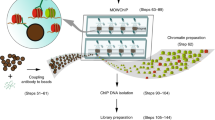
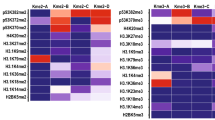
Abstract
Variability in the quality of antibodies to histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) is a widely recognized hindrance in epigenetics research. Here, we produced recombinant antibodies to the trimethylated lysine residues of histone H3 with high specificity and affinity and no lot-to-lot variation. These recombinant antibodies performed well in common epigenetics applications, and enabled us to identify positive and negative correlations among histone PTMs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strahl, B.D. & Allis, C.D. Nature 403, 41–45 (2000).
Kouzarides, T. Cell 128, 693–705 (2007).
Barski, A. et al. Cell 129, 823–837 (2007).
Rea, S. et al. Nature 406, 593–599 (2000).
Egelhofer, T.A. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 91–93 (2011).
Fuchs, S.M. & Strahl, B.D. Epigenomics 3, 247–249 (2011).
Nishikori, S. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 424, 391–399 (2012).
Cobaugh, C.W., Almagro, J.C., Pogson, M., Iverson, B. & Georgiou, G. J. Mol. Biol. 378, 622–633 (2008).
Feldhaus, M.J. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 163–170 (2003).
Weiss, G.A., Watanabe, C.K., Zhong, A., Goddard, A. & Sidhu, S.S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 8950–8954 (2000).
Fuchs, S.M., Krajewski, K., Baker, R.W., Miller, V.L. & Strahl, B.D. Curr. Biol. 21, 53–58 (2011).
Bulut-Karslioglu, A. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 1023–1030 (2012).
Blahnik, K.R. et al. PLoS ONE 6, e17121 (2011).
Bernstein, B.E. et al. Cell 120, 169–181 (2005).
Tan, M. et al. Cell 146, 1016–1028 (2011).
Zheng, Y. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 13549–13554 (2012).
Greiner, D., Bonaldi, T., Eskeland, R., Roemer, E. & Imhof, A. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 143–145 (2005).
Quinn, A.M. & Simeonov, A. Curr Chem Genomics 5, 95–105 (2011).
Haque, A., Andersen, J.N., Salmeen, A., Barford, D. & Tonks, N.K. Cell 147, 185–198 (2011).
Sidorin, E.V. & Solov'eva, T.F. Biochemistry (Moscow) 76, 295–308 (2011).
Chao, G. et al. Nat. Protoc. 1, 755–768 (2006).
Ackerman, M. et al. Biotechnol. Prog. 25, 774–783 (2009).
Wojcik, J. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 519–527 (2010).
Fellouse, F.A. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 373, 924–940 (2007).
Zhang, X. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 8534–8539 (2012).
Lehnertz, B. et al. Curr. Biol. 13, 1192–1200 (2003).
Ruthenburg, A.J. et al. Cell 145, 692–706 (2011).
Frietze, S., O'Geen, H., Blahnik, K.R., Jin, V.X. & Farnham, P.J. PLoS ONE 5, e15082 (2010).
O'Geen, H., Echipare, L. & Farnham, P.J. Methods Mol. Biol. 791, 265–286 (2011).
Negre, N. et al. Nature 471, 527–531 (2011).
Shechter, D., Dormann, H.L., Allis, C.D. & Hake, S.B. Nat. Protoc. 2, 1445–1457 (2007).
Garcia, B.A. et al. Nat. Protoc. 2, 933–938 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank K.D. Wittrup (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) for an antibody library, J. Lavinder and G. Georgiou for assistance in peptide procurement, J. Ahringer (Cambridge University) for sharing commercial antibodies, M. Gardel and Y. Beckham (University of Chicago) for the NIH 3T3 cell line and advice, A.A. Kossiakoff and M. Lugowski for access to cell culture equipment and microscopes, R. Hoey, N. Bharwani, A. Crofts and R. Ptashkin for technical assistance, S. Nishikori for helpful discussion, and members of the University of Chicago DNA sequencing and flow cytometry core facilities, and of the Institute for Genomics and Systems Biology High-throughput Genome Analysis facility. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants (R21 DA025725 and RC1 DA028779 to S.K., GM085394 to B.D.S., U01 HG004264 to K.P.W. and U01 ES017154 to P.J.F.), and the University of Chicago Comprehensive Cancer Center (to S.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.H. characterized commercial antibodies; T.H., A.K. and S.K. designed phage-display libraries and selection schemes; T.H., J.M.T. and K.M.S. performed selections and biophysical characterization of recombinant antibodies; K.K. and B.D.S. designed and made synthetic peptides; T.H., H.W., M.S., A.J.R., K.P.W., P.J.F. and S.K. designed ChIP experiments; T.H., H.W. and M.S. conducted ChIP experiments and data analysis; T.H., H.L., Y.Z. and S.K. designed IP-MS experiments; T.H. and H.L. performed IP-MS and data analysis: T.H. and S.K. designed HMT assay; T.H. conducted HMT assay. T.H. and S.K. wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
T.H., J.M.T., A.K. and S.K. are named as inventors in a provisional patent application (61/839,972) filed by the University of Chicago on the described materials.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Note (PDF 3321 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattori, T., Taft, J., Swist, K. et al. Recombinant antibodies to histone post-translational modifications. Nat Methods 10, 992–995 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2605
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2605
This article is cited by
-
Replication timing and epigenome remodelling are associated with the nature of chromosomal rearrangements in cancer
Nature Communications (2019)
-
HiBiT-qIP, HiBiT-based quantitative immunoprecipitation, facilitates the determination of antibody affinity under immunoprecipitation conditions
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Molecular and functional analysis of monoclonal antibodies in support of biologics development
Protein & Cell (2018)