Abstract
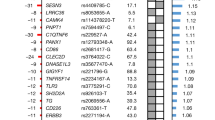
Rheumatoid arthritis is a common autoimmune disease with a complex genetic etiology. Here we identify a SNP in the promoter region of FCRL3, a member of the Fc receptor-like family, that is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (odds ratio = 2.15, P = 0.00000085). This polymorphism alters the binding affinity of nuclear factor-κB and regulates FCRL3 expression. We observed high FCRL3 expression on B cells and augmented autoantibody production in individuals with the disease-susceptible genotype. We also found associations between the SNP and susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. FCRL3 may therefore have a pivotal role in autoimmunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423, 356–361 (2003).
Gregersen, P.K., Silver, J. & Winchester, R.J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 30, 1205–1213 (1987).
Newton, J.L., Harney, S.M., Wordsworth, B.P. & Brown, M.A. A review of the MHC genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 5, 151–157 (2004).
Kochi, Y. et al. Analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients shows additional susceptibility markers besides the classic shared epitope susceptibility sequences. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 63–71 (2004).
Seldin, M.F., Amos, C.I., Ward, R. & Gregersen, P.K. The genetics revolution and the assault on rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 1071–1079 (1999).
Tsao, B.P. The genetics of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Trends Immunol. 24, 595–602 (2003).
Bowcock, A.M. & Cookson, W.O. The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13 Suppl 1, R43–R55 (2004).
Marrack, P., Kappler, J. & Kotzin, B.L. Autoimmune disease: why and where it occurs. Nat. Med. 7, 899–905 (2001).
Ueda, H. et al. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature 423, 506–511 (2003).
Becker, K.G. et al. Clustering of non-major histocompatibility complex susceptibility candidate loci in human autoimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9979–9984 (1998).
Tokuhiro, S. et al. An intronic SNP in a RUNX1 binding site of SLC22A4, encoding an organic cation transporter, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 35, 341–348 (2003).
Begovich, A.B. et al. A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 75, 330–337 (2004).
Davis, R.S., Wang, Y.H., Kubagawa, H. & Cooper, M.D. Identification of a family of Fc receptor homologs with preferential B cell expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9772–9777 (2001).
Davis, R.S. et al. Fc receptor homologs: newest members of a remarkably diverse Fc receptor gene family. Immunol. Rev. 190, 123–136 (2002).
Hatzivassiliou, G. et al. IRTA1 and IRTA2, novel immunoglobulin superfamily receptors expressed in B cells and involved in chromosome 1q21 abnormalities in B cell malignancy. Immunity 14, 277–289 (2001).
Miller, I., Hatzivassiliou, G., Cattoretti, G., Mendelsohn, C. & Dalla-Favera, R. IRTAs: a new family of immunoglobulinlike receptors differentially expressed in B cells. Blood 99, 2662–2669 (2002).
Xu, M.J., Zhao, R., Cao, H. & Zhao, Z.J. SPAP2, an Ig family receptor containing both ITIMs and ITAMs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 293, 1037–1046 (2002).
Ravetch, J.V. & Bolland, S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 275–290 (2001).
Kyogoku, C. et al. Fcgamma receptor gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: contribution of FCGR2B to genetic susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum. 46, 1242–1254 (2002).
Capon, F. et al. Fine mapping of the PSORS4 psoriasis susceptibility region on chromosome 1q21. J. Invest. Dermatol. 116, 728–730 (2001).
Dai, K.Z. et al. The T cell regulator gene SH2D2A contributes to the genetic susceptibility of multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun. 2, 263–268 (2001).
Jirholt, J. et al. Genetic linkage analysis of collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 3321–3328 (1998).
Sundvall, M. et al. Identification of murine loci associated with susceptibility to chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Genet. 10, 313–317 (1995).
Teuscher, C. et al. Evidence that Tmevd2 and eae3 may represent either a common locus or members of a gene complex controlling susceptibility to immunologically mediated demyelination in mice. J. Immunol. 159, 4930–4934 (1997).
Podolin, P.L. et al. Congenic mapping of the insulin-dependent diabetes (Idd) gene, Idd10, localizes two genes mediating the Idd10 effect and eliminates the candidate Fcgr1. J. Immunol. 159, 1835–1843 (1997).
Nieto, A. et al. Involvement of Fcgamma receptor IIIA genotypes in susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 43, 735–739 (2000).
Radstake, T.R. et al. Role of Fcgamma receptors IIA, IIIA, and IIIB in susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 30, 926–933 (2003).
Devlin, B. & Risch, N. A comparison of linkage disequilibrium measures for fine-scale mapping. Genomics 29, 311–322 (1995).
Cordell, H.J. & Clayton, D.G. A unified stepwise regression procedure for evaluating the relative effects of polymorphisms within a gene using case/control or family data: application to HLA in type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70, 124–141 (2002).
