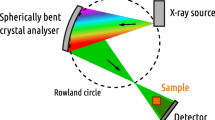
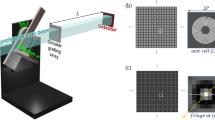
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) X-ray imaging methods have advanced tremendously during recent years. Traditional tomography uses absorption as the contrast mechanism, but for many purposes its sensitivity is limited. The introduction of diffraction1,2,3,4, small-angle scattering5,6,7, refraction8,9,10, and phase11,12,13,14 contrasts has increased the sensitivity, especially in materials composed of light elements (for example, carbon and oxygen). X-ray spectroscopy15,16,17,18,19, in principle, offers information on element composition and chemical environment. However, its application in 3D imaging over macroscopic length scales has not been possible for light elements. Here we introduce a new hard-X-ray spectroscopic tomography with a unique sensitivity to light elements. In this method, dark-field section images are obtained directly without any reconstruction algorithms. We apply the method to acquire the 3D structure and map the chemical bonding in selected samples relevant to materials science. The novel aspects make this technique a powerful new imaging tool, with an inherent access to the molecular-level chemical environment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larson, B. C., Yang, W., Ice, G. E., Budai, J. D. & Tischler, J. Z. Three-dimensional X-ray structural microscopy with submicrometre resolution. Nature 415, 887–890 (2002).
Schmidt, S. et al. Watching the growth of bulk grains during recrystallization of deformed metals. Science 305, 229–232 (2004).
Jensen, D. J. et al. X-ray microscopy in four dimensions. Mater. Today 9, 18–25 (2006).
Bleuet, P. et al. Probing the structure of heterogeneous diluted materials by diffraction tomography. Nature Mater. 7, 468–472 (2008).
Levine, L. E. & Long, G. G. X-ray imaging with ultra-small-angle X-ray scattering as a contrast mechanism. J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 757–765 (2004).
Schroer, C. G. et al. Mapping the local nanostructure inside a specimen by tomographic small-angle X-ray scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 164102 (2006).
Pfeiffer, F. et al. Hard-X-ray dark-field imaging using a grating interferometer. Nature Mater. 7, 134–137 (2008).
Chapman, D. et al. Diffraction enhanced X-ray imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 42, 2015–2025 (1997).
Bravin, A. Exploiting the X-ray refraction contrast with an analyser: The state of the art. J. Phys. D 36, A24–A29 (2003).
Fernández, M. et al. Human breast cancer in vitro: Matching histo-pathology with small-angle X-ray scattering and diffraction enhanced X-ray imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 2991–3006 (2005).
Davis, T. J., Gao, D., Gureyev, T. E., Stevenson, A. W. & Wilkins, S. W. Phase-contrast imaging of weakly absorbing materials using hard X-rays. Nature 373, 595–598 (1995).
Wilkins, S. W., Gureyev, T. E., Gao, D., Pogany, A. & Stevenson, A. W. Phase-contrast imaging using polychromatic hard X-rays. Nature 384, 335–338 (1996).
Snigirev, A., Snigireva, I., Kohn, V., Kuznetsov, S. & Schelokov, I. On the possibilities of X-ray phase contrast microimaging by coherent high-energy synchrotron radiation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66, 5486–5492 (1995).
Pfeiffer, F., Weitkamp, T., Bunk, O. & David, C. Phase retrieval and differential phase-contrast imaging with low-brilliance X-ray sources. Nature Phys. 2, 258–261 (2006).
Ade, H. et al. Chemical contrast in X-ray microscopy and spatially resolved XANES microscopy of organic specimens. Science 258, 972–975 (1992).
Schroer, C. G. et al. Mapping the chemical states of an element inside a sample using tomographic X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3360–3362 (2003).
Golosio, B. et al. Nondestructive three-dimensional elemental microanalysis by combined helical X-ray microtomographies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2199–2201 (2004).
Pascarelli, S., Mathon, O., Muñoz, M., Mairs, T. & Susini, J. Energy-dispersive absorption spectroscopy for hard-X-ray micro-XAS applications. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 13, 351–358 (2006).
Ade, H. & Stoll, H. Near-edge X-ray absorption fine-structure microscopy of organic and magnetic materials. Nature Mater. 8, 281–290 (2009).
Schülke, W. Electron Dynamics by Inelastic X-Ray Scattering (Oxford Univ. Press, 2007).
Shvyd’ko, Y. V., Stoupin, S., Cunsolo, A., Said, A. H. & Huang, X. High-reflectivity high-resolution X-ray crystal optics with diamonds. Nature Phys. 6, 196–199 (2010).
Hart, M. Synchrotron radiation—its application to high-speed, high-resolution X-ray-diffraction topography. J. Appl. Cryst. 8, 436–444 (1975).
Baruchel, J. et al. Phase imaging using highly coherent X-rays: Radiography, tomography, diffraction topography. J. Synchrotron Rad. 7, 196–201 (2000).
Mao, W. L. et al. Bonding changes in compressed superhard graphite. Science 302, 425–427 (2003).
Meng, Y. et al. The formation of s p3 bonding in compressed BN. Nature Mater. 3, 111–114 (2004).
Lee, S. K. et al. Probing of bonding changes in B2O3 glasses at high pressure with inelastic X-ray scattering. Nature Mater. 4, 851–854 (2005).
Verbeni, R. et al. Multiple-element spectrometer for non-resonant inelastic X-ray spectroscopy of electronic excitations. J. Synchrotron Rad. 16, 469–476 (2009).
Cai, Y. Q. et al. Optical design and performance of the Taiwan inelastic X-ray scattering beamline (BL12XU) at SPring-8. AIP Conf. Proc. 705, 340–343 (2004).
Fister, T. T. et al. Multielement spectrometer for efficient measurement of the momentum transfer dependence of inelastic X-ray scattering. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 063901 (2006).
Hignette, O., Cloetens, P., Rostaing, G., Bernard, P. & Morawe, C. Efficient sub 100 nm focusing of hard X rays. Rev. Sci. Instrum 76, 063709 (2005).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank L. Simonelli, V. Giordano, G. Vankó, H. Suhonen, A. Kallonen, C. Henriquet, C. Ponchut, and T. Ahlgren for their support, help, and invaluable discussions. T.P. and K.H. were supported by the Academy of Finland under the contract 1127462, and S.H. by University of Helsinki research funds (project 490076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.H., T.P., R.V., G.M. and K.H. designed and carried out the experiments and wrote the paper; S.H. and T.P. analysed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huotari, S., Pylkkänen, T., Verbeni, R. et al. Direct tomography with chemical-bond contrast. Nature Mater 10, 489–493 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3031
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3031
This article is cited by
-
Pressure driven spin transition in siderite and magnesiosiderite single crystals
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
X-ray induced dimerization of cinnamic acid: Time-resolved inelastic X-ray scattering study
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
A new X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy for extraterrestrial materials using a muon beam
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Pair distribution function computed tomography
Nature Communications (2013)
-
The chemistry inside
Nature (2011)