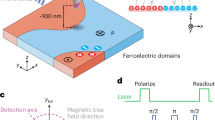
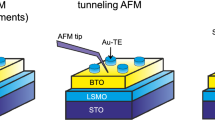
Abstract
Control of the density of mobile charge carriers using electric fields is widely used in a variety of metal–insulator–semiconductor structures and is the governing principle behind the operation of field-effect transistors. Ferroelectric materials possessing a switchable and non-volatile polarization field can be used as insulating layers, revealing new opportunities for device applications1,2. Advances in material processing and in particular complex oxide thin-film growth mean that high-quality field-effect devices can be based on ferroelectric/metallic oxide heterostructures3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11. In addition, advances in local probe techniques such as atomic force microscopy allow them to be used in the imaging and study of small ferroelectric domain structures in bulk crystals12 and thin films13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20. Meanwhile, scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy have established themselves as powerful techniques for atomic manipulation and nanometre-resolution electron tunnelling spectroscopy21,22. Here, a scanning tunnelling microscope is used to investigate the ferroelectric field effect in all-perovskite heterostructures. Scanning tunnelling spectroscopy allows us to probe the local electronic properties of the polarized channel of a ferroelectric field-effect device as a function of the field orientation. This technique can be used to read and write ferroelectric field-induced regions with a size as low as 20 nm.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott, J. F. & Paz de Araujo, C. A. Ferroelectric memories. Science 246, 1400–1405 (1989).
Auciello, O., Scott, J. F. & Ramesh, R. The physics of ferroelectric memories. Phys. Today 51, 22–27 (1998).
Watanabe, Y. Epitaxial all-perovskite ferroelectric field effect transistor with a memory retention. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 1770–1772 (1995).
Ahn, C. H. et al. Ferroelectric field effect in epitaxial thin film oxide SrCuO2/Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.58)O3 heterostructures. Science 269, 373–376 (1995).
Mathews, S., Ramesh, R., Venkatesan, T. & Benedetto, J. Ferroelectric field effect transistor based on epitaxial perovskite heterostructures. Science 276, 238–240 (1997).
Ahn, C. H., Triscone, J.-M. & Mannhart, J. Electric field effect on correlated oxide systems. Nature 424, 1015–1018 (2003).
Schrott, A. G., Misewich, J. A., Nagarajan, V. & Ramesh, R. Ferroelectric field-effect transistor with a SrRuxTi1−xO3 channel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4770–4772 (2003).
Wu, T. et al. Electroresistance and electronic phase separation in mixed-valent manganites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5998–6001 (2001).
Hong, X., Posadas, A., Lin, A. & Ahn, C. H. Ferroelectric-field-induced tuning of magnetism in the colossal magnetoresistive oxide La1−xSrxMnO3 . Phys. Rev. B 68, 134415 (2003).
Kanki, T., Park, Y.-G., Tanaka, H. & Kawai, T. Electrical-field control of metal-insulator transition at room temperature in Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3/La1-xBaxMnO3 field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4860–4862 (2003).
Zhao, T. et al. Colossal magnetoresitive manganite-based ferroelectric field-effect transistor on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 750–752 (2004).
Eng, L. M., Friedrich, M., Fousek, J. & Günter, P. Deconvolution of topographic and ferroelectric contrast by noncontact and friction mode microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol B 14, 1191–1196 (1996).
Güthner, P. & Dransfeld, K. Local poling of ferroelectic polymers by scanning force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 1137–1139 (1992).
Gruverman, A., Auciello, O., Hatano, J. & Tokumoto, H. Scanning force microscopy as a tool for nanoscale study of ferroelectric domains. Ferroelectrics 184, 11–20 (1996).
Hidaka, T. et al. Formation and observation of 50 nm polarized domains in PbZr1−xTixO3 thin film using scanning probe microscope. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 2358–2359 (1996).
Tybell, T., Ahn, C. H. & Triscone, J.-M. Ferroelectricity in thin perovskite films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 856–858 (1999).
Paruch, P., Tybell, T. & Triscone, J.-M. Nanoscale control of ferroelectric polarization and domain size in epitaxial PZT thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 530–532 (2001).
Ahn, C., Rabe, K. M. & Triscone, J.-M. Ferroelectricity at the nanoscale: local polarization in oxide thin films and heterostructures. Science 303, 488–491 (2004).
Cho, Y. et al. Tbit/inch2 ferroelectric data storage based on scanning non-linear dielectric microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 4401–4403 (2002).
Ahn, C. H. et al. Local, nonvolatile electronic writing of epitaxial Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3/SrRuO3 heterostructures. Science 276, 1100–1103 (1997).
Eigler, D. M. & Schweizer, E. K. Positioning single atoms with a scanning tunnelling microscope. Nature 344, 524–526 (1990).
Crommie, M. F., Lutz, C. P. & Eigler, D. M. Confinement of electrons to quantum corrals on a metal surface. Science 262, 218–220 (1993).
Eom, C. B. et al. Fabrication and properties of epitaxial ferroelectric heterostructures with SrRuO3 isotropic metallic electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 63, 2570–2572 (1993).
Kuffer, O., Maggio-Aprile, I., Renner, C., Triscone, J.-M. & Fischer, Ø. Piezoelectric response of epitaxial Pb(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 films measured by scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 1701–1703 (2000).
Gupta, A., Hussey, B. W. & Shaw, T. M. Epitaxial growth of thin films of SrTi1−xRuxO3−δ by pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Res. Soc. Bull. 31, 1463–1470 (1996).
Kuffer, O. & Fischer, Ø. Low temperature growth of pseudocubic perovskites by rf magnetron sputtering for the realization of epitaxial ferroelectric-based heterostructures. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 0141031 (2005).
Watanabe, Y., Okano, M. & Masuda, A. Surface conduction on insulating BaTiO3 crystal suggesting an intrinsic surface electron layer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 332–335 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank Ch. Renner, J.-M. Triscone, T. Tybell and M. R. Eskildsen for valuable discussions, and A. P. Petrovic for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and through the National Centre of Competence in Research 'Materials with Novel Electronic Properties—MaNEP'.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuffer, O., Maggio-Aprile, I. & Fischer, Ø. Nanoscale ferroelectric field-effect writing and reading using scanning tunnelling spectroscopy. Nature Mater 4, 378–382 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1364
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1364
This article is cited by
-
Giant Electroresistive Ferroelectric Diode on 2DEG
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Effect of Mechanical Loads on Stability of Nanodomains in Ferroelectric Ultrathin Films: Towards Flexible Erasing of the Non-Volatile Memories
Scientific Reports (2014)