Abstract
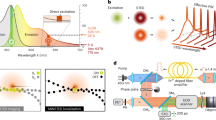
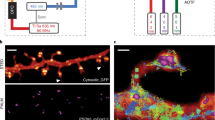
We report attainment of subdiffraction resolution using stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy with GFP-labeled samples. The ∼70 nm lateral resolution attained in this study is demonstrated by imaging GFP-labeled viruses and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of a mammalian cell. Our results mark the advent of nanoscale biological microscopy with genetically encoded markers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pawley, J.B. (ed.) Handbook of biological confocal microscopy (Springer, New York, 2006).
Conchello, J-A. & Lichtman, J.W. Nat. Methods 2, 920–931 (2005).
Hell, S.W. & Wichmann, J. Opt. Lett. 19, 780–782 (1994).
Klar, T.A., Jakobs, S., Dyba, M., Egner, A. & Hell, S.W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8206–8210 (2000).
Hell, S.W. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1347–1355 (2003).
Westphal, V. & Hell, S.W. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 143903 (2005).
Willig, K.I., Rizzoli, S.O., Westphal, V., Jahn, R. & Hell, S.W. Nature 440, 935–939 (2006).
Kittel, R.J. et al. Science 312, 1051–1054 (2006).
Sieber, J.J., Willig, K.I., Heintzmann, R., Hell, S.W. & Lang, T. Biophys. J. 90, 2843–2851 (2006).
Dyba, M., Jakobs, S. & Hell, S.W. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1303–1304 (2003).
Schäfer, F.P. Dye Lasers (Springer, Berlin, 1973).
Charpilienne, A. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29361–29367 (2001).
Griesbeck, O., Baird, G.S., Campbell, R.E., Zacharias, D.A. & Tsien, R.Y. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29188–29194 (2001).
Campbell, R.E. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7877–7882 (2002).
Shaner, N.C., Steinbach, P.A. & Tsien, R.Y. Nat. Methods 2, 905–909 (2005).
Acknowledgements
Purified GFP-VLPs were provided by J. Cohen and the plasmid eGFP-ER by P. Lipp. We thank S. Verrier, T. Rosenmund, A.C. Schauss, J.J. Sieber and T. Müller for providing samples, A. Schönle for help with the software ImSpector, V. Westphal and B. Harke for valuable discussions, as well as J. Keller and B. Rankin for critical reading. We thank R.Y. Tsien for providing the plasmids coding for mCitrine, mStrawbery and mRFP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willig, K., Kellner, R., Medda, R. et al. Nanoscale resolution in GFP-based microscopy. Nat Methods 3, 721–723 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth922
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth922
This article is cited by
-
Spheroscope: A custom-made miniaturized microscope for tracking tumour spheroids in microfluidic devices
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Single-particle virology
Biophysical Reviews (2020)
-
Compressive three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy with speckle-saturated fluorescence excitation
Nature Communications (2019)
-
STED super-resolved microscopy
Nature Methods (2018)
-
In vivo mouse and live cell STED microscopy of neuronal actin plasticity using far-red emitting fluorescent proteins
Scientific Reports (2017)