature 459, 410–413 (2009).
Kim, H. et al. Structural colour printing using a magnetically tunable and lithographically fixable photonic crystal. Nature Photon. 3, 534–540 (2009).
Ulichney, R. Digital Halftoning (MIT Press, 1987).
Kawata, S., Sun, H., Tanaka, T. & Takada, K. Finer features for functional microdevices. Nature 412, 697–698 (2001).
Barnes, W. L., Dereux, A. & Ebbesen, T. W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003).
Fang, N., Lee, H., Sun, C. & Zhang, X. Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver superlens. Science 308, 534–537 (2005).
Højlund-Nielsen, E., Greibe, T., Mortensen, N. A. & Kristensen, A. Single-spot e-beam lithography for defining large arrays of nano-holes. Microelectron. Eng. 121, 104–107 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Commission through the FP7MMP Integrated project PLAST4FUTURE (NMP2-SE-2012-314345). The authors thank C. Smith and K. T. Sørensen for technical support and W. Yan, J. Clausen and S. Xiao for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.Z., N.A.M. and A.K. conceived the ideas. X.Z. and E.H.-N. fabricated the nanoimprinted samples. X.Z. performed the simulations. C.V. suggested and built the optical setup for laser printing. X.Z. and C.V. developed the codes. X.Z. implemented the laser printing and prepared the figures. A.K. and N.A.M. provided feedback on the experiments. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 3199 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary Movie 1 (MP4 7883 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary Movie 2 (GIF 18871 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Vannahme, C., Højlund-Nielsen, E. et al. Plasmonic colour laser printing. Nature Nanotech 11, 325–329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.285
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.285
This article is cited by
-
High-speed laser writing of structural colors for full-color inkless printing
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Versatile full-colour nanopainting enabled by a pixelated plasmonic metasurface
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Spiral phase plate for generation of scalar vortex beam made on fused silica by laser-induced microplasma
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2023)
-
Large-scale controllable fabrication of aluminum nanobowls for surface plasmon-enhanced fluorescence
Nano Research (2023)
-
Wear-resistant surface coloring by ultrathin optical coatings
PhotoniX (2022)