Abstract
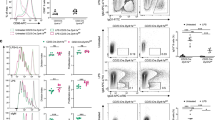
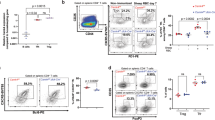
Immunoglobulin class switching is crucial for the generation of antibody diversity in humoral immunity and, when deregulated, also has severe pathological consequences. How the magnitude of immunoglobulin isotype switching is controlled is still poorly understood. Here we identify the kinase TBK1 as a pivotal negative regulator of class switching to the immunoglobulin A (IgA) isotype. B cell–specific ablation of TBK1 in mice resulted in uncontrolled production of IgA and the development of nephropathy-like disease signs. TBK1 negatively regulated IgA class switching by attenuating noncanonical signaling via the transcription factor NF-κB, an action that involved TBK1-mediated phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of the NF-κB-inducing kinase NIK. Our findings establish TBK1 as a pivotal negative regulator of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway and identify a unique mechanism that controls IgA production.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 October 2012
In the version of this article initially published online, the word "isotype" was misspelled in the fourth line of the abstract. The third sentence of the abstract should read, "Here we identify the kinase TBK1 as a pivotal negative regulator of class switching to the immunoglobulin A (IgA) isotype." The error has been corrected for the print, PDF and HTML versions of this article.
References
Macpherson, A.J., McCoy, K.D., Johansen, F.E. & Brandtzaeg, P. The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal Immunol. 1, 11–22 (2008).
Park, M.A., Li, J.T., Hagan, J.B., Maddox, D.E. & Abraham, R.S. Common variable immunodeficiency: a new look at an old disease. Lancet 372, 489–502 (2008).
Papista, C., Berthelot, L. & Monteiro, R.C. Dysfunctions of the Iga system: a common link between intestinal and renal diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 8, 126–134 (2011).
Wang, J. et al. Dysregulated LIGHT expression on T cells mediates intestinal inflammation and contributes to IgA nephropathy. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 826–835 (2004).
McCarthy, D.D., Chiu, S., Gao, Y., Summers-deLuca, L.E. & Gommerman, J.L. BAFF induces a hyper-IgA syndrome in the intestinal lamina propria concomitant with IgA deposition in the kidney independent of LIGHT. Cell. Immunol. 241, 85–94 (2006).
McCarthy, D.D. et al. Mice overexpressing BAFF develop a commensal flora-dependent, IgA-associated nephropathy. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 3991–4002 (2011).
Cazac, B.B. & Roes, J. TGF-β receptor controls B cell responsiveness and induction of IgA in vivo. Immunity 13, 443–451 (2000).
Litinskiy, M.B. et al. DCs induce CD40-independent immunoglobulin class switching through BLyS and APRIL. Nat. Immunol. 3, 822–829 (2002).
Castigli, E. et al. TACI and BAFF-R mediate isotype switching in B cells. J. Exp. Med. 201, 35–39 (2005).
Castigli, E. et al. Impaired IgA class switching in APRIL-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3903–3908 (2004).
Cerutti, A. The regulation of IgA class switching. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 421–434 (2008).
Tezuka, H. et al. Prominent role for plasmacytoid dendritic cells in mucosal T cell-independent IgA induction. Immunity 34, 247–257 (2011).
Hayden, M.S. & Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell 132, 344–362 (2008).
Vallabhapurapu, S. & Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27, 693–733 (2009).
Sun, S.C. The noncanonical NF-κB pathway. Immunol. Rev. 246, 125–140 (2012).
Tucker, E. et al. A novel mutation in the Nfkb2 gene generates an NF-κB2 “super repressor”. J. Immunol. 179, 7514–7522 (2007).
Shinkura, R. et al. Alymphoplasia is caused by a point mutation in the mouse gene encoding Nf-κb-inducing kinase. Nat. Genet. 22, 74–77 (1999).
Caamano, J.H. et al. Nuclear factor (NF)-κB2 (p100/p52) is required for normal splenic microarchitecture and B cell-mediated immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 187, 185–196 (1998).
Franzoso, G. et al. Mice deficient in nuclear factor (NF)-κB/p52 present with defects in humoral responses, germinal center reactions, and splenic microarchitecture. J. Exp. Med. 187, 147–159 (1998).
Snapper, C.M. et al. B cells lacking RelB are defective in proliferative responses, but undergo normal B cell maturation to Ig secretion and Ig class switching. J. Exp. Med. 184, 1537–1541 (1996).
Mackay, F. & Schneider, P. TACI, an enigmatic BAFF/APRIL receptor, with new unappreciated biochemical and biological properties. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19, 263–276 (2008).
Hauer, J. et al. TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) 3 serves as an inhibitor of TRAF2/5-mediated activation of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway by TRAF-binding TNFRs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 2874–2879 (2005).
Chang, S.K., Arendt, B.K., Darce, J.R., Wu, X. & Jelinek, D.F. A role for BLyS in the activation of innate immune cells. Blood 108, 2687–2694 (2006).
Stadanlick, J.E. et al. Tonic B cell antigen receptor signals supply an NF-κB substrate for prosurvival BLyS signaling. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1379–1387 (2008).
Suzuki, K., Meek, B., Doi, Y., Honjo, T. & Fagarasan, S. Two distinctive pathways for recruitment of naive and primed IgM+ B cells to the gut lamina propria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 2482–2486 (2005).
Fitzgerald, K.A. et al. IKKɛ and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 (2003).
