Abstract
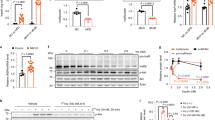
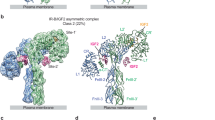
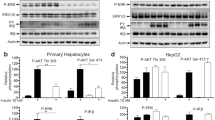
Met is the transmembrane tyrosine kinase cell surface receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and is structurally related to the insulin receptor (INSR) tyrosine kinase. Here we report that the HGF-Met axis regulates metabolism by stimulating hepatic glucose uptake and suppressing hepatic glucose output. We show that Met is essential for an optimal hepatic insulin response by directly engaging INSR to form a Met-INSR hybrid complex, which culminates in a robust signal output. We also found that the HGF-Met system restores insulin responsiveness in a mouse model of insulin refractoriness. These results provide new insights into the molecular basis of hepatic insulin resistance and suggest that HGF may have therapeutic potential for type 2 diabetes in the clinical setting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarnegar, R. & Michalopoulos, G.K. The many faces of hepatocyte growth factor: from hepatopoiesis to hematopoiesis. J. Cell Biol. 129, 1177–1180 (1995).
Birchmeier, C., Birchmeier, W., Gherardi, E. & Vande Woude, G.F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 915–925 (2003).
Borowiak, M. et al. Met provides essential signals for liver regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 10608–10613 (2004).
Corso, S., Comoglio, P.M. & Giordano, S. Cancer therapy: can the challenge be MET? Trends Mol. Med. 11, 284–292 (2005).
Huh, C.-G. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor/c-met signaling pathway is required for efficient liver regeneration and repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4477–4482 (2004).
De Meyts, P. Insulin and its receptor: structure, function and evolution. Bioessays 26, 1351–1362 (2004).
Lemmon, M.A. & Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 141, 1117–1134 (2010).
Hanke, S. & Mann, M. The phosphotyrosine interactome of the insulin receptor family and its substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2. Mol. Cell Proteomics 8, 519–534 (2009).
Johnston, A.M., Pirola, L. & Van Obberghen, E. Molecular mechanisms of insulin receptor substrate protein-mediated modulation of insulin signalling. FEBS Lett. 546, 32–36 (2003).
Myers, M.G. Jr. & White, M.F. Insulin signal transduction and the IRS proteins. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36, 615–658 (1996).
Saltiel, A.R. & Kahn, C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414, 799–806 (2001).
Gross, D.N., Wan, M. & Birnbaum, M.J. The role of FOXO in the regulation of metabolism. Curr. Diab. Rep. 9, 208–214 (2009).
Wang, X. et al. A mechanism of cell survival: sequestration of Fas by the HGF receptor Met. Mol. Cell 9, 411–421 (2002).
Song, E. et al. RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat. Med. 9, 347–351 (2003).
Taniguchi, C.M., Ueki, K. & Kahn, R. Complementary roles of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in the hepatic regulation of metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 718–727 (2005); erratum 115, 1388 (2005).
Surwit, R.S. et al. Alprazolam reduces stress hyperglycemia in ob/ob mice. Psychosom. Med. 48, 278–282 (1986).
Turner, S.M., Linfoot, P.A., Neese, R.A. & Hellerstein, M.K. Sources of plasma glucose and liver glycogen in fasted ob/ob mice. Acta Diabetol. 42, 187–193 (2005).
Appasamy, R. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor, blood clearance, organ uptake, and biliary excretion in normal and partially hepatectomized rats. Lab. Invest. 68, 270–276 (1993).
Liu, M.L., Mars, W.M., Zarnegar, R. & Michalopoulos, G.K. Uptake and distribution of hepatocyte growth factor in normal and regenerating adult rat liver. Am. J. Pathol. 144, 129–140 (1994).
Bertola, A. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor induces glucose uptake in 3T3–L1 adipocytes through A Gab1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Glut4 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10325–10332 (2007).
Perdomo, G. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor is a novel stimulator of glucose uptake and metabolism in skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13700–13706 (2008).
DeAngelis, T., Morrione, A. & Baserga, R. Mutual interaction and reciprocal down-regulation between c-met and insulin receptor substrate-1. J. Cell. Physiol. 224, 658–663 (2010).
Tomita, K. et al. Pioglitazone prevents alcohol-induced fatty liver in rats through up-regulation of c-Met. Gastroenterology 126, 873–885 (2004).
Jiang, J.G., Johnson, C. & Zarnegar, R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated transcriptional up-regulation of the hepatocyte growth factor gene promoter via a novel composite cis-acting element. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25049–25056 (2001).
Kosone, T. et al. HGF ameliorates a high-fat diet-induced fatty liver. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 293, G204–G210 (2007).
Marsenic, O. Glucose control by the kidney: an emerging target in diabetes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 53, 875–883 (2009).
Mellado-Gil, J. et al. Disruption of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling enhances pancreatic beta-cell death and accelerates the onset of diabetes. Diabetes 60, 525–536 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We thank G.K. Michalopoulos and S. Strom (University of Pittsburgh) for providing primary rodent and human hepatocyte cultures. We also thank A. Eaker and C. Johnson for their technical assistance. This study was supported by an R01 grant (R01NIAA001871301) awarded to R.Z. by the US National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.Z. developed the hypothesis, designed the experimental approaches and interpreted data. A.F. and J.M. performed experiments, collected data and performed analyses. M.C.D. helped with the histological studies and data interpretation. J.L. performed the gene array studies. J.S. and X.T. performed mouse injection experiments, mouse tissue harvesting, immunohistostaining and other technical assays.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1309 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fafalios, A., Ma, J., Tan, X. et al. A hepatocyte growth factor receptor (Met)−insulin receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat Med 17, 1577–1584 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2531
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2531
This article is cited by
-
Basal MET phosphorylation is an indicator of hepatocyte dysregulation in liver disease
Molecular Systems Biology (2024)
-
Potential mechanisms underlying the effect of hepatocyte growth factor on liver injury in short bowel syndrome model rats
Pediatric Surgery International (2023)
-
β2-adrenergic receptor promotes liver regeneration partially through crosstalk with c-met
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2021)
-
HGF can reduce accumulation of inflammation and regulate glucose homeostasis in T2D mice
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2021)