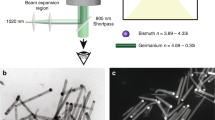
Abstract
Semiconductor nanowires have received much attention owing to their potential use as building blocks of miniaturized electrical1, nanofluidic2 and optical devices3. Although chemical nanowire synthesis procedures have matured and now yield nanowires with specific compositions4 and growth directions5, the use of these materials in scientific, biomedical and microelectronic applications is greatly restricted owing to a lack of methods to assemble nanowires into complex heterostructures with high spatial and angular precision. Here we show that an infrared single-beam optical trap can be used to individually trap, transfer and assemble high-aspect-ratio semiconductor nanowires into arbitrary structures in a fluid environment. Nanowires with diameters as small as 20 nm and aspect ratios of more than 100 can be trapped and transported in three dimensions, enabling the construction of nanowire architectures that may function as active photonic devices. Moreover, nanowire structures can now be assembled in physiological environments, offering new forms of chemical, mechanical and optical stimulation of living cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, W. U., Chen, C., Lin, K. H., Fang, Y. & Lieber, C. M. Label-free detection of small-molecule-protein interactions by using nanowire nanosensors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3208–3212 (2005).
Karnik, R. et al. Electrostatic control of ions and molecules in nanofluidic transistors. Nano Lett. 5, 943–948 (2005).
Sirbuly, D. J., Law, M., Yan, H. Q. & Yang, P. D. Semiconductor nanowires for subwavelength photonics integration. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 15190–15213 (2005).
Xia, Y. N. et al. One-dimensional nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater. 15, 353–389 (2003).
Kuykendall, T. et al. Crystallographic alignment of high-density gallium nitride nanowire arrays. Nature Mater. 3, 524–528 (2004).
Smith, P. A. et al. Electric-field assisted assembly and alignment of metallic nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1399–1401 (2000).
Chen, M. et al. Tuning the response of magnetic suspensions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3310–3312 (2003).
Messer, B., Song, J. H. & Yang, P. D. Microchannel networks for nanowire patterning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 10232–10233 (2000).
Yang, P. Nanotechnology: Wires on water. Nature 425, 243–244 (2003).
Law, M., Goldberger, J. & Yang, P. D. Semiconductor nanowires and nanotubes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 34, 83–122 (2004).
Nugent-Glandorf, L. & Perkins, T. T. Measuring 0.1-nm motion in 1 ms in an optical microscope with differential back-focal-plane detection. Opt. Lett. 29, 2611–2613 (2004).
Korda, P., Spalding, G. C., Dufresne, E. R. & Grier, D. G. Nanofabrication with holographic optical tweezers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 1956–1957 (2002).
Ashkin, A., Dziedzic, J. M., Bjorkholm, J. E. & Chu, S. Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt. Lett. 11, 288–290 (1986).
Grier, D. G. A revolution in optical manipulation. Nature 424, 810–816 (2003).
Sato, S., Harada, Y. & Waseda, Y. Optical trapping of microscopic metal particles. Opt. Lett. 19, 1807–1809 (1994).
Svoboda, K. & Block, S. M. Optical trapping of metallic Rayleigh particles. Opt. Lett. 19, 930–932 (1994).
Friese, M. E. J., Nieminen, T. A., Heckenberg, N. R. & Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. Optical alignment and spinning of laser-trapped microscopic particles. Nature 394, 348–350 (1998).
Yu, T., Cheong, F. C. & Sow, C. H. The manipulation and assembly of CuO nanorods with line optical tweezers. Nanotechnol. 15, 1732–1736 (2004).
Gauthier, R. C. Theoretical investigation of the optical trapping force and torque on cylindrical micro-objects. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 14, 3323–3333 (1997).
Gauthier, R. C., Ashman, M. & Grover, C. P. Experimental confirmation of the optical-trapping properties of cylindrical objects. Appl. Opt. 38, 4861–4869 (1999).
Shelton, W. A., Bonin, K. D. & Walker, T. G. Nonlinear motion of optically torqued nanorods. Phys. Rev. E 71, 036204 (2005).
Kress, H., Stelzer, E. H. K. & Rohrbach, A. Tilt angle dependent three-dimensional-position detection of a trapped cylindrical particle in a focused laser beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4271–4273 (2004).
Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H., Nieminen, T. A., Friese, M. E. J. & Heckenberg, N. R. Optical trapping of absorbing particles. Adv. Quant. Chem. 30, 469–492 (1998).
Wu, Y. Y. & Yang, P. D. Melting and welding semiconductor nanowires in nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 13, 520–523 (2001).
Johnson, J. C., Yan, H. Q., Yang, P. D. & Saykally, R. J. Optical cavity effects in ZnO nanowire lasers and waveguides. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 8816–8828 (2003).
Thompson, R. E., Larson, D. R. & Webb, W. W. Precise nanometer localization analysis for individual fluorescent probes. Biophys. J. 82, 2775–2783 (2002).
Gelles, J., Schnapp, B. J. & Sheetz, M. P. Tracking kinesin-driven movements with nanometre-scale precision. Nature 331, 450–453 (1988).
Ashkin, A., Dziedzic, J. M. & Yamane, T. Optical trapping and manipulation of single cells using infrared-laser beams. Nature 330, 769–771 (1987).
Sirbuly, D. J. et al. Optical routing and sensing with nanowire assemblies. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7800–7805 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Choy, J. Feigelman, C. Hodges, the Yang Lab (A. Tao, H. Yan, A. Hochbaum and D. Sirbuly) and M. van Duijn. P.J.P. thanks the NSF for Graduate Research Support and H.S. thanks the Hertz Foundation. This work was supported in part by the University of California, Berkeley (J.L.), the Beckman Foundation and the Department of Energy (P.Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures 1, 2 and 3; movie legends (PDF 222 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary movie 1 (AVI 106 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary movie 2 (AVI 278 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary movie 3 (AVI 2798 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pauzauskie, P., Radenovic, A., Trepagnier, E. et al. Optical trapping and integration of semiconductor nanowire assemblies in water. Nature Mater 5, 97–101 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1563
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1563
This article is cited by
-
Auto-alignment of CdS nanowires via optical tweezers
Applied Physics A (2022)
-
Optical tweezers beyond refractive index mismatch using highly doped upconversion nanoparticles
Nature Nanotechnology (2021)
-
Optical trapping using transverse electromagnetic (TEM)-like mode in a coaxial nanowaveguide
Frontiers of Optoelectronics (2021)
-
Structured Back Focal Plane Interferometry (SBFPI)
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Optically oriented attachment of nanoscale metal-semiconductor heterostructures in organic solvents via photonic nanosoldering
Nature Communications (2019)