Abstract
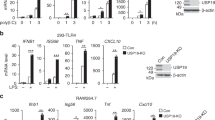
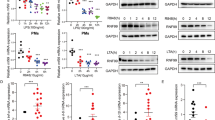
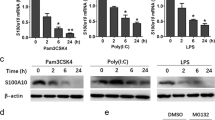
The intensity and duration of immune responses are controlled by many proteins that modulate Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. TANK has been linked to positive regulation of the transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB. Here we demonstrate that TANK is not involved in interferon responses and is a negative regulator of proinflammatory cytokine production induced by TLR signaling. TLR-induced polyubiquitination of the ubiquitin ligase TRAF6 was upregulated in Tank−/− macrophages. Notably, Tank−/− mice spontaneously developed fatal glomerulonephritis owing to deposition of immune complexes. Autoantibody production in Tank−/− mice was abrogated by antibiotic treatment or the absence of interleukin 6 (IL-6) or the adaptor MyD88. Our results demonstrate that constitutive TLR signaling by intestinal commensal microflora is suppressed by TANK.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira, S., Uematsu, S. & Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124, 783–801 (2006).
Beutler, B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430, 257–263 (2004).
Medzhitov, R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 449, 819–826 (2007).
Kawai, T., Adachi, O., Ogawa, T., Takeda, K. & Akira, S. Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 11, 115–122 (1999).
Yamamoto, M. et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 301, 640–643 (2003).
O'Neill, L.A. & Bowie, A.G. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 353–364 (2007).
Kawagoe, T. et al. Sequential control of Toll-like receptor-dependent responses by IRAK1 and IRAK2. Nat. Immunol. 9, 684–691 (2008).
Wang, C. et al. TAK1 is a ubiquitin-dependent kinase of MKK and IKK. Nature 412, 346–351 (2001).
Honda, K., Takaoka, A. & Taniguchi, T. Type I interferon gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 25, 349–360 (2006).
Marshak-Rothstein, A. Toll-like receptors in systemic autoimmune disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 823–835 (2006).
Christensen, S.R. & Shlomchik, M.J. Regulation of lupus-related autoantibody production and clinical disease by Toll-like receptors. Semin. Immunol. 19, 11–23 (2007).
Lau, C.M. et al. RNA-associated autoantigens activate B cells by combined B cell antigen receptor/Toll-like receptor 7 engagement. J. Exp. Med. 202, 1171–1177 (2005).
Pisitkun, P. et al. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 312, 1669–1672 (2006).
Viglianti, G.A. et al. Activation of autoreactive B cells by CpG dsDNA. Immunity 19, 837–847 (2003).
Liew, F.Y., Xu, D., Brint, E.K. & O'Neill, L.A. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 446–458 (2005).
Kobayashi, K. et al. IRAK-M is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 110, 191–202 (2002).
Brint, E.K. et al. ST2 is an inhibitor of interleukin 1 receptor and Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and maintains endotoxin tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 5, 373–379 (2004).
Wald, D. et al. SIGIRR, a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor-interleukin 1 receptor signaling. Nat. Immunol. 4, 920–927 (2003).
Nakagawa, R. et al. SOCS1 participates in negative regulation of LPS responses. Immunity 17, 677–687 (2002).
Reiley, W.W. et al. Regulation of T cell development by the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD. Nat. Immunol. 7, 411–417 (2006).
Lee, E.G. et al. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-κB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science 289, 2350–2354 (2000).
Kuhn, R., Lohler, J., Rennick, D., Rajewsky, K. & Muller, W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75, 263–274 (1993).
Kobayashi, M. et al. Toll-like receptor-dependent production of IL-12p40 causes chronic enterocolitis in myeloid cell-specific Stat3-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 111, 1297–1308 (2003).
Rakoff-Nahoum, S., Hao, L. & Medzhitov, R. Role of toll-like receptors in spontaneous commensal-dependent colitis. Immunity 25, 319–329 (2006).
Cheng, G. & Baltimore, D. TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF- and CD 40L-mediated NF-κB activation. Genes Dev. 10, 963–973 (1996).
Rothe, M. et al. I-TRAF is a novel TRAF-interacting protein that regulates TRAF-mediated signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8241–8246 (1996).
Chin, A.I. et al. TANK potentiates tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase activation through the germinal center kinase pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 6665–6672 (1999).
Li, C. et al. Downstream regulator TANK binds to the CD40 recognition site on TRAF3. Structure 10, 403–411 (2002).
Pomerantz, J.L. & Baltimore, D. NF-κB activation by a signaling complex containing TRAF2, TANK and TBK1, a novel IKK-related kinase. EMBO J. 18, 6694–6704 (1999).
