Abstract
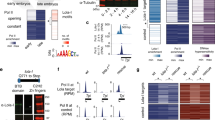
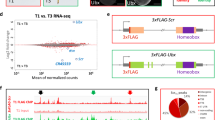
We tested whether transcription activator–like effectors (TALEs) could mediate repression and activation of endogenous enhancers in the Drosophila genome. TALE repressors (TALERs) targeting each of the five even-skipped (eve) stripe enhancers generated repression specifically of the focal stripes. TALE activators (TALEAs) targeting the eve promoter or enhancers caused increased expression primarily in cells normally activated by the promoter or targeted enhancer, respectively. This effect supports the view that repression acts in a dominant fashion on transcriptional activators and that the activity state of an enhancer influences TALE binding or the ability of the VP16 domain to enhance transcription. In these assays, the Hairy repression domain did not exhibit previously described long-range transcriptional repression activity. The phenotypic effects of TALER and TALEA expression in larvae and adults are consistent with the observed modulations of eve expression. TALEs thus provide a novel tool for detection and functional modulation of transcriptional enhancers in their native genomic context.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spitz, F. & Furlong, E.E.M. Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 613–626 (2012).
The ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489, 57–74 (2012).
Frankel, N. Multiple layers of complexity in cis-regulatory regions of developmental genes. Dev. Dyn. 241, 1857–1866 (2012).
Small, S., Blair, A. & Levine, M. Regulation of even-skipped stripe 2 in the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 11, 4047–4057 (1992).
Davis, G.K., Srinivasan, D.G., Wittkopp, P.J. & Stern, D.L. The function and regulation of Ultrabithorax in the legs of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol. 308, 621–631 (2007).
Klingler, M., Soong, J., Butler, B. & Gergen, J.P. Disperse versus compact elements for the regulation of runt stripes in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 177, 73–84 (1996).
Boch, J. et al. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 326, 1509–1512 (2009).
Moscou, M.J. & Bogdanove, A.J. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science 326, 1501 (2009).
Mahfouz, M.M. et al. Targeted transcriptional repression using a chimeric TALE-SRDX repressor protein. Plant Mol. Biol. 78, 311–321 (2012).
Morbitzer, R., Römer, P., Boch, J. & Lahaye, T. Regulation of selected genome loci using de novo-engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE)-type transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 21617–21622 (2010).
Maeder, M.L. et al. Robust, synergistic regulation of human gene expression using TALE activators. Nat. Methods 10, 243–245 (2013).
Perez-Pinera, P. et al. Synergistic and tunable human gene activation by combinations of synthetic transcription factors. Nat. Methods 10, 239–242 (2013).
Cong, L., Zhou, R., Kuo, Y.-c., Cunniff, M. & Zhang, F. Comprehensive interrogation of natural TALE DNA-binding modules and transcriptional repressor domains. Nat. Commun. 3, 968 (2012).
Garg, A., Lohmueller, J.J., Silver, P.A. & Armel, T.Z. Engineering synthetic TAL effectors with orthogonal target sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 7584–7595 (2012).
Li, Y., Moore, R., Guinn, M. & Bleris, L. Transcription activator-like effector hybrids for conditional control and rewiring of chromosomal transgene expression. Sci. Rep. 2, 897 (2012).
Geissler, R. et al. Transcriptional activators of human genes with programmable DNA-specificity. PLoS ONE 6, e19509 (2011).
Zhang, F. et al. Efficient construction of sequence-specific TAL effectors for modulating mammalian transcription. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 149–153 (2011).
Cermak, T. et al. Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e82 (2011).
Gray, S. & Levine, M. Short-range transcriptional repressors mediate both quenching and direct repression within complex loci in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 10, 700–710 (1996).
Li, L.M. & Arnosti, D.N. Long- and short-range transcriptional repressors induce distinct chromatin states on repressed genes. Curr. Biol. 21, 406–412 (2011).
Cai, H.N., Arnosti, D.N. & Levine, M. Long-range repression in the Drosophila embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 9309–9314 (1996).
Harding, K., Rushlow, C., Doyle, H.J., Hoey, T. & Levine, M. Cross-regulatory interactions among pair-rule genes in Drosophila. Science 233, 953–959 (1986).
