Abstract
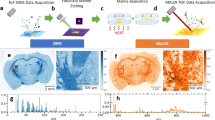
We have developed a method for integrating three dimensional–volume reconstructions of spatially resolved matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (MALDI IMS) ion images of whole mouse heads with high-resolution images from other modalities in an animal-specific manner. This approach enabled us to analyze proteomic profiles from MALDI IMS data with corresponding in vivo data provided by magnetic resonance imaging.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaurand, P. et al. Am. J. Pathol. 165, 1057–1068 (2004).
Chaurand, P., Schwartz, S.A. & Caprioli, R.M. J. Proteome Res. 3, 245–252 (2004).
Khatib-Shahidi, S. et al. Anal. Chem. 78, 6448–6456 (2006).
Reyzer, M.L. et al. J. Mass Spectrom. 38, 1081–1092 (2003).
Reyzer, M.L. et al. Cancer Res. 64, 9093–9100 (2004).
Stoeckli, M. et al. Nat. Med. 7, 493–496 (2001).
Crecelius, A.C. et al. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 1093–1099 (2005).
Andersson, M., Groseclose, M.R., Deutch, A.Y. & Caprioli, R.M. Nat. Methods 5, 101–108 (2008).
Paxinos, G. & Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. (San Diego, Academic Press, 2001).
Studholme, C., Hill, D.L.G. & Hawkes, D.J. Pattern Recognit. 32, 71–86 (1999).
Schwartz, S.A. et al. Cancer Res. 65, 7674–7681 (2005).
Atlas, S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain and Spine. (Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank J. True, R. Baheza and the staff of the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science Center for Small Animal Imaging for their assistance in collecting the imaging data presented here. Financial support was provided by the US National Institutes of Health Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, Cancer Institute, Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.K.S. helped to develop the techniques presented here and assisted in collecting and analyzing the results. S.K.-S. helped to acquire the blockface and MALDI IMS data. T.E.Y. helped to acquire the in vivo magnetic resonance data. K.M. implanted and provided the mouse with a tumor-laden brain. M.E. provided support and expertise with the tumor model. D.S.C. provided expertise in collecting the MALDI IMS data. B.M.D. helped to develop accurate coregistration techniques for the MALDI IMS and magnetic resonance alignment. R.M.C. provided support and expertise for the MALDI IMS data collection. J.C.G. helped to develop the techniques presented here and provided expertise with data analysis and magnetic resonance data collection.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1821 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
Reconstructed blockface volume of a whole mouse head. (MOV 3915 kb)
Supplementary Movie 2
Blockface reconstruction results for whole animals. (MOV 3365 kb)
Supplementary Movie 3
Coregistered volumetric MALDI IMS data with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging in a tumor-laden mouse brain. (MOV 9343 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, T., Khatib-Shahidi, S., Yankeelov, T. et al. Integrating spatially resolved three-dimensional MALDI IMS with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Methods 5, 57–59 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1147
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1147
This article is cited by
-
Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Integration with Other Imaging Modalities for Greater Molecular Understanding of Biological Tissues
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2018)
-
Feasibility Assessment of a MALDI FTICR Imaging Approach for the 3D Reconstruction of a Mouse Lung
Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry (2017)
-
MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry: a step forward in the anatomopathological characterization of stenotic aortic valve tissue
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Three-dimensional imaging of lipids and metabolites in tissues by nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2015)