Abstract
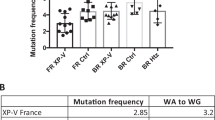
To determine whether DNA polymerase η plays a role in the hypermutation of immunoglobulin variable genes, we examined the frequency and pattern of substitutions in variable VH6 genes from the peripheral blood lymphocytes of three patients with xeroderma pigmentosum variant disease, whose polymerase η had genetic defects. The frequency of mutation was normal but the types of base changes were different: there was a decrease in mutations at A and T and a concomitant rise in mutations at G and C. We propose that more than one polymerase contributes to hypermutation and that if one is absent, others compensate. The data indicate that polymerase η is involved in generating errors that occur predominantly at A and T and that another polymerase(s) may preferentially generate errors opposite G and C.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wood, R. D., Gearhart, P. J. & Neuberger, M. S. Hypermutation in antibody genes. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 356, 1–125 (2001).
Jacob, J., Kelsoe, G., Rajewsky, K. & Weiss, U. Intraclonal generation of antibody mutants in germinal centres. Nature 354, 389–392 (1991).
Gearhart, P. J. & Bogenhagen, D. F. Clusters of point mutations are found exclusively around rearranged antibody variable genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 80, 3439–3443 (1983).
Betz, A. G. et al. Elements regulating somatic hypermutation of an immunoglobulin κ gene: critical role for the intron enhancer/matrix attachment region. Cell 77, 239–248 (1994).
Lebecque, S. G. & Gearhart, P. J. Boundaries of somatic mutation in rearranged immunoglobulin genes: 5′ boundary is near the promoter, and 3′ boundary is about 1 kb from V(D)J gene. J. Exp. Med. 172, 1717–1727 (1990).
Smith, D. S. et al. Di- and trinucleotide target preferences of somatic mutagenesis in normal and autoreactive B cells. J. Immunol. 156, 2642–2652 (1996).
Foster, S. J., Dörner, T. & Lipsky, P. E. Targeting and subsequent selection of somatic hypermutations in the human Vκ repertoire. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 3122–3132 (1999).
Rogozin, I. B. & Kolchanov, N. A. Somatic hypermutagenesis in immunoglobulin genes. II. Influence of neighbouring base sequences on mutagenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1171, 11–18 (1992).
Bross, L. et al. DNA double-strand breaks in immunoglobulin genes undergoing somatic hypermutation. Immunity 13, 589–597 (2000).
Papavasiliou, F. N. & Schatz, D. G. Cell-cycle-regulated DNA double-strand breaks in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes. Nature 408, 216–221 (2000).
Johnson, R.E., Washington, M.T., Haracska, L., Prakash, S. & Prakash, L. Eukaryotic polymerases ι and ζ act sequentially to bypass DNA lesions. Nature 406, 1015–1019 (2000).
Wittschieben, J. et al. Disruption of the developmentally regulated Rev3l gene causes embryonic lethality. Curr. Biol. 10, 1217–1220 (2000).
Johnson, R. E., Washington, M. T., Prakash, S. & Prakash, L. Fidelity of human DNA polymerase η. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7447–7450 (2000).
Matsuda, T., Bebenek, K., Masutani, C., Hanaoka, F. & Kunkel, T. A. Low fidelity DNA synthesis by human DNA polymerase-η. Nature 404, 1011–1013 (2000).
Masutani, C., Kusumoto, R., Iwai, S. & Hanaoka, F. Mechanisms of accurate translesion synthesis by human DNA polymerase η. EMBO J. 19, 3100–3109 (2000).
Tissier, A., McDonald, J. P., Frank, E. G. & Woodgate, R. Polι, a remarkably error- prone human DNA polymerase. Genes Dev. 14, 1642–1650 (2000).
Domínguez, O. et al. DNA polymerase mu (Pol μ), homologous to TdT, could act as a DNA mutator in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 19, 1731–1742 (2000).
Aoufouchi, S. et al. Two novel human and mouse DNA polymerases of the polX family. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 3684–3693 (2000).
Sharief, F. S., Vojta, P. J., Ropp, P. A. & Copeland W. C. Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), the eighth human DNA polymerase. Genomics 59, 90–96 (1999).
Ohashi, E. et al. Fidelity and processivity of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase κ, the product of the human DINB1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 39678–39684 (2000).
García-Díaz, M. et al. DNA polymerase lambda (Pol λ),, a novel eukaryotic DNA polymerase with a potential role in meiosis. J. Mol. Biol. 301, 851–867 (2000).
Masutani, C. et al. The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase η. Nature 399, 700–704 (1999).
Johnson, R. E., Kondratick, C. M., Prakash, S. & Prakash, L. hRAD30 mutations in the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum. Science 285, 263–265 (1999).
Lehmann, A. R. et al. Xeroderma pigmentosum cells with normal levels of excision repair have a defect in DNA synthesis after UV-irradiation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 72, 219–223 (1975).
Wang, Y. C., Maher, V. M., Mitchell, D. L. & McCormick, J. J. Evidence from mutation spectra that the UV hypermutability of xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells reflects abnormal, error-prone replication on a template containing photoproducts. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 4276–4283 (1993).
Winter, D. B., Phung, Q. H., Wood, R. D. & Gearhart, P. J. Differential expression of DNA polymerase ɛ in resting and activated B lymphocytes is consistent with an in vivo role in replication and not repair. Mol. Immunol. 37, 125–131 (2000).