Nomura, F., Kawai, T., Nakanishi, K. & Akira, S. NF-κB activation through IKK-i-dependent I-TRAF/TANK phosphorylation. Genes Cells 5, 191–202 (2000).
Fitzgerald, K.A. et al. IKKε and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 (2003).
Sharma, S. et al. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 300, 1148–1151 (2003).
Hemmi, H. et al. The roles of two IκB kinase-related kinases in lipopolysaccharide and double stranded RNA signaling and viral infection. J. Exp. Med. 199, 1641–1650 (2004).
Kato, H. et al. Cell type-specific involvement of RIG-I in antiviral response. Immunity 23, 19–28 (2005).
Hacker, H. et al. Specificity in Toll-like receptor signalling through distinct effector functions of TRAF3 and TRAF6. Nature 439, 204–207 (2006).
Oganesyan, G. et al. Critical role of TRAF3 in the Toll-like receptor-dependent and -independent antiviral response. Nature 439, 208–211 (2006).
Guo, B. & Cheng, G. Modulation of the interferon antiviral response by the TBK1/IKKi adaptor protein TANK. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 11817–11826 (2007).
Sasai, M. et al. Cutting edge: NF-κB-activating kinase-associated protein 1 participates in TLR3/Toll-IL-1 homology domain-containing adapter molecule-1-mediated IFN regulatory factor 3 activation. J. Immunol. 174, 27–30 (2005).
Ryzhakov, G. & Randow, F. SINTBAD, a novel component of innate antiviral immunity, shares a TBK1-binding domain with NAP1 and TANK. EMBO J. 26, 3180–3190 (2007).
Wertz, I.E. et al. De-ubiquitination and ubiquitin ligase domains of A20 downregulate NF-kappaB signalling. Nature 430, 694–699 (2004).
Brummelkamp, T.R., Nijman, S.M., Dirac, A.M. & Bernards, R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-κB. Nature 424, 797–801 (2003).
Trompouki, E. et al. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-κB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 424, 793–796 (2003).
Sun, L., Deng, L., Ea, C.K., Xia, Z.P. & Chen, Z.J. The TRAF6 ubiquitin ligase and TAK1 kinase mediate IKK activation by BCL10 and MALT1 in T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell 14, 289–301 (2004).
He, J.Q. et al. Rescue of TRAF3-null mice by p100 NF-κB deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2413–2418 (2006).
Suematsu, S. et al. IgG1 plasmacytosis in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7547–7551 (1989).
Boone, D.L. et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1052–1060 (2004).
Turer, E.E. et al. Homeostatic MyD88-dependent signals cause lethal inflamMation in the absence of A20. J. Exp. Med. 205, 451–464 (2008).
Xavier, R.J. & Podolsky, D.K. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 448, 427–434 (2007).
Elson, C.O. et al. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease reveal innate, adaptive, and regulatory mechanisms of host dialogue with the microbiota. Immunol. Rev. 206, 260–276 (2005).
Sato, S. et al. Essential function for the kinase TAK1 in innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1087–1095 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Yasui (Osaka University) for Il6−/− mice and plasmids; colleagues in our laboratories; E. Kamada for secretarial assistance; Y. Fujiwara, M. Kumagai and R. Abe for technical assistance; and S. Sato for discussions. Supported by the Special Coordination Funds of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan, the Global Center of Excellence Program of Japan, and the US National Institutes of Health (P01 AI070167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.K., O.T. and S.A. designed the research and analyzed data; T.K. generated Tank−/− mice and did most of the experiments; Y.T., Y.I. and T.T. did histological examination of kidneys; H.K. provided advice; and T.K., O.T. and S.A. prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4 (PDF 523 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawagoe, T., Takeuchi, O., Takabatake, Y. et al. TANK is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling and is critical for the prevention of autoimmune nephritis. Nat Immunol 10, 965–972 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1771
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1771
This article is cited by
-
Temporal multiomic modeling reveals a B-cell receptor proliferative program in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia (2021)
-
TBKBP1 and TBK1 form a growth factor signalling axis mediating immunosuppression and tumourigenesis
Nature Cell Biology (2019)
-
RNA-binding proteins in immune regulation: a focus on CCCH zinc finger proteins
Nature Reviews Immunology (2017)
-
Cellular and molecular regulation of innate inflammatory responses
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2016)
-
Keratin 8 limits TLR-triggered inflammatory responses through inhibiting TRAF6 polyubiquitination
Scientific Reports (2016)