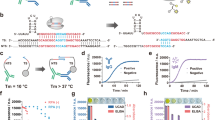
Abstract
The ability to detect antigens immunologically is limited by the affinity of the antibodies and the amount of antigens. We have now succeeded in creating a modular, facile amplification system, termed fluorescent amplification catalyzed by T7 polymerase technique (FACTT). Such a system can detect protein targets specifically at subfemtomolar levels (∼0.08 fM). We describe here the detection of Her2 (also known as Neu) from rodent and human sera. FACTT is adaptable to high-throughput screening and automation and provides a practical method to enhance current ELISAs in medical practice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porstmann, T. & Kiessig, S.T. Enzyme immunoassay techniques. An overview. J. Immunol. Methods 150, 5–21 (1992).
Porstmann, B., Porstmann, T., Nugel, E. & Evers, U. Which of the commonly used marker enzymes gives the best results in colorimetric and fluorimetric enzyme immunoassays: horseradish peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase or beta-galactosidase? J. Immunol. Methods 79, 27–37 (1985).
Zhang, H.T., Kacharmina, J.E., Miyashiro, K., Greene, M.I. & Eberwine, J. Protein quantification from complex protein mixtures using a proteomics methodology with single-cell resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5497–5502 (2001).
Jones, L.J., Yue, S.T., Cheung, C.Y. & Singer, V.L. RNA quantitation by fluorescence-based solution assay: RiboGreen reagent characterization. Anal. Biochem. 265, 368–374 (1998).
Slamon, D.J. et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 244, 707–712 (1989).
Cohen, J.A. et al. Expression pattern of the neu (NGL) gene-encoded growth factor receptor protein (p185neu) in normal and transformed epithelial tissues of the digestive tract. Oncogene 4, 81–88 (1989).
Lodato, R.F., Maguire, H.C., Jr., Greene, M.I., Weiner, D.B. & LiVolsi, V.A. Immunohistochemical evaluation of c-erbB-2 oncogene expression in ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast. Mod. Pathol. 3, 449–454 (1990).
Maguire, H.C., Jr. & Greene, M.I. Neu (c-erbB-2), a tumor marker in carcinoma of the female breast. Pathobiology 58, 297–303 (1990).
Williams, T.M., Weiner, D.B., Greene, M.I. & Maguire, H.C., Jr. Expression of c-erbB-2 in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Pathobiology 59, 46–52 (1991).
Jardines, L., Weiss, M., Fowble, B. & Greene, M. neu(c-erbB-2/HER2) and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in breast cancer. Pathobiology 61, 268–282 (1993).
Kandl, H., Seymour, L. & Bezwoda, W.R. Soluble c-erbB-2 fragment in serum correlates with disease stage and predicts for shortened survival in patients with early-stage and advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 70, 739–742 (1994).
Fehm, T., Maimonis, P., Katalinic, A. & Jager, W.H. The prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 serum protein in metastatic breast cancer. Oncology 55, 33–38 (1998).
Yamauchi, H. et al. Prediction of response to antiestrogen therapy in advanced breast cancer patients by pretreatment circulating levels of extracellular domain of the HER-2/c-neu protein. J. Clin. Oncol. 15, 2518–2525 (1997).
Park, B.W. et al. Rationally designed anti-HER2/neu peptide mimetic disables P185HER2/neu tyrosine kinases in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 194–198 (2000).
Di Leo, A., Dowsett, M., Horten, B. & Penault-Llorca, F. Current status of HER2 testing. Oncology 63, 25–32 (2002).
Vogel, C.L. et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 719–726 (2002).
Saghatchian, M. et al. Serum HER-2 extracellular domain: Relationship with clinicobiological presentation and prognostic value before and after primary treatment in 701 breast cancer patients. Int. J. Biol. Markers 19, 14–22 (2004).
Luftner, D. et al. Discordant results obtained for different methods of HER-2/neu testing in breast cancer — a question of standardization, automation and timing. Int. J. Biol. Markers 19, 1–13 (2004).
Schweitzer, B. et al. Inaugural article: immunoassays with rolling circle DNA amplification: a versatile platform for ultrasensitive antigen detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 10113–10119 (2000).
Schweitzer, B. et al. Multiplexed protein profiling on microarrays by rolling-circle amplification. Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 359–365 (2002).
Tannous, B.A., Laios, E. & Christopoulos, T.K. T7 RNA polymerase as a self-replicating label for antigen quantification. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, e140 (2002).
Arnold, S. et al. Kinetic modeling and simulation of in vitro transcription by phage T7 RNA polymerase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 72, 548–561 (2001).
Nam, J.M., Thaxton, C.S. & Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science 301, 1884–1886 (2003).
Lubec, G., Krapfenbauer, K. & Fountoulakis, M. Proteomics in brain research: potentials and limitations. Prog. Neurobiol. 69, 193–211 (2003).
Li, P., Li, Y., Li, J.Y. & Liu, J. Characterization and utilization of two novel anti-erbB-2 monoclonal antibodies in detection of soluble ErbB-2 for breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Lett. 193, 139–148 (2003).
Zhang, H. et al. Shared antigenic epitopes and pathobiological functions of anti-p185(her2/neu) monoclonal antibodies. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 67, 15–25 (1999).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Abramson Family Cancer Research Institute to M.I.G. We thank X. (G.) Xu for the control sera from healthy volunteers and A. Massey for the preparation of the illustration for FACTT in Figure 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Cheng, X., Richter, M. et al. A sensitive and high-throughput assay to detect low-abundance proteins in serum. Nat Med 12, 473–477 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1378
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1378
This article is cited by
-
The successes and future prospects of the linear antisense RNA amplification methodology
Nature Protocols (2018)
-
Direct ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensing of pathogenic DNA using homogeneous target-initiated transcription amplification
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Monitoring serum HER2 levels in breast cancer patients
SpringerPlus (2015)
-
Is “liquid biopsy” useful for assessing HER2 status in gastric cancer?
Journal of Gastroenterology (2015)
-
Sensitive monitoring of RNA transcription levels using a graphene oxide fluorescence switch
Chinese Science Bulletin (2013)