Abstract
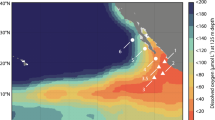
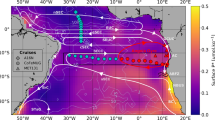
Nitrite is a central intermediate in the marine nitrogen cycle, and is generally found at low concentrations in the ocean. However, nitrite accumulates at the base of the sunlit surface ocean. The origin of this ubiquitous feature, known as the primary nitrite maximum, is debated and has been difficult to resolve through short-term isotope tracer incubations. Here, we use measurements of the dual isotopic composition of nitrite to evaluate the sources, sinks and average rates of nitrite turnover in the primary nitrite maximum in the Arabian Sea. We determined the rate of abiotic oxygen isotope exchange between nitrite and water, as well as equilibrium isotope effects, under a variety of conditions in a series of laboratory experiments. We used these data to model nitrite isotope data from several sites in the Arabian Sea. The results suggest that ammonia oxidation is the primary source of nitrite at most sites. Steady-state nitrite turnover times of 33–178 days correspond to ammonia oxidation rates of 9–30 nM per day at these sites. We suggest that a similar approach could be used to determine the rates of nitrite turnover in other environments, including the secondary nitrite maximum in low-oxygen regions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dore, J. E. & Karl, D. M. Nitrification in the euphotic zone as a source for nitrite, nitrate, and nitrous oxide at Station ALOHA. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41, 1619–1628 (1996).
Kiefer, D. A., Olson, R. J. & Holmhansen, O. Another look at nitrite and chlorophyll maxima in central North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. 23, 1199–1208 (1976).
Lipschultz, F., Zafiriou, O. C. & Ball, L. A. Seasonal fluctuations of nitrite concentrations in the deep oligotrophic ocean. Deep-Sea Res. II 43, 403–419 (1996).
Zafiriou, O. C., Ball, L. A. & Hanley, Q. Trace nitrite in oxic waters. Deep-Sea Res. A 39, 1329–1347 (1992).
Brandhorst, W. Nitrification and denitrification in the Eastern Tropical North Pacific. Journal du Conseil Permanent International pour l’Exploration de la Mer 25, 2–20 (1959).
Codispoti, L. A. & Christensen, J. P. Nitrification, denitrification and nitrous-oxide cycling in the eastern tropical South-Pacific ocean. Mar. Chem. 16, 277–300 (1985).
Codispoti, L. A. Interesting times for marine N2O. Science 327, 1339–1340 (2010).
Freing, A., Wallace, D. W. R. & Bange, H. W. Global oceanic production of nitrous oxide. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 367, 1245–1255 (2012).
Lomas, M. W. & Lipschultz, F. Forming the primary nitrite maximum: Nitrifiers or phytoplankton? Nature Med. 51, 2453–2467 (2006).
Dugdale, R. C. & Goering, J. J. Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12, 196–206 (1967).
Harrison, W. G. & Harris, L. R. Isotope-dilution and its effects on measurements of nitrogen and phosphorus uptake by oceanic microplankton. Mar. Ecol. 27, 253–261 (1986).
Clark, D. R., Rees, A. P. & Joint, I. Ammonium regeneration and nitrification rates in the oligotrophic Atlantic Ocean: Implications for new production estimates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 53, 52–62 (2008).
Jenkins, W. J. Oxygen utilization rates in North-Atlantic sub-tropical gyre and primary production in oligotrophic systems. Nature 300, 246–248 (1982).
Platt, T. et al. Biological production of the oceans—the case for a consensus. Mar. Ecol. 52, 77–88 (1989).
Karl, D. M., Laws, E. A., Morris, P., Williams, P. J. L. & Emerson, S. Global carbon cycle—metabolic balance of the open sea. Nature 426, 32–32 (2003).
Luz, B. & Barkan, E. Assessment of oceanic productivity with the triple-isotope composition of dissolved oxygen. Science 288, 2028–2031 (2000).
Knapp, A. N., Sigman, D. M., Lipschultz, F., Kustka, A. B. & Capone, D. G. Interbasin isotopic correspondence between upper-ocean bulk DON and subsurface nitrate and its implications for marine nitrogen cycling. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 25, GB4004 (2011).
Casciotti, K. L., McIlvin, M. & Buchwald, C. Oxygen isotopic exchange and fractionation during bacterial ammonia oxidation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 55, 753–762 (2010).
Buchwald, C., Santoro, A. E., McIlvin, M. R. & Casciotti, K. L. Oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate and nitrite produced by nitrifying cocultures in and natural marine assemblages. Limnol. Oceanogr. 57, 1361–1375 (2012).
Granger, J., Sigman, D. M., Needoba, J. A. & Harrison, P. J. Coupled nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation of nitrate during assimilation by cultures of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 49, 1763–1773 (2004).
Granger, J., Sigman, D. M., Rohde, M. M., Maldonado, M. T. & Tortell, P. D. N and O isotope effects during nitrate assimilation by unicellular prokaryotic and eukaryotic plankton cultures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 74, 1030–1040 (2010).
Casciotti, K. L., Böhlke, J. K., McIlvin, M. R., Mroczkowski, S. J. & Hannon, J. E. Oxygen isotopes in nitrite: Analysis, calibration, and equilibration. Anal. Chem. 79, 2427–2436 (2007).
