Abstract
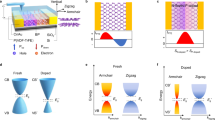
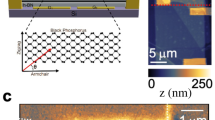
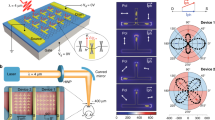
The ability to detect light over a broad spectral range is central to practical optoelectronic applications and has been successfully demonstrated with photodetectors of two-dimensional layered crystals such as graphene and MoS2. However, polarization sensitivity within such a photodetector remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate a broadband photodetector using a layered black phosphorus transistor that is polarization-sensitive over a bandwidth from ∼400 nm to 3,750 nm. The polarization sensitivity is due to the strong intrinsic linear dichroism, which arises from the in-plane optical anisotropy of this material. In this transistor geometry, a perpendicular built-in electric field induced by gating can spatially separate the photogenerated electrons and holes in the channel, effectively reducing their recombination rate and thus enhancing the performance for linear dichroism photodetection. The use of anisotropic layered black phosphorus in polarization-sensitive photodetection might provide new functionalities in novel optical and optoelectronic device applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geim, A. K. & Grigorieva, I. V. Van der Waals heterostructures. Nature 499, 419–425 (2013).
Wang, Q. H., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kis, A., Coleman, J. N. & Strano, M. S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Nanotech. 7, 699–712 (2012).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438, 197–200 (2005).
Zhang, Y. B., Tan, Y. W., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry's phase in graphene. Nature 438, 201–204 (2005).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Room-temperature quantum Hall effect in graphene. Science 315, 1379–1379 (2007).
Bolotin, K. I., Ghahari, F., Shulman, M. D., Stormer, H. L. & Kim, P. Observation of the fractional quantum Hall effect in graphene. Nature 462, 196–199 (2009).
Chen, Y. L. et al. Experimental realization of a three-dimensional topological insulator, Bi2Te3 . Science 325, 178–181 (2009).
Zhang, H. J. et al. Topological insulators in Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 with a single Dirac cone on the surface. Nature Phys. 5, 438–442 (2009).
Mak, K. F., He, K. L., Shan, J. & Heinz, T. F. Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity. Nature Nanotech. 7, 494–498 (2012).
Zeng, H. L., Dai, J. F., Yao, W., Xiao, D. & Cui, X. D. Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping. Nature Nanotech. 7, 490–493 (2012).
Cao, T. et al. Valley-selective circular dichroism of monolayer molybdenum disulphide. Nature Commun. 3, 887 (2012).
Li, L. K. et al. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nature Nanotech. 9, 372–377 (2014).
Liu, H. et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 8, 4033–4041 (2014).
Low, T. et al. Tunable optical properties of multilayers black phosphorus thin films. Phys. Rev. B 90, 075434 (2014).
Xu, Y. et al. Large-gap quantum spin Hall insulators in tin films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 136804 (2013).
Buscema, M. et al. Fast and broadband photoresponse of few-layer black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 14, 3347–3352 (2014).
Lopez-Sanchez, O., Lembke, D., Kayci, M., Radenovic, A. & Kis, A. Ultrasensitive photodetectors based on monolayer MoS2 . Nature Nanotech. 8, 497–501 (2013).
Xia, F., Wang, H. & Jia, Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nature Commun. 5, 4458 (2014).
Qiao, J., Kong, X., Hu, Z. X., Yang, F. & Ji, W. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nature Commun. 5, 4475 (2014).
Low, T. et al. Plasmons and screening in monolayer and multilayer black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 106802 (2014).
Low, T., Engel, M., Steiner, M. & Avouris, P. Origin of photoresponse in black phosphorus photo-transistors. Phys. Rev. B 90, 081408 (2014).
Fei, R. et al. Enhanced thermoelectric efficiency via orthogonal electrical and thermal conductances in phosphorene. Nano Lett. 14, 6393–6399 (2014).
Engel, M., Steiner, M. & Avouris, P. A black phosphorus photo-detector for multispectral, high-resolution imaging. Nano Lett. 14, 6414–6417 (2014).
Buscema, M., Groenendijk, D. J., Steele, G. A., van der Zant, H. S. J. & Castellanos-Gomez, A. Photovoltaic effect in few-layer black phosphorus PN junctions defined by local electrostatic gating. Nature Commun. 5, 4651 (2014).
Deng, Y. et al. Black phosphorus-monolayer MoS2 van der Waals heterojunction p–n diode. ACS Nano 8, 8292–8299 (2014).
Kamalakar, M. V., Madhushankar, B. N., Dankert, A. & Dash, S. P. Low Schottky barrier black phosphorus field-effect devices with ferromagnetic tunnel contacts. Small http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smll.201402900 (2015).