Sebastiani, P. et al. Minimal haplotype tagging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 9900–9905 (2003).
Tsunoda, T. et al. Variation of gene-based SNPs and linkage disequilibrium patterns in the human genome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 1623–1632 (2004).
Pritchard, J.K., Stephens, M. & Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155, 945–959 (2000).
Pritchard, J.K. & Rosenberg, N.A. Use of unlinked genetic markers to detect population stratification in association studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 220–228 (1999).
Kaijzel, E.L. et al. Allele-specific quantification of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) transcription and the role of promoter polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy individuals. Genes Immun. 2, 135–144 (2001).
Takemura, S. et al. Lymphoid neogenesis in rheumatoid synovitis. J. Immunol. 167, 1072–1080 (2001).
Weyand, C.M. & Goronzy, J.J. Ectopic germinal center formation in rheumatoid synovitis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 987, 140–149 (2003).
Alarcon, G.S. et al. Suppression of rheumatoid factor production by methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Evidence for differential influences of therapy and clinical status on IgM and IgA rheumatoid factor expression. Arthritis Rheum. 33, 1156–1161 (1990).
Suzuki, K. et al. High diagnostic performance of ELISA detection of antibodies to citrullinated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 32, 197–204 (2003).
Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S. et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 48, 2741–2749 (2003).
Capon, F., Semprini, S., Dallapiccola, B. & Novelli, G. Evidence for interaction between psoriasis-susceptibility loci on chromosomes 6p21 and 1q21. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 1798–1800 (1999).
Suzuki, A. et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 34, 395–402 (2003).
Barton, A. et al. A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population is not associated in a United Kingdom population. Arthritis Rheum. 50, 1117–1121 (2004).
Jorgensen, T.N., Gubbels, M.R. & Kotzin, B.L. New insights into disease pathogenesis from mouse lupus genetics. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 16, 787–793 (2004).
Edwards, J.C. et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2572–2581 (2004).
Gray, D. et al. Observations on memory B-cell development. Semin. Immunol. 9, 249–254 (1997).
van Eijk, M., Defrance, T., Hennino, A. & de Groot, C. Death-receptor contribution to the germinal-center reaction. Trends Immunol. 22, 677–682 (2001).
Arnett, F.C. et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31, 315–324 (1988).
Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 1725 (1997).
Aikawa, Y., Yamamoto, M., Yamamoto, T., Morimoto, K. & Tanaka, K. An anti-rheumatic agent T-614 inhibits NF-kappaB activation in LPS- and TNF-alpha-stimulated THP-1 cells without interfering with IkappaBalpha degradation. Inflamm. Res. 51, 188–194 (2002).
Hoshino, M. et al. Identification of the stef gene that encodes a novel guanine nucleotide exchange factor specific for Rac1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17837–17844 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Kanno and other members of the Laboratory for Rheumatic Diseases for technical assistance; H. Kawakami for expertise in computer programming; M. Yukioka, S. Tohma, Y. Nishioka, T. Matsubara, S. Wakitani, R. Teshima, N. Ishikawa, K. Ito, K. Ito, K. Kuma, H. Tamai and T. Akamizu for clinical sample collection; M. Ishikawa and Y. Amasaki for preparation of the second population study; M. Nagashima and S. Yoshino for sampling rheumatoid arthritis synovium; and K. Nagatani and Y. Komagata for advice. This work was supported by grants from the Japanese Millennium Project, the US National Institutes of Health and the Korean Molecular and Cellular BioDiscovery Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Stratification analysis of case-control samples using STRUCTURE software. (PDF 53 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
FCRL3 expression in RA synovium from two patients (RA2, RA3). (PDF 209 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Case-control association analysis of the FCRL region. (PDF 21 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Replication study of FCRL3 association with RA. (PDF 15 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
FCRL3 haplotype structure in different ethnic groups. (PDF 30 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Primer sequences for ASTQ. (PDF 6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kochi, Y., Yamada, R., Suzuki, A. et al. A functional variant in FCRL3, encoding Fc receptor-like 3, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and several autoimmunities. Nat Genet 37, 478–485 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1540
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1540
This article is cited by
-
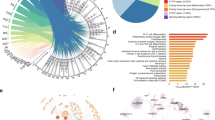
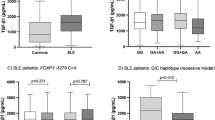
Identification of the immune-related biomarkers in Behcet’s disease by plasma proteomic analysis
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of Interleukin − 4, Interleukin-18, FCRL3 and sPLA2IIa genes and their association in pathogenesis of endometriosis
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Two genetic variants explain the association of European ancestry with multiple sclerosis risk in African-Americans
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Novel missense mutation in PTPN22 in a Chinese pedigree with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2018)
-
Fc receptor-like 3 (−169T>C) polymorphism increases the risk of tendinopathy in volleyball athletes: a case control study
BMC Medical Genetics (2018)