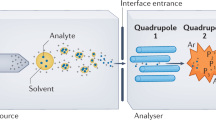
Abstract
Targeted mass spectrometry (MS) is becoming widely used in academia and in pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries for sensitive and quantitative detection of proteins, peptides and post-translational modifications. Here we describe the increasing importance of targeted MS technologies in clinical proteomics and the potential key roles these techniques will have in bridging biomedical discovery and clinical implementation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lawson, A.M. The scope of mass spectrometry in clinical chemistry. Clin. Chem. 21, 803–824 (1975).
Zhu, X. & Desiderio, D.M. Peptide quantification by tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 15, 213–240 (1996).
Grebe, S.K.G. & Singh, R.J.J. LC-MS/MS in the clinical laboratory—where to from here? Clin. Biochem. Rev. 32, 5–31 (2011).
Yost, R.A. & Enke, C.G. Triple quadrupole mass spectrometry for direct mixture analysis and structure elucidation. Anal. Chem. 51, 1251–1264 (1979).
Picotti, P. & Aebersold, R. Selected reaction monitoring-based proteomics: workflows, potential, pitfalls and future directions. Nat. Methods 9, 555–566 (2012).
Barr, J.R. et al. Isotope dilution–mass spectrometric quantification of specific proteins: model application with apolipoprotein A-I. Clin. Chem. 42, 1676–1682 (1996).
Gerber, S.A., Rush, J., Stemman, O., Kirschner, M.W. & Gygi, S.P. Absolute quantification of proteins and phosphoproteins from cell lysates by tandem MS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6940–6945 (2003).
Keshishian, H., Addona, T., Burgess, M., Kuhn, E. & Carr, S.A. Quantitative, multiplexed assays for low abundance proteins in plasma by targeted mass spectrometry and stable isotope dilution. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 2212 (2007).
Addona, T.A. et al. Multi-site assessment of the precision and reproducibility of multiple reaction monitoring-based measurements of proteins in plasma. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 633–641 (2009).
Brun, V., Masselon, C., Garin, J. & Dupuis, A. Isotope dilution strategies for absolute quantitative proteomics. J. Proteomics 72, 740–749 (2009).
Abbatiello, S.E., Mani, D.R., Keshishian, H. & Carr, S.A. Automated detection of inaccurate and imprecise transitions in quantitative assays of peptides by multiple monitoring mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 56, 291–305 (2010).
Reiter, L. et al. mProphet: automated data processing and statistical validation of large-scale SRM experiments. Nat. Methods 8, 430–435 (2011).
Remily-Wood, E.R. et al. A database of reaction monitoring mass spectrometry assays elucidating therapeutic response in cancer. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 5, 383–396 (2011).
Hüttenhain, R. et al. Reproducible quantification of cancer-associated proteins in body fluids using targeted proteomics. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 142ra94 (2012).
Addona, T.A. et al. A pipeline that integrates the discovery and verification of plasma protein biomarkers reveals candidate markers for cardiovascular disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 635–643 (2011).
Fortin, T. et al. Clinical quantitation of prostate-specific antigen biomarker in the low nanogram/milliliter range by conventional bore liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry multiple reaction monitoring coupling and correlation with ELISA tests. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 8, 1006–1015 (2009).
Shi, T. et al. Antibody-free, targeted mass-spectrometric approach for quantification of proteins at low picogram per milliliter levels in human plasma/serum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 15395–15400 (2012).
Berna, M.J. et al. Quantification of NTproBNP in rat serum using immunoprecipitation and LC/MS/MS: a biomarker of drug-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Anal. Chem. 80, 561–566 (2008).
Anderson, N.L. et al. Mass spectrometric quantitation of peptides and proteins using stable isotope standards and capture by anti-peptide antibodies (SISCAPA). J. Proteome Res. 3, 235–244 (2004).
Whiteaker, J.R., et al. Evaluation of large scale quantitative proteomic assay development using peptide affinity-based mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 10, M110.005645. (2011).
Neubert, H., Gale, J. & Muirhead, D. Online high-flow peptide immunoaffinity enrichment and nanoflow LC-MS/MS: assay development for total salivary pepsin/pepsinogen. Clin. Chem. 56, 1413–1423 (2010).
Whiteaker, J.R. et al. Sequential multiplexed analyte quantification using peptide immunoaffinity enrichment coupled to mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, M111.015347 (2012).
Kuhn, E., et al. Inter-laboratory evaluation of automated, multiplexed peptide immunoaffinity enrichment coupled to multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry for quantifying proteins in plasma. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, M111.013854. (2012).
