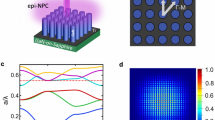
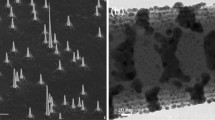
Abstract
Ultraviolet laser radiation has been adopted in a wide range of applications as diverse as water purification, flexible displays, data storage, sterilization, diagnosis and bioagent detection1,2,3. Success in developing semiconductor-based, compact ultraviolet laser sources, however, has been extremely limited. Here, we report that defect-free disordered AlGaN core–shell nanowire arrays, formed directly on a Si substrate, can be used to achieve highly stable, electrically pumped lasers across the entire ultraviolet AII (UV-AII) band (∼320–340 nm) at low temperatures. The laser threshold is in the range of tens of amps per centimetre squared, which is nearly three orders of magnitude lower than those of previously reported quantum-well lasers4,5,6. This work also reports the first demonstration of electrically injected AlGaN-based ultraviolet lasers monolithically grown on a Si substrate, and offers a new avenue for achieving semiconductor lasers in the ultraviolet B (UV-B) (280–320 nm) and ultraviolet C (UV-C) (<280 nm) bands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindenauer, K. G. & Darby, J. L. Ultraviolet disinfection of wastewater: effect of dose on subsequent photoreactivation. Water Res. 28, 805–817 (1994).
Chwirot, B. W. et al. Ultraviolet laser-induced fluorescence of human stomach tissues: detection of cancer tissues by imaging techniques. Lasers Surg. Med. 21, 149–158 (1997).
Ramanujam, P. S. & Berg, R. H. Photodimerization in dipeptides for high capacity optical digital storage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1665–1667 (2004).
Yoshida, H., Yamashita, Y., Kuwabara, M. & Kan, H. Demonstration of an ultraviolet 336 nm AlGaN multiple-quantum-well laser diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 241106 (2008).
Kneissl, M., Treat, D. W., Teepe, M., Miyashita, N. & Johnson, N. M. Ultraviolet AlGaN multiple-quantum-well laser diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4441–4443 (2003).
Yoshida, H., Yamashita, Y., Kuwabara, M. & Kan, H. A 342-nm ultraviolet AlGaN multiple-quantum-well laser diode. Nature Photon. 2, 551–554 (2008).
Iida, K. et al. 350.9 nm UV laser diode grown on low-dislocation-density AlGaN. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, L499 (2004).
Masui, S. et al. 365 nm ultraviolet laser diodes composed of quaternary AlInGaN alloy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42, L1318 (2003).
Yoshida, H., Takagi, Y., Kuwabara, M., Amano, H. & Kan, H. Entirely crack-free ultraviolet GaN/AlGaN laser diodes grown on 2-in. sapphire substrate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46, 5782 (2007).
Haeger, D. A. et al. 384 nm laser diode grown on a ( ) semipolar relaxed AlGaN buffer layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 161107 (2012).
Guo, W. et al. Stimulated emission and optical gain in AlGaN heterostructures grown on bulk AlN substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 103108 (2014).
Francesco Pecora, E. et al. Sub-250 nm light emission and optical gain in AlGaN materials. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 013106 (2013).
Zhang, J., Zhao, H. & Tansu, N. Effect of crystal-field split-off hole and heavy-hole bands crossover on gain characteristics of high Al-content AlGaN quantum well lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 111105 (2010).
Zhang, J., Zhao, H. & Tansu, N. Large optical gain AlGaN-delta-GaN quantum wells laser active regions in mid- and deep-ultraviolet spectral regimes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 171111 (2011).
Park, S-H. Optical gain characteristics of non-polar Al-rich AlGaN/AlN quantum well structures. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 063105 (2011).
Gradečak, S., Qian, F., Li, Y., Park, H-G. & Lieber, C. M. GaN nanowire lasers with low lasing thresholds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 173111 (2005).
Johnson, J. C. et al. Single gallium nitride nanowire lasers. Nature Mater. 1, 106–110 (2002).
