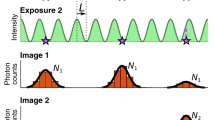
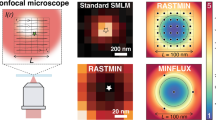
Abstract
Super-localization microscopy encompasses techniques that depend on the accurate localization of individual molecules from generally low-light images. The obtainable localization accuracies, however, are ultimately limited by the image detector's pixelation and noise. We present the ultrahigh accuracy imaging modality (UAIM), which allows users to obtain accuracies approaching the accuracy that is achievable only in the absence of detector pixelation and noise, and which we found can experimentally provide a >200% accuracy improvement over conventional low-light imaging.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson, M.A., Lew, M.D. & Moerner, W.E. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 41, 321–342 (2012).
Lidke, K.A., Rieger, B., Jovin, T.M. & Heintzmann, R. Opt. Express 13, 7052–7062 (2005).
Betzig, E. et al. Science 313, 1642–1645 (2006).
Ram, S., Prabhat, P., Chao, J., Ward, E.S. & Ober, R.J. Biophys. J. 95, 6025–6043 (2008).
Pavani, S.R.P. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2995–2999 (2009).
van de Linde, S. et al. Nat. Protoc. 6, 991–1009 (2011).
Hynecek, J. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 48, 2238–2241 (2001).
Larkin, J.D., Publicover, N.G. & Sutko, J.L. J. Microsc. 241, 54–68 (2011).
Ober, R.J., Ram, S. & Ward, E.S. Biophys. J. 86, 1185–1200 (2004).
Patterson, G.H. J. Microsc. 243, 1–7 (2011).
Carlton, P.M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 16016–16022 (2010).
Chao, J., Ward, E.S. & Ober, R.J. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 23, 349–379 (2012).
Mortensen, K.I., Churchman, L.S., Spudich, J.A. & Flyvbjerg, H. Nat. Methods 7, 377–381 (2010).
Matsuo, K., Teich, M.C. & Saleh, B.E.A. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 32, 2615–2623 (1985).
Hollenhorst, J.N. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 37, 781–788 (1990).
Hynecek, J. & Nishiwaki, T. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 50, 239–245 (2003).
Basden, A.G., Haniff, C.A. & Mackay, C.D. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 345, 985–991 (2003).
Rohr, K. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 7, 7–22 (1997).
Ades, E.W. et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 99, 683–690 (1992).
Zheng, W. & Zhao, Q. Brain Res. 958, 371–380 (2002).
Born, M. & Wolf, E. Principles of Optics 7th edn. (Cambridge University Press, 1999).
Ram, S., Ward, E.S. & Ober, R.J. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 17, 27–57 (2006).
Olivo-Marin, J.C. Pattern Recognit. 35, 1989–1996 (2002).
Chao, J., Ward, E.S. & Ober, R.J. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 14, 1075–1087 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grant R01 GM085575 from the US National Institutes of Health and in part by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas. We thank D. Kim and S. You for their assistance with data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C., S.R. and R.J.O. conceived the experiments, designed the experiments and analyzed the data. J.C. and S.R. performed the experiments. E.S.W. and R.J.O. provided the experimental materials and computing resources. All authors wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3, Supplementary Tables 1–3 and Supplementary Notes 1–15 (PDF 1891 kb)
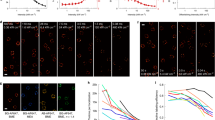
Single-molecule tracking of an ErbB2 cell surface receptor labeled with anti- ErbB2 Fab Atto 647N
The left panel shows the UAIM image, which was acquired at a 1,000 × magnification with an EMCCD camera. The top right panel shows the compacted version of the UAIM image, which was created by a 10 × 10 binning. The bottom right plot shows the two-dimensional trajectory of the ErbB2 receptor that is highlighted by the red box (red arrow) in the UAIM image (compacted image). The trajectory is color-coded from red to green to blue to indicate increasing time, and the video is played at the acquisition speed. For display purposes, the UAIM images were multiplied by a constant and then piecewise linearly adjusted, and the compacted images were piecewise linearly adjusted. Scale bars, 1 μm. (MOV 37032 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, J., Ram, S., Ward, E. et al. Ultrahigh accuracy imaging modality for super-localization microscopy. Nat Methods 10, 335–338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2396
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2396
This article is cited by
-
Quantum correlation enhanced super-resolution localization microscopy enabled by a fibre bundle camera
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Towards digital photon counting cameras for single-molecule optical nanoscopy
Optical Nanoscopy (2014)
-
Fluorophore localization algorithms for super-resolution microscopy
Nature Methods (2014)
-
Plasmon point spread functions: How do we model plasmon-mediated emission processes?
Frontiers of Physics (2014)
-
Video-rate nanoscopy using sCMOS camera–specific single-molecule localization algorithms
Nature Methods (2013)