Sale, J. E. & Neuberger, M. S. TdT-accessible breaks are scattered over the immunoglobulin V domain in a constitutively hypermutating B cell line. Immunity 9, 859–869 (1998).
Denepoux, S. et al. Induction of somatic mutation in a human B cell line in vitro. Immunity 6, 35–46 (1997).
Kraemer, K. H. & Slor, H. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Clin. Dermatol. 3, 33–69 (1985).
Berth-Jones, J. & Graham-Brown, R. A. C. Xeroderma pigmentosum variant: response to etretinate. Brit. J. Dermatol. 122, 559–561 (1990).
Sanz, I. et al. The smaller human VH gene families display remarkably little polymorphism. EMBO J. 8, 3741–3748 (1989).
Corbett, S. J., Tomlinson, I. M., Sonnhammer, E. L. L., Buck, D. & Winter, G. Sequence of the human immunoglobulin diversity (D) segment locus: a systematic analysis provides no evidence for the use of DIR segments, inverted D segments, “minor” D segments or D-D recombination. J. Mol. Biol. 270, 587–597 (1997).
Rosner, K. et al. Impact of age on hypermutation of immunoglobulin variable genes in humans. J. Clin. Immunol. 21, 102–115 (2001).
Johnson, R. E., Prakash, S. & Prakash, L. Efficient bypass of a thymine-thymine dimer by yeast DNA polymerase, polη. Science 283, 1001–1004 (1999).
Nelson, J. R., Lawrence, C. W. & Hinkle, D. C. Thymine-thymine dimer bypass by yeast DNA polymerase ζ. Science 272, 1646–1649 (1996).
Yamada, A., Masutani, C., Iwai, S. & Hanaoka, F. Complementation of defective translesion synthesis and UV light sensitivity in xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells by human and mouse DNA polymerase η. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 2473–2480 (2000).
Kannouche, P. et al. Domain structure, localization, and function of DNA polymerase η, defective in xeroderma pigmentosum variant cells. Genes Dev. 15, 158–172 (2001).
Brezinschek, H. P., Foster, S. J., Dörner, T., Brezinschek, R. I. & Lipsky, P. E. Pairing of variable heavy and variable κ chains in individual naive and memory B cells. J. Immunol. 160, 4762–4767 (1998).
Rosner, K. et al. Third complementarity-determining region of mutated VH immunoglobulin genes contains shorter V, D, J., P, and N components than nonmutated genes. Immunology 103, (in the press, 2001).
Winter, D. B. et al. Altered spectra of hypermutation in antibodies from mice deficient for the DNA mismatch repair protein PMS2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6953–6958 (1998).
Goodman, M. F. & Tippin, B. The expanding polymerase universe. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 101–109 (2000).
Spencer, J., Dunn, M. & Dunn-Walters, D. K. Characteristics of sequences around individual nucleotide substitutions in IgVH genes suggest different GC and AT mutators. J. Immunol. 162, 6596–6601 (1999).
Rogozin, I. B., Pavlov, Y. I., Bebenek, K., Matsuda, T. & Kunkel, T. A. Correlation between hotspots for somatic mutation in immunoglobulin genes and DNA synthesis errors by DNA polymerase η. Nature Immunol. 2, 530–536 (2001).
Phung, Q. H. et al. Increased hypermutation at G and C nucleotides in immunoglobulin variable genes from mice deficient in the MSH2 mismatch repair protein. J. Exp. Med. 187, 1745–1751 (1998).
Wiesendanger, M., Kneitz, B., Edelmann, W. & Scharff, M. D. Somatic hypermutation in MutS homologue (MSH)3-, MSH6-, and MSH3/MSH6-deficient mice reveals a role for the MSH2-MSH6 heterodimer in modulating the base substitution pattern. J. Exp. Med. 191, 579–584 (2000).
Kim, N., Bozet, G., Lo, J.C. & Storb, U. Different mismatch repair deficiencies all have the same effects on somatic hypermutation: intact primary mechanism accompanied by secondary modifications. J. Exp. Med. 190, 21–30 (1999).
Pâques, F. & Haber, J. E. Multiple pathways of recombination induced by double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Micro. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63, 349–404 (1999).
Frank, E. G. et al. Altered nucleotide misinsertion fidelity associated with polι-dependent replication at the end of a DNA template. EMBO J. 20 (in the press, 2001).
Tissier, A. et al. Misinsertion and bypass of thymine-thymine dimers by human DNA polymerase ι. EMBO J. 19, 5259–5266 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Tarone for statistical analyses, B. C. Broughton for the sequence analysis of the mutations in polymerase η in XP7BR and XP11BR, C. F. Arlett for the blood samples of XP7BR and XP11BR and F. Hanoaka for supplying intron information for murine polymerase η. We also thank R. Wood, K. Rosner and V. Bohr for critical comments and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, X., Winter, D., Kasmer, C. et al. DNA polymerase η is an A-T mutator in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin variable genes. Nat Immunol 2, 537–541 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/88740
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/88740
This article is cited by
-
In crystallo observation of three metal ion promoted DNA polymerase misincorporation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Unravelling roles of error-prone DNA polymerases in shaping cancer genomes
Oncogene (2021)
-
FAM72A antagonizes UNG2 to promote mutagenic repair during antibody maturation
Nature (2021)
-
Large deletions in immunoglobulin genes are associated with a sustained absence of DNA Polymerase η
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Multifaceted activities of DNA polymerase η: beyond translesion DNA synthesis
Current Genetics (2019)