Fawcett, S. E., Lomas, M., Casey, J. R., Ward, B. B. & Sigman, D. M. Assimilation of upwelled nitrate by small eukaryotes in the Sargasso Sea. Nature Geosci. 4, 717–722 (2011).
Montoya, J. P. & Voss, M. Nitrogen cycling in suboxic waters: Isotopic signatures of nitrogen transformation in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone. Past Present Water Column Anoxia 64, 259–281 (2006).
Checkley, D. M. & Miller, C. A. Nitrogen isotope fractionation by oceanic zooplankton. Deep-Sea Res. A 36, 1449–1456 (1989).
Macko, S. A., Estep, M. L. F., Engel, M. H. & Hare, P. E. Kinetic fractionation of stable nitrogen isotopes during amino-acid transamination. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 2143–2146 (1986).
Waser, N. A. D., Harrison, P. J., Nielsen, B., Calvert, S. E. & Turpin, D. H. Nitrogen isotope fractionation during the uptake and assimilation of nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, and urea by a marine diatom. Limnol. Oceanogr. 43, 215–224 (1998).
Santoro, A. E. & Casciotti, K. L. Enrichment and characterization of ammonia-oxidizing archaea from the open ocean: phylogeny, physiology and stable isotope fractionation. ISME J. 5, 1796–1808 (2011).
Casciotti, K. L. Inverse kinetic isotope fractionation during bacterial nitrite oxidation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 2061–2076 (2009).
Buchwald, C. & Casciotti, K. L. Oxygen isotopic fractionation and exchange during bacterial nitrite oxidation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 55, 1064–1074 (2010).
Yool, A., Martin, A. P., Fernandez, C. & Clark, D. R. The significance of nitrification for oceanic new production. Nature 447, 999–1002 (2007).
Newell, S. E., Babbin, A. R., Jayakumar, A. & Ward, B. B. Ammonia oxidation rates and nitrification in the Arabian Sea. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 25, GB4016 (2011).
Lipschultz, F. et al. Bacterial transformations of inorganic nitrogen in the oxygen-deficient waters of the eastern tropical South-Pacific ocean. Deep-Sea Res. A 37, 1513–1541 (1990).
Ward, B. B., Olson, R. J. & Perry, M. J. Microbial nitrification rates in the primary nitrite maximum off Southern-California. Deep-Sea Res. A 29, 247–255 (1982).
Dore, J. E., Popp, B. N., Karl, D. M. & Sansone, F. J. A large source of atmospheric nitrous oxide from subtropical North Pacific surface waters. Nature 396, 63–66 (1998).
Santoro, A. E., Buchwald, C., McIlvin, M. R. & Casciotti, K. L. Isotopic signature of N2O produced by marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea. Science 333, 1282–1285 (2011).
Bunton, C. A., Halevi, E. A. & Llewellyn, D. R. Oxygen exchange between nitric acid and water. J. Chem. Soc. 4913–4916 (1952).
Betts, R. H. & Voss, R. H. Kinetics of oxygen exchange between sulfite ion and water. Canad. J. Chem. 48, 2035–2041 (1970).
Gomori, G. Preparation of buffers for use in enzyme studies. Methods Enzymol. 1, 138–146 (1955).
Robert-Baldo, G. L., Morris, M. J. & Byrne, R. H. Spectrophotometric determination of seawater pH using phenol red. Anal. Chem. 57, 2564–2567 (1985).
Durst, R. A. & Staples, B. R. Tris/tris HCl-standard buffer for use in physiologic pH range. Clin. Chem. 18, 206–208 (1972).
McIlvin, M. R. & Altabet, M. A. Chemical conversion of nitrate and nitrite to nitrous oxide for nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis in freshwater and seawater. Anal. Chem. 77, 5589–5595 (2005).
Strickland, J. D. H. & Parsons, T. R. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Canada 167, 1–310 (1972).
Clayton, T. D. & Byrne, R. H. Spectrophotometric seawater pH measurements—total hydrogen-ion concentration scale calibration of M-Cresol purple and at-sea results. Deep-Sea Res. I 40, 2115–2129 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank M. McIlvin and B. Peters for help collecting data. We would like to thank the chief scientist B. Ward and the captain and crew of the R/V Revelle for assistance in the collection of nitrite isotope samples in the Arabian Sea. Financial support was provided from NSF/OCE 07-48674 and 11-40404 to K.L.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.B. and K.L.C. designed the experiments and the model formulations. C.B. performed the experiments and model calculations. C.B. and K.L.C. authored the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1230 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchwald, C., Casciotti, K. Isotopic ratios of nitrite as tracers of the sources and age of oceanic nitrite. Nature Geosci 6, 308–313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1745
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1745
This article is cited by
-
Microscale dynamics promote segregated denitrification in diatom aggregates sinking slowly in bulk oxygenated seawater
Communications Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Nitrate isotope dynamics in the lower euphotic-upper mesopelagic zones of the western South China Sea
Acta Oceanologica Sinica (2023)
-
Sources and transformations of nitrite in the Amundsen Sea in summer 2019 and 2020 as revealed by nitrogen and oxygen isotopes
Acta Oceanologica Sinica (2023)
-
Nitrite isotope characteristics and associated soil N transformations
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The Abiotic Nitrite Oxidation by Ligand-Bound Manganese (III): The Chemical Mechanism
Aquatic Geochemistry (2021)