Sparbier, K. et al. Immuno-MALDI-TOF MS: new perspectives for clinical applications of mass spectrometry. Proteomics 9, 1442–1450 (2009).
Rifai, N., Gillette, M.A. & Carr, S.A. Protein biomarker discovery and validation: the long and uncertain path to clinical utility. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 971–983 (2006).
Anderson, N.L. The clinical plasma proteome: a survey of clinical assays for proteins in plasma and serum. Clin. Chem. 56, 177–185 (2010).
Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. et al. Functional proteomics can define prognosis and predict pathologic complete response in patients with breast cancer. Clin. Proteomics 8, 11 (2011).
Ng, A.H.C., Uddayasankar, U. & Wheeler, A.R. Immunoassays in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 397, 991–1007 (2010).
Ellington, A.A., Kullo, I.J., Bailey, K.R. & Klee, G.G. Antibody-based protein multiplex platforms: technical and operational challenges. Clin. Chem. 56, 186–193 (2010).
Brody, E.N., Gold, L., Lawn, R.M., Walker, J.J. & Zichi, D. High-content affinity-based proteomics: unlocking protein biomarker discovery. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 10, 1013–1022 (2010).
Thiviyanathan, V. & Gorenstein, D.G. Aptamers and the next generation of diagnostic reagents. Proteomics Clin. Appl. advance online publication 23 October 2012 (doi:10.1002/prca.201200042).
Makawita, S. & Diamandis, E.P. The bottleneck in the cancer biomarker pipeline and protein quantification through mass spectrometry–based approaches: current strategies for candidate verification. Clin. Chem. 56, 212–222 (2010).
Smith, R.D. Mass spectrometry in biomarker applications: from untargeted discovery to targeted verification, and implications for platform convergence and clinical application. Clin. Chem. 58, 528–530 (2012).
Percy, A.J., Chambers, A.G., Yang, J., Domanski, D. & Borchers, C.H. Comparison of standard-flow and nano-flow liquid chromatography systems for MRM-based quantitation of putative plasma biomarker proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 404, 1089–1101 (2012).
Whiteaker, J.R. et al. A targeted proteomics-based pipeline for verification of biomarkers in plasma. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 625–634 (2011).
Domanski, D. et al. MRM-based multiplexed quantitation of 67 putative cardiovascular disease biomarkers in human plasma. Proteomics 12, 1222–1243 (2012).
Pan, S. et al. Multiplex targeted proteomic assay for biomarker detection in plasma: a pancreatic cancer biomarker case study. J. Proteome Res. 11, 1937–1948 (2012).
Wang, Q. et al. Mutant proteins as cancer-specific biomarkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 2444–2449 (2011).
Hoofnagle, A.N., Becker, J.O., Wener, M.H. & Heinecke, J.W. Quantification of thyroglobulin, a low-abundance serum protein, by immunoaffinity peptide enrichment and tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 54, 1796–1804 (2008).
Jaffe, J.D. et al. Accurate inclusion mass screening: a bridge from unbiased discovery to targeted assay development for biomarker verification. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 7, 1952–1962 (2008).
Gillet, L.C. et al. Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data independent acquisition: a new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, 1–17 (2012).
Gallien, S. et al. Targeted proteomic quantification on quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Mol. Cell. Proteomics advance online publication 7 September 2012 (doi:10.1074/mcp.O112.019802).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Gaffney for her help with graphics. This work was supported in part by the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and by grants from the US National Cancer Institute (U24CA160034, part of the Clinical Proteomics Tumor Analysis Consortium initiative, to S.A.C.) and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (HHSN268201000033C and R01HL096738 to S.A.C.). S.A.C. and M.A.G. acknowledge the financial support of the Women's Cancer Research Fund of the Entertainment Industry Foundation and the Komen Foundation for funding portions of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillette, M., Carr, S. Quantitative analysis of peptides and proteins in biomedicine by targeted mass spectrometry. Nat Methods 10, 28–34 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2309
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2309
This article is cited by
-
Quantification of putative ovarian cancer serum protein biomarkers using a multiplexed targeted mass spectrometry assay
Clinical Proteomics (2024)
-
Proteomic discovery of prognostic protein biomarkers for persisting problems after mild traumatic brain injury
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
LINE-1 ORF1p as a candidate biomarker in high grade serous ovarian carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics define the natural history of autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease
Nature Medicine (2023)
-
Plasma protein biomarker model for screening Alzheimer disease using multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry
Scientific Reports (2022)