Volume 11
-
No. 12 December 2005
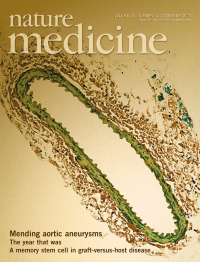
Abdominal aortic aneurysms can lead to aortic rupture and death. As shown by Aoki and colleagues on page 1330 of this issue, inhibition of Jnk kinase can cause regression of aortic aneurysms in mouse models. The cover image shows decreased dilation and more normal morphology of an aorta after treatment with a Jnk inhibitor.
-
No. 11 November 2005
Drugs that block chloride transport in the developing cerebral cortex may be useful to treat neonatal seizures, as shown by Staley and colleagues on page 1205 of this issue. Image of the cerebral cortex courtesy of Tom Deerinck (University of California, San Diego).
-
No. 10 October 2005
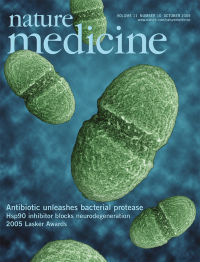
Acyldepsipeptides, a new class of antibiotics, have activity against Gram-positive bacteria-such as Enterococcus faecalis (shown here)-in vitro and in vivo (see page 1082). Photo by Nathan Shankar, University of Oklahoma. Courtesy of the Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture.
-
No. 9 September 2005
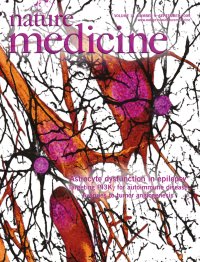
Epilepsy is thought to be a disorder of neuronal communication. But evidence presented in this issue by Tian and colleagues (p. 973) shows that astrocytes (black cells in this image) are actively involved in the pathogenesis of seizures, releasing glutamate in a calcium-dependent manner. Original image courtesy of the authors.
-
No. 8 August 2005
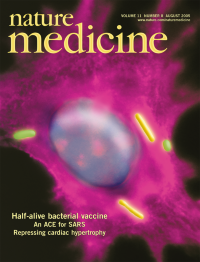
In this issue, Dubensky and colleagues show that killed but metabolically active (KBMA) microbes synthesize and secrete protein, but are unable to replicate due to their genetic and chemical attenuation. This image is based on a micrograph of a dendritic cell that has phagocytosed several KBMA Listeria monocytogenes (green). Protein secretion by this nonreplicating bacterium allows its escape into the cytosol and polymerization of host-cell actin (purple), which can be seen colocalized with the cytosolic bacterium (yellow). This new vaccine represents a safer alternative to traditional live Listeria-based vaccines and could have broad-ranging application in infectious disease and cancer. Image courtesy of Keith Bahjat and Maurice Tani.
-
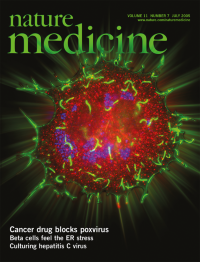
No. 7 July 2005
To escape from cells, vaccinia viruses are propelled on the tip of an actin-filled protuberance toward an opposing cell. The cover image shows an infected 3T3 cell in which the so-called actin tails are visible (green). Viral replication centers are shown in blue. In this issue, Kalman and colleagues show that Abl-family kinases (red) are required for release of the viruses from the actin tails and they find that inhibitors of Abl-family kinases can prevent the spread of virus and disable poxvirus pathogenesis in mice. Image courtesy of Daniel Kalman.
-
No. 6 June 2005
Simultaneous imaging of tumor blood vessels (red) and collagen fibers (blue) using two-photon microscopy and quantum dots. In this issue, Jain and colleagues show that quantum dots can be customized to concurrently image and differentiate tumor vessels from both the perivascular cells and the matrix. Image courtesy of Mark Stroh, Lance L. Munn and Edward B. Brown.
-
No. 5 May 2005
Two-photon fluorescence image of a section of mouse cerebellum immunostained for the inositol 1,4,5- trisphosphate receptor (concentrated in Purkinje neurons; green), actin (red) and DNA in cell nuclei (blue). In this issue, Wang and colleagues report on an essential role for the DNA damage response in the prevention of ataxia and cerebellar defects in a mouse model of Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Image courtesy of Thomas Deerinck and Mark Ellisman, the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research, University of California, San Diego.
-
No. 4 April 2005
Scanning electron micrograph of glomeruli in the human kidney. BMP agonists protect against renal fibrosis. In this issue, Dressler and colleagues (page 387) identify the first endogenous BMP enhancer and explore its role in kidney disease. SPL/Photo Researchers, Inc.
Supplement
-
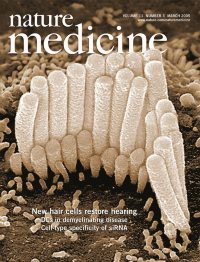
No. 3 March 2005
Hair cells in the mammalian cochlea are crucial for hearing. In this issue, Raphael and colleagues (p. 271) show that gene therapy with Atoh1 can promote the growth of new hair cells, leading to recovery of hearing in deaf guinea pigs. Photo courtesy of Yehoash Raphael
-
No. 2 February 2005
Electron micrograph of an islet of Langerhans cell in the mammalian pancreas. The red spots in white spaces are membrane-bound secretory granules containing insulin and glucagons. Two papers in this issue (pages 183 and 191) explore the relationship between inflammation and insulin resistance. SPL/Photo Researchers, Inc.
-
No. 1 January 2005
Endometriosis is a disorder in which the tissue lining of the uterus (the endometrium) is also found outside the uterus, and is associated with an increased risk of endometrioid ovarian cancer. In this issue (pages 63-70), Dinulescu and coworkers present the first genetic models of endometriosis and endometrioid ovarian adenocarcinoma, providing new avenues for insight into these diseases. The cover depicts endometrial tissue, with mucus-secreting cells in blue, secretions in pink and ciliated cells in yellow. Credit: P.M. Motta & S. Makabe/Photo Researchers, Inc.