Xu, H. et al. Single-mode lasing of GaN nanowire-pairs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 113106 (2012).
Heo, J., Jahangir, S., Xiao, B. & Bhattacharya, P. Room-temperature polariton lasing from GaN nanowire array clad by dielectric microcavity. Nano Lett. 13, 2376–2380 (2013).
Wu, C. Y. et al. Plasmonic green nanolaser based on a metal-oxide-semiconductor structure. Nano Lett. 11, 4256–4260 (2011).
Kouno, T., Kishino, K., Suzuki, T. & Sakai, M. Lasing actions in GaN tiny hexagonal nanoring resonators. IEEE Photon. J. 2, 1027–1033 (2010).
Frost, T. et al. Monolithic electrically injected nanowire array edge-emitting laser on (001) silicon. Nano Lett. 14, 4535–4541 (2014).
Painter, O. et al. Two-dimensional photonic band-gap defect mode laser. Science 284, 1819–1821 (1999).
Matsubara, H. et al. GaN photonic-crystal surface-emitting laser at blue–violet wavelengths. Science 319, 445–457 (2008).
Sakai, M. et al. Random laser action in GaN nanocolumns. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 151109 (2010).
Yu, S. F., Yuen, C., Lau, S. P., Park, W. I. & Yi, G-C. Random laser action in ZnO nanorod arrays embedded in ZnO epilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3241–3243 (2004).
Liu, C. Y. et al. Electrically pumped near-ultraviolet lasing from ZnO/MgO core/shell nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 063115 (2011).
Liu, X. Y., Shan, C. X., Wang, S. P., Zhang, Z. Z. & Shen, D. Z. Electrically pumped random lasers fabricated from ZnO nanowire arrays. Nanoscale 4, 2843–2846 (2012).
Chu, S. et al. Electrically pumped waveguide lasing from ZnO nanowires. Nature Nanotech. 6, 506–510 (2011).
Lo, M-H., Cheng, Y-J., Liu, M-C., Kuo, H-C. & Wang, S. C. Lasing at exciton transition in optically pumped gallium nitride nanopillars. Opt. Express 19, 17960–17965 (2011).
Nguyen, H. P. T. et al. Breaking the carrier injection bottleneck of phosphor-free nanowire white light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 13, 5437–5442 (2013).
Sampath, A. V. et al. Growth of AlGaN containing nanometer scale compositional inhomogeneities for ultraviolet light emitters. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 29, 03C134 (2011).
Pierret, A., Bougerol, C., Gayral, B., Kociak, M. & Daudin, B. Probing alloy composition gradient and nanometer-scale carrier localization in single AlGaN nanowires by nanocathodoluminescence. Nanotechnology 24, 305703 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and US Army Research Office under Grant W911NF-12-1-0477. Part of the work was performed in the McGill University Micro Fabrication Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.H.L. fabricated the devices and carried out the experimental measurements. X.L. performed the device design and contributed to the theoretical calculations, device fabrication and measurements. K.H.L. and X.L. made equal contributions. S.Z. conducted the MBE growth of nanowires and contributed to the TEM analysis. Q.W. contributed to the preliminary works on device characteristics. Z.M. conceived the experiments and supervised and led the project. The paper was written by K.H.L. and Z.M. with contributions from the other authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1043 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Liu, X., Wang, Q. et al. Ultralow-threshold electrically injected AlGaN nanowire ultraviolet lasers on Si operating at low temperature. Nature Nanotech 10, 140–144 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.308
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2014.308
This article is cited by
-
Short-wave infrared cavity resonances in a single GeSn nanowire
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Ultralow threshold surface emitting ultraviolet lasers with semiconductor nanowires
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Observation of polarity-switchable photoconductivity in III-nitride/MoSx core-shell nanowires
Light: Science & Applications (2022)
-
Mid-infrared photon sensing using InGaN/GaN nanodisks via intersubband absorption
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Dual-wavelength switchable single-mode lasing from a lanthanide-doped resonator
Nature Communications (2022)