Dresselhaus, G. Optical absorption band edge in anisotropic crystals. Phys. Rev. 105, 135–138 (1957).
Blakemore, J. S. & Nomura, K. C. Intrinsic optical absorption in tellurium. Phys. Rev. 127, 1024–1029 (1962).
Wang, J. F., Gudiksen, M. S., Duan, X. F., Cui, Y. & Lieber, C. M. Highly polarized photoluminescence and photodetection from single indium phosphide nanowires. Science 293, 1455–1457 (2001).
Nanot, S. et al. Broadband, polarization-sensitive photodetector based on optically-thick films of macroscopically long, dense, and aligned carbon nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 3, 1335 (2013).
Liao, Y. L. & Zhao, Y. Design of wire-grid polarizer with effective medium theory. Opt. Quantum Electron. 46, 641–647 (2014).
Miyamaru, F. & Hangyo, M. Polarization response of two-dimensional metallic photonic crystals studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 43, 1412–1415 (2004).
Guillaumee, M. et al. Polarization sensitive silicon photodiodes using nanostructured metallic grids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 193503 (2009).
Han, C. Q. et al. Electronic structures of black phosphorus studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 90, 085101 (2014).
Lee, M. M., Teuscher, J., Miyasaka, T., Murakami, T. N. & Snaith, H. J. Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338, 643–647 (2012).
Stranks, S. D. et al. Electron–hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013).
Jacobs-Gedrim, R. B. et al. Extraordinary photoresponse in two-dimensional In2Se3 nanosheets. ACS Nano 8, 514–521 (2014).
Cho, J. H. et al. Printable ion–gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nature Mater. 7, 900–906 (2008).
Kawasaki, M. & Iwasa, Y. Electronics: ‘cut and stick’ ion gels. Nature 489, 510–511 (2012).
Yuan, H. T. et al. Zeeman-type spin splitting controlled by an electric field. Nature Phys. 9, 563–569 (2013).
Yu, W. J. et al. Highly efficient gate-tunable photocurrent generation in vertical heterostructures of layered materials. Nature Nanotech. 8, 952–958 (2013).
Kim, C. O. et al. High photoresponsivity in an all-graphene p–n vertical junction photodetector. Nature Commun. 5, 3249 (2014).
Liu, C. H., Chang, Y. C., Norris, T. B. & Zhong, Z. H. Graphene photodetectors with ultra-broadband and high responsivity at room temperature. Nature Nanotech. 9, 273–278 (2014).
Hu, L., Dalgleish, S., Matsushita, M. M., Yoshikawa, H. & Awaga, K. Storage of an electric field for photocurrent generation in ferroelectric-functionalized organic devices. Nature Commun. 5, 3279 (2014).
Kresse, G. & Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics for liquid-metals. Phys. Rev. B 47, 558–561 (1993).
Kresse, G. & Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
Perdew, J. P., Burke, K. & Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Hohenberg, P. & Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 136, B864 (1964).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering (contract no. DE-AC02-76SF00515). X.L., F.A., A.G.C. and M.L.B. acknowledge support from the Department of Energy (grant no. DE-FG07-ER46426). A.G.C. acknowledges the support of a Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship. G.J.Y and X.H.C acknowledge the support from Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.T.Y., H.Y.H. and Y.C. conceived and designed the experiments. H.T.Y. performed sample fabrication and transport measurements. H.T.Y., X.G.L., F.A., A.G.C. and M.B. performed optical measurements. W.L. and Z.X.S. performed ARPES measurement. G.X., B.L. and S.C.Z. performed DFT calculations and theoretical analyses. X.G.L. performed the band bending calculation. J.S. performed transmission electron microscopy analysis. G.J.Y and X.H.C. grew the high-quality BP crystals. Y.H., M.B., Z.X.S., S.C.Z., X.H.C., H.Y.H. and Y.C. supervised the project and all authors contributed to data discussions. H.T.Y. wrote the manuscript, with input from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1542 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary Movie 1 (MOV 65854 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, H., Liu, X., Afshinmanesh, F. et al. Polarization-sensitive broadband photodetector using a black phosphorus vertical p–n junction. Nature Nanotech 10, 707–713 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.112
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.112
This article is cited by
-
Multidimensional detection enabled by twisted black arsenic–phosphorus homojunctions
Nature Nanotechnology (2024)
-
Long operating lifetime mid-infrared LEDs based on black phosphorus
Nature Communications (2023)
-
An anisotropic van der Waals dielectric for symmetry engineering in functionalized heterointerfaces
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Pseudospin-selective Floquet band engineering in black phosphorus
Nature (2023)