Sharma, S. et al. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 300, 1148–1151 (2003).
McWhirter, S.M. et al. IFN-regulatory factor 3-dependent gene expression is defective in Tbk1-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 233–238 (2004).
Hemmi, H. et al. The roles of two IκB kinase-related kinases in lipopolysaccharide and double stranded RNA signaling and viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1641–1650 (2004).
Perry, A.K., Chow, E.K., Goodnough, J.B., Yeh, W.C. & Cheng, G. Differential requirement for TANK-binding kinase-1 in type I interferon responses to toll-like receptor activation and viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1651–1658 (2004).
Bonnard, M. et al. Deficiency of T2K leads to apoptotic liver degeneration and impaired NF-κB-dependent gene transcription. EMBO J. 19, 4976–4985 (2000).
Tomino, Y. IgA nephropathy: lessons from an animal model, the ddY mouse. J. Nephrol. 21, 463–467 (2008).
Kim, R.J. et al. IL-4-induced AID expression and its relevance to IgA class switch recombination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 361, 398–403 (2007).
Lorenz, M., Jung, S. & Radbruch, A. Switch transcripts in immunoglobulin class switching. Science 267, 1825–1828 (1995).
Muramatsu, M. et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102, 553–563 (2000).
Hiscott, J. Triggering the innate antiviral response through IRF-3 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 15325–15329 (2007).
Clément, J.F., Meloche, S. & Servant, M.J. The IKK-related kinases: from innate immunity to oncogenesis. Cell Res. 18, 889–899 (2008).
Sakurai, D. et al. TACI regulates IgA production by APRIL in collaboration with HSPG. Blood 109, 2961–2967 (2007).
Bossen, C. et al. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor family members in the mouse and human. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 13964–13971 (2006).
Yin, L. et al. Defective lymphotoxin-β receptor-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity in NIK-deficient mice. Science 291, 2162–2165 (2001).
Kawai, T. & Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 (2010).
Clark, K., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. & Cohen, P. The TRAF-associated protein TANK facilitates cross-talk within the IκB kinase family during Toll-like receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 17093–17098 (2011).
Razani, B. et al. Negative feedback in non-canonical NF-κB signaling modulates NIK stability through IKKα-mediated phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 3, ra41 (2010).
Liao, G., Zhang, M., Harhaj, E.W. & Sun, S.C. Regulation of the NF-κB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 26243–26250 (2004).
Clark, K. et al. Novel cross-talk within the IKK family controls innate immunity. Biochem. J. 434, 93–104 (2011).
Sun, S.-C., Ganchi, P.A., Beraud, C., Ballard, D.W. & Greene, W.C. Autoregulation of the NF-κB transactivator Rel A (p65) by multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors containing ankyrin motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 1346–1350 (1994).
Tenoever, B.R. et al. Multiple functions of the IKK-related kinase IKKɛ in interferon-mediated antiviral immunity. Science 315, 1274–1278 (2007).
Xiao, G. & Sun, S.C. Negative regulation of the nuclear factor κB-inducing kinase by a cis-acting domain. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21081–21085 (2000).
Reiley, W., Zhang, M., Wu, X., Graner, E. & Sun, S.-C. Regulation of the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD by IκB kinase γ-dependent phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 3886–3895 (2005).
Reiley, W.W. et al. Regulation of T cell development by the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Nat. Immunol. 7, 411–417 (2006).
Uhlik, M. et al. NF-κB-inducing kinase and IκB kinase participate in human T-cell leukemia virus I Tax-mediated NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21132–21136 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank Amgen for Map3k14-deficent mice; the Water Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research for Nfkb2Lym1 mice; S.S. Watowich (University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center) for Ifnar1−/− mice; S. Akira (Osaka University) for Flag-tagged IKKɛ (IKKi); G. Cheng (University of California, Los Ageles) for Flag-tagged mouse NIK and mouse NIK(S809A,S812A,S815A) expressed by a pcDNA vector; M. Karin (University of California, San Diego) for hemagglutinin-tagged IKKα and IKKα(SSEE); X. Qin (Sun Yat-Sen University) for packaging vectors psPAX2 and pMD2; C. Wang (Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences) for Flag-tagged TBK1 and TBK1(K38A); M.P. Cancro (University of Pennsylvania) for NIH3T3 cell lines; and personnel of the animal facility, flow cytometry, DNA analysis and histology core facilities at MD Anderson Cancer Center for technical assistance. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (AI057555, AI064639, GM084459 and T32CA009598).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.J. designed and did the research, prepared the figures, and wrote part of the manuscript; Y.X., J.-H.C., J.Y., H.H., G.C.B., M.C. and X.C. contributed experiments; R.S. contributed reagents; and S.-C.S. designed the research and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7 and Table 1 (PDF 1166 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Xiao, Y., Chang, JH. et al. The kinase TBK1 controls IgA class switching by negatively regulating noncanonical NF-κB signaling. Nat Immunol 13, 1101–1109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2423
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2423
This article is cited by
-
IKKε and TBK1 prevent RIPK1 dependent and independent inflammation
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Cytosolic DNA sensors in neurodegenerative diseases: from physiological defenders to pathological culprits
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2024)
-
Prospects for gene replacement therapies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Nature Reviews Neurology (2023)
-
The role of TBK1 in cancer pathogenesis and anticancer immunity
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
Myeloid TBK1 Deficiency Induces Motor Deficits and Axon Degeneration Through Inflammatory Cell Infiltration
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)