Abstract
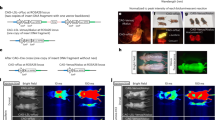
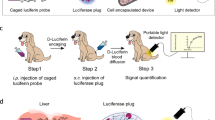
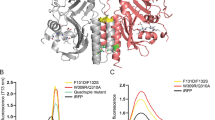
The use of R. reniformis luciferase (RLuc) as a reporter gene in small-animal imaging has been hampered by its 481 nm peaked emission spectrum, as blue wavelengths are strongly attenuated in biological tissues. To overcome this, we generated variants of RLuc with bathochromic (red) shifts of up to 66 nm (547 nm peak) that also had greater stability and higher light emission than native RLuc.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissleder, R. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 316–317 (2001).
Bhaumik, S. & Gambhir, S.S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 377–382 (2002).
Shah, K., Tang, Y., Breakefield, X. & Weissleder, R. Oncogene 22, 6865–6872 (2003).
Tannous, B.A., Kim, D.E., Fernandez, J.L., Weissleder, R. & Breakefield, X.O. Mol. Ther. 11, 435–443 (2005).
Venisnik, K.M. et al. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 19, 453–460 (2006).
Venisnik, K.M., Olafsen, T., Gambhir, S.S. & Wu, A.M. Mol. Imaging Biol.; published online 19 June 2007 (doi: 10.1007/s11307-007-0101-8).
So, M.K., Xu, C., Loening, A.M., Gambhir, S.S. & Rao, J. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 339–343 (2006).
Zhao, H. et al. J. Biomed. Opt. 10, 41210 (2005).
Shimomura, O. & Teranishi, K. Luminescence 15, 51–58 (2000).
Loening, A.M., Fenn, T.D., Wu, A.M. & Gambhir, S.S. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 19, 391–400 (2006).
Shimomura, O., Musicki, B. & Kishi, Y. Biochem. J. 251, 405–410 (1988).
Inouye, S. & Shimomura, O. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 233, 349–353 (1997).
De, A. & Gambhir, S.S. FASEB J. 19, 2017–2019 (2005).
Wang, L., Jackson, W.C., Steinbach, P.A. & Tsien, R.Y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16745–16749 (2004).
Viviani, V.R., Oehlmeyer, T.L., Arnoldi, F.G. & Brochetto-Braga, M.R. Photochem. Photobiol. 81, 843–848 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Stanford Bio-X Graduate Fellowship (A.M.L.), US National Cancer Institute (NCI) CA114747 ICMIC P50 (S.S.G.), NCI CA119367 CCNE U54 (SSG), NCI R01 CA082214 (SSG), and the NCI Small Animal Imaging Resource Program. We thank B. Rice and T. Troy of Caliper Life Sciences for help with the spectra measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Stanford University has filed a patent application that includes portions of the research described in this manuscript.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Tables 1–3, Supplementary Methods. (PDF 933 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loening, A., Wu, A. & Gambhir, S. Red-shifted Renilla reniformis luciferase variants for imaging in living subjects. Nat Methods 4, 641–643 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1070
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth1070
This article is cited by
-
Illuminating the mechanism and allosteric behavior of NanoLuc luciferase
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Catalytic mechanism for Renilla-type luciferases
Nature Catalysis (2023)
-
Bioluminescent imaging systems boosting near-infrared signals in mammalian cells
Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences (2023)
-
Crystal structure of semi-synthetic obelin-v after calcium induced bioluminescence implies coelenteramine as the main reaction product
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Color-tunable bioluminescence imaging portfolio for cell imaging
Scientific Reports (2021)