Frasch, M., Warrior, R., Tugwood, J. & Levine, M. Molecular analysis of even-skipped mutants in Drosophila development. Genes Dev. 2, 1824–1838 (1988).
Fujioka, M., Emi-Sarker, Y., Yusibova, G.L., Goto, T. & Jaynes, J.B. Analysis of an even-skipped rescue transgene reveals both composite and discrete neuronal and early blastoderm enhancers, and multi-stripe positioning by gap gene repressor gradients. Development 126, 2527–2538 (1999).
Small, S., Arnosti, D.N. & Levine, M. Spacing ensures autonomous expression of different stripe enhancers in the even-skipped promoter. Development 119, 762–772 (1993).
Tracey, W.D., Ning, X., Klingler, M., Kramer, S.G. & Gergen, J.P. Quantitative analysis of gene function in the Drosophila embryo. Genetics 154, 273–284 (2000).
Nüsslein-Volhard, C. & Wieschaus, E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287, 795–801 (1980).
Staller, M.V. et al. Depleting gene activities in early Drosophila embryos with the “maternal-Gal4-shRNA” system. Genetics 193, 51–61 (2013).
Manoukian, A.S. & Krause, H.M. Concentration-dependent activities of the even-skipped protein in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 6, 1740–1751 (1992).
Small, S., Blair, A. & Levine, M. Regulation of even-skipped stripe 2 in the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 11, 4047–4057 (1992).
Ludwig, M.Z., Manu, Kittler, R., White, K.P. & Kreitman, M. Consequences of eukaryotic enhancer architecture for gene expression dynamics, development, and fitness. PLoS Genet. 7, e1002364 (2011).
Clyde, D.E. et al. A self-organizing system of repressor gradients establishes segmental complexity in Drosophila. Nature 426, 849–853 (2003).
Jiang, J., Hoey, T. & Levine, M. Autoregulation of a segmentation gene in Drosophila: combinatorial interaction of the even-skipped homeo box protein with a distal enhancer element. Genes Dev. 5, 265–277 (1991).
Wunderlich, Z. et al. Dissecting sources of quantitative gene expression pattern divergence between Drosophila species. Mol. Syst. Biol. 8, 604 (2012).
Ludwig, M.Z. et al. Functional evolution of a cis-regulatory module. PLoS Biol. 3, e93 (2005).
Berg, O.G., Winter, R.B. & von Hippel, P.H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 1. Models and theory. Biochemistry 20, 6929–6948 (1981).
Barolo, S. & Levine, M. hairy mediates dominant repression in the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 16, 2883–2891 (1997).
Kaplan, T. et al. Quantitative models of the mechanisms that control genome-wide patterns of transcription factor binding during early Drosophila development. PLoS Genet. 7, e1001290 (2011).
Li, X.-Y. et al. The role of chromatin accessibility in directing the widespread, overlapping patterns of Drosophila transcription factor binding. Genome Biol. 12, R34 (2011).
Davidson, E.H. The Regulatory Genome: Gene Regulatory Networks in Development and Evolution (Academic Press, 2006).
Pfeiffer, B.D. et al. Refinement of tools for targeted gene expression in Drosophila. Genetics 186, 735–755 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Martin and A. DePace (Harvard Medical School) for the eveS2-lacZ enhancer flies; E. Preger-Ben Noon and C. Standley for comments on the manuscript; and B. Pfeiffer, M. Schroeder, R. Mann and the entire Stern lab for discussion. We also thank the Janelia Farm Research Campus community for facilitating this work and for providing an inspiring scientific environment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C. conceived of, designed and executed the experiments and analyzed the data, with mentorship from D.L.S. J.C. and D.L.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures and Note
Supplementary Figures 1–8 and Supplementary Note 1 (PDF 51029 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crocker, J., Stern, D. TALE-mediated modulation of transcriptional enhancers in vivo. Nat Methods 10, 762–767 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2543
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2543
This article is cited by
-
Rationally-engineered reproductive barriers using CRISPR & CRISPRa: an evaluation of the synthetic species concept in Drosophila melanogaster
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
A multiplexable TALE-based binary expression system for in vivo cellular interaction studies
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Quantitatively predictable control of Drosophila transcriptional enhancers in vivo with engineered transcription factors
Nature Genetics (2016)
-
Genome engineering of woody plants: past, present and future
Journal of Wood Science (2016)